Page 10
Page 10
WATER CIRCUIT
∏
π
∫
∂
∑
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION
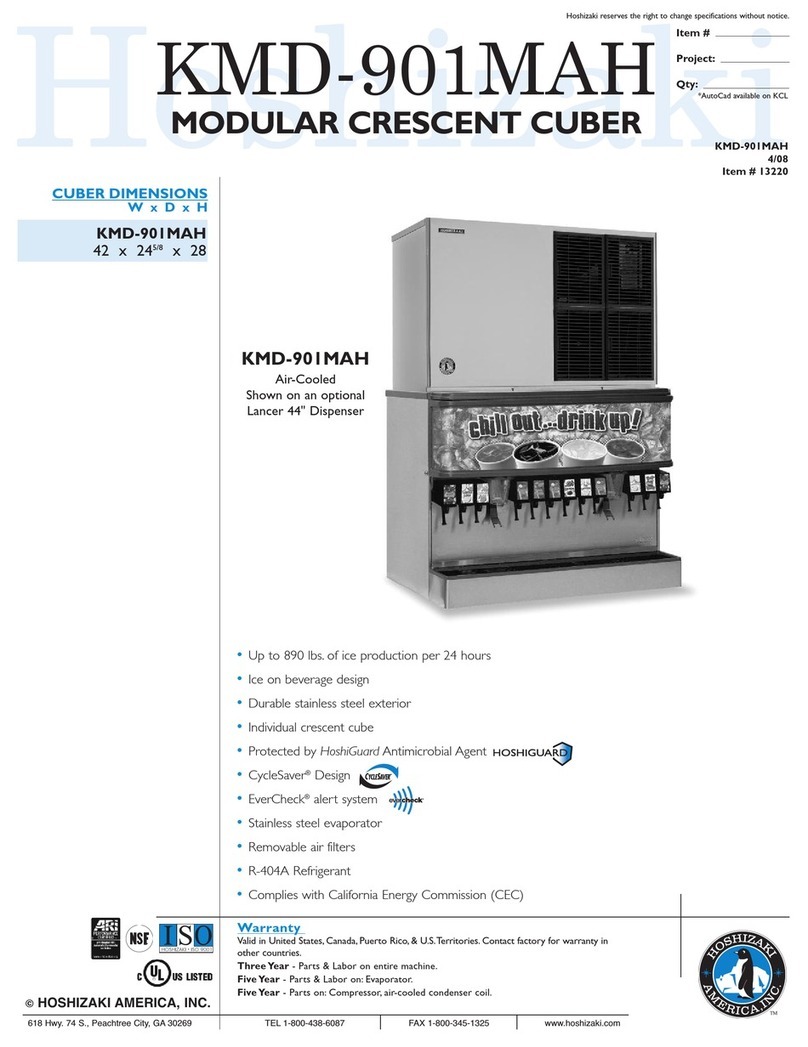
In the Scotsman ACM 25, the water to make ice
is continually moved or circulated by a small
electricpumpthatsprays the water under gentle
pressurethroughthetwosprayjetsintotheeight
inverted cube molds.
Part of the water that hits the cold refrigerated
molds freezes, building gradually into full ice
cubes bell shaped.
FREEZING CYCLE (How it works)
Thehotgasrefrigerant,pumpedanddischarged
bythecompressor,passesthroughthecondenser
wherethefanblowingaircausesthechangingof
it into liquid.
The liquid line takes the refrigerant from the
condensertothecapillarytube.Duringthetravel
intothecapillarytube,theliquidrefrigerantlooses
gradually its temperature and pressure, then it
reaches the evaporator coils.
Because of the water sprayed against the
evaporator molds and coil, the liquid refrigerant
senses the heat of this water and starts boiling,
changing, as a consequence, from liquid into
vapor state.
The vapor refrigerant is sucked back to the
compressor through the suction line.
Thefreezingcycleiscontrolledbyatemperature
controlwhichdeterminesaswellthelengthofthe
cycle and consequently the size of the ice cube.
Duringthisphase,thecontactpointofthetempe-
rature control maintains closed the circuit of the
water pump which constantly sprays the water
under the evaporator mold cups up to the point
that the ice cubes reach their full size.
HARVEST CYCLE (How it works)
As soon as the temperature control senses the
temperature in the evaporator corresponding to
thefullsizecubes,thecontactmovestoclosethe
circuitoftheHotGasValveCoilandconsequently
to open the circuit of the water pump which
momentarily stops.
The hot gas refrigerant discharged by the
compressor is now diverted through the opened
hot gas valve to the evaporator coil.
The hot gas circulares through the evaporator
coil raising the temperature around the cube
cups sufficiently to release the ice cubes.
The released ice cubes drop by gravity into the
storage bin.
The temperature control bulb, due to the warm
temperature in the evaporator moves again the
contact de-energizing the hot gas valve and
energizing the water circulating pump starting a
new freezing cycle.
∑
❼
❾
HARVEST CYCLE
∏
π❻
Ω∫
∂
FREEZING CYCLE
∑
∏
π
∫
❻
∂
❼
Ω
❾
①EVAPORATOR
≠BIN
③SPRAY TUBE
④WATER PUMP
∞WATER RESERVOIR
①EVAPORATOR
≠ACCUMULATOR
③CAPILLARY TUBE
④SUCTION LINE
∞COMPRESSOR
±HOT GAS SOLENOID
±VALVE CLOSED
≤CONDENSER
≥FAN MOTOR
⑨DRIER
①EVAPORATOR
≠ACCUMULATOR
③CAPILLARY TUBE
④SUCTION LINE
∞COMPRESSOR
±HOT GAS SOLENOID
±VALVE OPENED
≤CONDENSER
≥FAN MOTOR
⑨DRIER