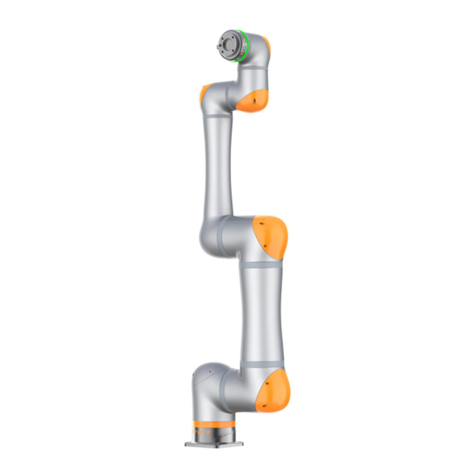
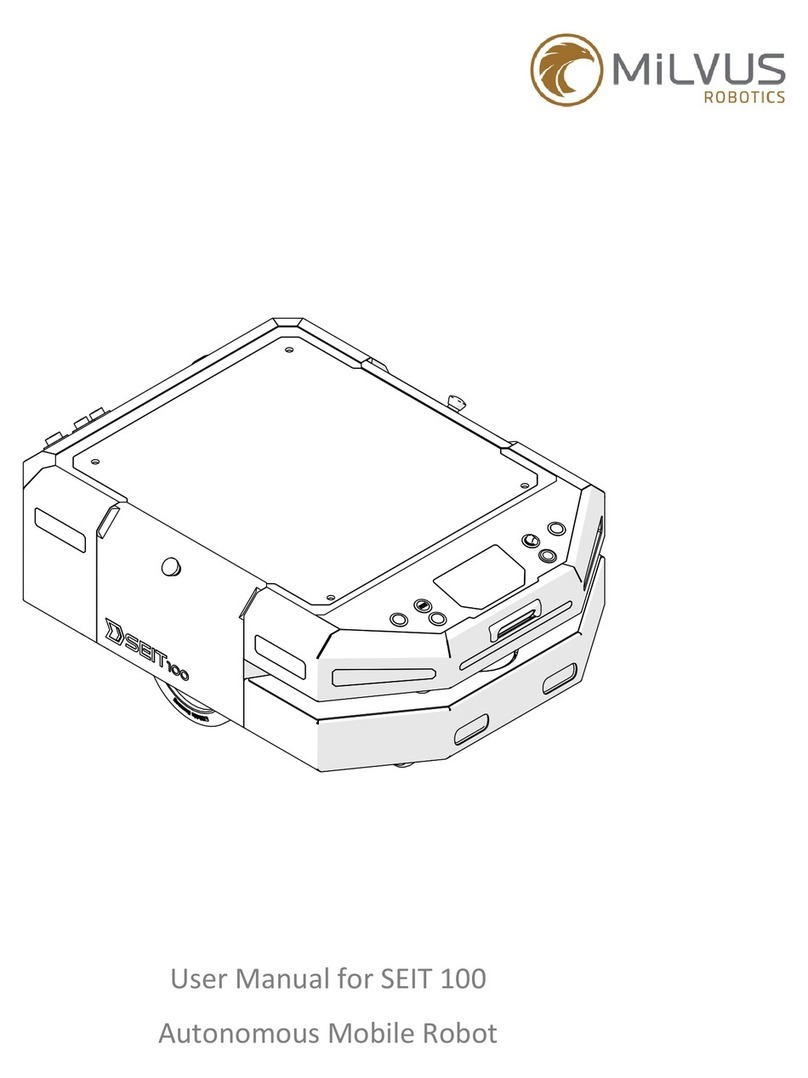
ROKAE NB220 Series User manual
Other ROKAE Robotics manuals
ROKAE
ROKAE xMate CR7-C Assembly instructions

ROKAE
ROKAE xMate CR18 Assembly instructions

ROKAE
ROKAE XB10 Series User manual

ROKAE
ROKAE NB25 Series User manual

ROKAE
ROKAE XB4 Series User manual

ROKAE
ROKAE xMate CR7 Assembly instructions

ROKAE
ROKAE xMate ER7 Assembly instructions

ROKAE
ROKAE NB12 User manual
ROKAE
ROKAE xMate CR17/5-C Assembly instructions

ROKAE
ROKAE XB12 Series User manual
ROKAE
ROKAE xMate SR3 Assembly instructions

ROKAE
ROKAE xMate ER3 Pro Assembly instructions

ROKAE
ROKAE XB7 Series User manual
ROKAE
ROKAE xMate CR20-C Assembly instructions

ROKAE
ROKAE XB16 User manual

ROKAE
ROKAE xMate CR20 Assembly instructions
ROKAE
ROKAE xMate CR12-C Assembly instructions

ROKAE
ROKAE xMate CR12 Assembly instructions

ROKAE
ROKAE xMate CR12 Assembly instructions

ROKAE
ROKAE xMate ER7 Pro Assembly instructions