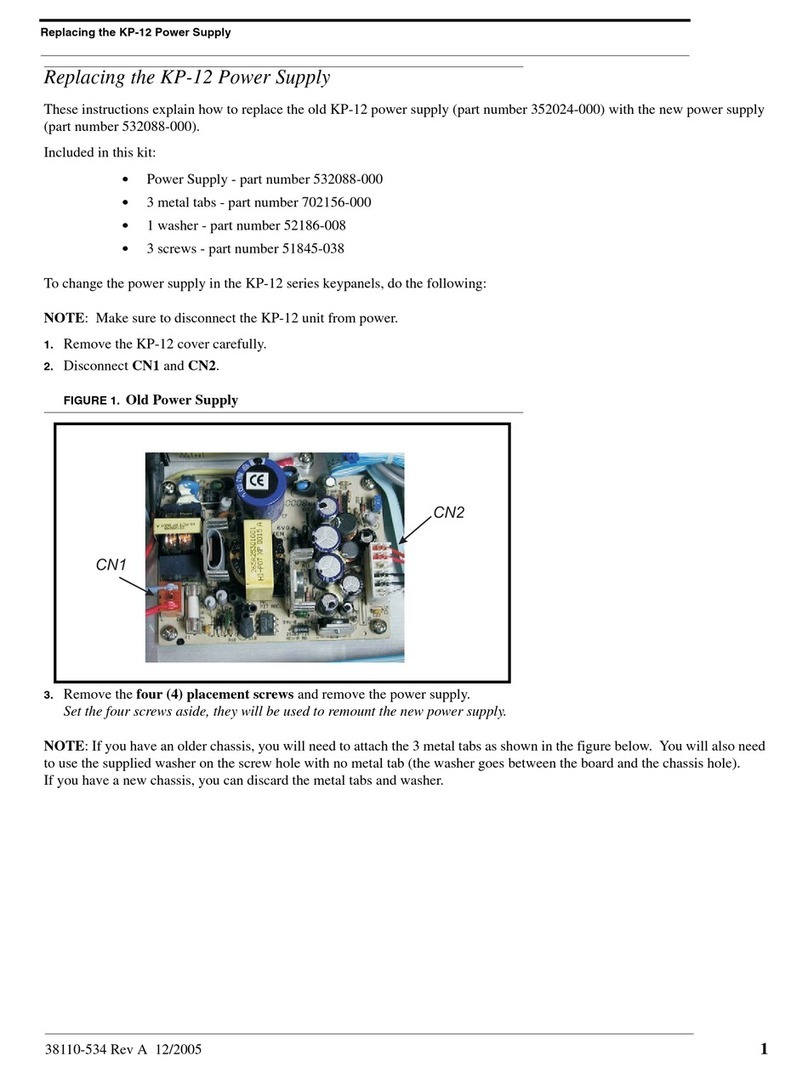
PROPRIETARY NOTICE
The product information and design disclosed herein were
originated by and are the property of Telex Communications, Inc.
Telex reserves all patent, proprietary design, manufacturing,
reproduction, use and sales rights thereto, and to any article
disclosed therein, except to the extent rights are expressly granted to
others.
COPYRIGHT NOTICE
Copyright 2005 by Telex Communications, Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction, in whole or in part, without prior written permission
from Telex is prohibited.
WARRANTY NOTICE
See the enclosed warranty card for further details.
CUSTOMER SUPPORT
Technical questions should be directed to:
Customer Service Department
Telex Communications, Inc.
12000 Portland Avenue South
Burnsville, MN 55337 U.S.A.
Telephone: (800) 392-3497
Fax: (800) 323-0498
RETURN SHIPPING INSTRUCTIONS PROCEDURE
FOR RETURNS
If a repair is necessary, contact the dealer where this unit was
purchased. If repair through the dealer is not possible, obtain a
RETURN AUTHORIZATION from:
Customer Service Department
Telex Communications, Inc.
Telephone: (800) 392-3497
Fax: (800) 323-0498
DO NOT RETURN ANY EQUIPMENT DIRECTLY TO THE
FACTORY WITHOUT FIRST OBTAINING A RETURN
AUTHORIZATION.
Be prepared to provide the company name, address, phone number,
a person to contact regarding the repair, the type and quantity of
equipment, a description of the problem and the serial number(s).
SHIPPING TO THE MANUFACTURER
All shipments of product should be made via UPS Ground or best
available shipper, prepaid. Any shipment upgrades will be paid by
the customer. The equipment should be shipped in the original
packing carton. If the original carton is not available, use any
suitable container that is rigid and of adequate size. If a substitute
container is used, the equipment should be wrapped in paper and
surrounded with at least four inches of excelsior or similar shock-
absorbing material. All shipments must be sent to the following
address and must include a Return Authorization.
Factory Service Department
Telex Communications, Inc.
1930 West 1st Street
Blue Earth, MN 56013 U. S. A.
Attn.: Service
Upon completion of any repair, the equipment will be returned via
United Parcel Service or specified shipper, collect.