SIASUN GCR20-1100 User manual

GCR20-1100
Collaborative Robot
User Manual
(Hardware)
Model: GCR20-1100 V2.0
SIASUN Co.,Ltd.

Copyright © SIASUN Co., Ltd. 2019.All rights reserved.
This document and parts must not be reproduced or copied by any third party without the written
permission of SIASUN Co., Ltd.
Trademark Statement
The words or images like “SIASUN”、“新松”、“SIASUN 新松” and etc are protected by trademark
registration. The registered trademark information can be found in the open trademark registration
information.
All other trademarks or registered trademarks mentioned in this manual are the property of their respective
owners.
Attention
Your purchase of products, services or features, etc., shall be subject to the commercial contract and terms
and conditions of SIASUN Co., Ltd. All or part of the products, services or features described in this
manual may not be within the scope of your purchase or use. Unless otherwise agreed in the contract,
SIASUN Co., Ltd. makes no representations or warranties, either express or implied, with respect to the
contents of this manual.
Due to product version upgrade or other reasons, the contents of this manual will be updated from time to
time. Unless otherwise agreed, this manual is used only as a guide, and all statements, information and
recommendations in this manual do not constitute any guarantee either express or implied.
SIASUN Co., Ltd.
Address:NO.257 Jinzang Rd. Pudong New District, ShangHai Zip:201206
Website:http://www.siasun-in.com

Content
1Preface............................................................................................................................................................ 1
1.1 Intended Audience ............................................................................................................................ 1
1.2 Representation of Warnings and Notes ........................................................................................... 2
1.3 Special Statement ............................................................................................................................. 3
1.4 Revision History............................................................................................................................... 3
2Safety ............................................................................................................................................................. 4
2.1 Abstract ............................................................................................................................................. 4
2.2 Limitation of Liability...................................................................................................................... 4
2.3 Risk Assessment ............................................................................................................................... 5
2.4 Safety Operations ............................................................................................................................. 6
2.4.1 Emergency Stop ................................................................................................................... 6
2.4.2 Movement without Drive Power......................................................................................... 6
2.5 The Risk of Collision ....................................................................................................................... 8
3Production Introduction.............................................................................................................................. 12
3.1 Overview......................................................................................................................................... 12
3.2 Robot ............................................................................................................................................... 13
3.2.1 Introduction ........................................................................................................................ 13
3.2.2 Base Input Panel Description ............................................................................................ 14
3.2.3 Tool Flange......................................................................................................................... 15
3.3 Control System ............................................................................................................................... 17
3.4 Control Box..................................................................................................................................... 18
3.4.1 Introduction ........................................................................................................................ 18
3.4.2 Tool Flange I/O Description.............................................................................................. 18
3.4.3 Control Box External Interface ......................................................................................... 19
3.4.4 Control Box Power Supply Cable..................................................................................... 21
3.5 Demonstrator................................................................................................................................... 22
4Technical Data............................................................................................................................................. 23
4.1 Robot Technical Data ..................................................................................................................... 23
4.1.1 Basic Data........................................................................................................................... 23
4.1.2 Working Space.................................................................................................................... 24
4.1.3 Robot joint coordinates...................................................................................................... 25
4.1.4 Robot zero position and positive direction....................................................................... 25
4.1.5 Tool Flange Data................................................................................................................ 27
4.1.6 Base Data............................................................................................................................ 28
4.2 Load................................................................................................................................................. 29
4.2.1 Basic Load data.................................................................................................................. 29
4.2.2 Payload Diagram................................................................................................................ 30
4.3 Control System Technical Data ..................................................................................................... 31
4.4 I/O data............................................................................................................................................ 31
4.5 Stop time and distance.................................................................................................................... 32
4.5.1 Introduction ........................................................................................................................ 32
4.5.2 Stop time and distance for Axis 1-4 in Stop 0.................................................................. 32
4.6 Nameplates and Labels................................................................................................................... 34

5Installation and commissioning.................................................................................................................. 36
5.1 Mechanical Installation.................................................................................................................. 36
5.1.1 Base module Installation.................................................................................................... 36
5.1.2 Tool Flange Installation ..................................................................................................... 37
5.1.3 Control box installation ..................................................................................................... 37
5.2 Electrical installation...................................................................................................................... 38
5.2.1 Introduction ........................................................................................................................ 38
5.2.2 Electrical Warning and Cautions....................................................................................... 38
5.2.3 Control Box I/O.................................................................................................................. 40
5.2.4 Tool Flange I/O .................................................................................................................. 47
6Transportation and storage ......................................................................................................................... 49
6.1 Transportation................................................................................................................................. 49
6.1.1 Preconditions...................................................................................................................... 49
6.1.2 Robot Packaging ................................................................................................................ 49
6.1.3 Packaging Pose................................................................................................................... 50
6.1.4 Packaging Size ................................................................................................................... 51
6.2 Storage............................................................................................................................................. 52
6.2.1 Preconditions...................................................................................................................... 52
6.2.2 Procedure............................................................................................................................ 52
7Maintenance and repair............................................................................................................................... 53
7.1 Safety Instructions.......................................................................................................................... 53
7.2 Maintenance.................................................................................................................................... 55
7.2.1 Robot Cleaning................................................................................................................... 56
7.2.2 Control Box Cleaning........................................................................................................ 56
7.3 Repair .............................................................................................................................................. 57
Appendix A Reference ........................................................................................................................................ 58

1
1Preface
1.1 Intended Audience
This document provides operating instructions for the SIASUN Collaborative
Robot GCR20-1100, so that users can learn more about the robot basic
information and use the robot more safely and conveniently. Be sure to operate
this robot on the basis of careful reading and full understanding of this document.
This document applies for the following users:
On site robotic engineer
Robotic software engineer
Hardware installation engineer
On-site Maintenance engineer
System maintenance engineer
Operators must receive basic training before robot’s operation.

2
1.2 Representation of Warnings and Notes
The table below defines general hazards related symbols, please read through the
description carefully.
Symbol
Description
Used to warn of emergency situations that, if not avoided, could
result in death or serious personal injury.
Used to warn of potentially dangerous situations that, if not
avoided, could result in death or serious personal injury.
Used to warn of potentially dangerous situations that, if not
avoided, may result in moderate or minor personal injury.
Used to convey device or environmental security warnings that, if
not avoided, may result in damage to the device, loss of data,
degradation of device performance, or other unpredictable results.
Caution does NOT involve personal injury.
Used to highlight important / critical information, best practices
and tips.
"Tips" is not a safety warning message, does not involve
personal, equipment and environmental damage information.

3
1.3 Special Statement
This manual is only used as a guide. Its content (such as equipment appearance,
software interface) is based on laboratory equipment information. The content
provided in this manual is of general guidance and does not guarantee that all
usage scenarios cover all models. Due to the software upgrade and equipment
model inconsistency, the content provided in the manual may NOT be consistent
with the robot used by the user. Please take the information of user equipment as
the standard, this manual will no longer address the differences caused by the
above situations.
The maximum value provided in this manual is the maximum that a device
achieves in a lab-specific scenario that meets the appropriate standards (For
example, constant temperature, humidity, interference free environment, typical
operating conditions and etc.). In reality working situation, the maximum value of
equipment testing may NOT be consistent with the data provided in the manual,
due to different working conditions, specific working conditions and inconsistent
testing methods.
1.4 Revision History
Revision history contains all documentation changes. The newest documentation
contains changes in all previous versions.
Documentation version 0.1(2018-08)
The first time to integrate, initially add contents.
Documentation version 0.2(2018-09)
Formatting of Text, pictures, forms changed.
Documentation version 0.3(2019-02)
Update the description of the control box.
Documentation version 0.4(2019-04)
Update the portion of air pipe allocation.

4
2Safety
2.1 Abstract
This section describes important safety and risk assessments that you need to be
aware when installing, applying, and maintaining on robot and its components.
The user must read and fully understand this information before the robot is
powered on for the first time.
Before performing any operations, be sure to read all operating instructions
provided with the equipment, in particular, instructions that may endanger
personal safety and equipment safety, such as hazards, warnings, and cautions, to
minimize the chance of an accident. When this document differs from the
documentation shipped with the device, the documentation shipped with the
device shall prevail.
The technicians responsible for installing and maintaining the equipment must be
a trained person who has proper methods of operation and all safety precautions.
Only trained and qualified technicians are able to perform equipment installation
and maintenance.
2.2 Limitation of Liability
This information neither includes how to design, install and operate a complete
robot system, nor any peripherals that affect the overall system. In order to protect
personal safety, an outstanding system must be designed and installed in
accordance with the safety requirements stipulated in the standards and
regulations of the country where the robot is installed.
The robot integrator is responsible for ensuring that the robot system complies
with the applicable safety laws and regulations of the country or region where the
robot is located and that the necessary safety equipment for the protection of the
robot system operator is properly designed and correctly installed. Limitation of
Liability
Specifically including but not limited to the following:
Ensure that the robot system meets all basic requirements;

5
Perform a risk assessment of the complete system;
Ensure the design and installation of the entire system is accurate;
Make appropriate security settings in the software and ensure that
it will not be modified by the user;
Develop detailed operating instructions;
Issue a declaration of conformity;
Collect all information in technical documents;
Label the integrator's logo and contact information on the installed
robotic system.
SIASUN Co., Ltd. is committed to providing reliable safety information, but
does not assume responsibilities. It is important to declare that even if all
operations are carried out in a safe manner, there is no guarantee that the robot
system will not cause personal and property damage to the user.
2.3 Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is one of the most important tasks that integrators must
accomplish. The robot itself is a partially completed machine, and the safety of
the robot installation depends on how the robot is integrated (e.g. tools, obstacles
and other machineries).
It is recommended that integrators perform risk assessment in accordance with
ISO12100 (GB 15706) and ISO10218-2 (GB 11291.2). Alternatively, technical
specification ISO/T 15066 (GB/T 36008)may be selected as additional guidance.
Integrators performing a risk assessment should consider all procedures during the
entire lifespan of the robot, including but not limited to:
Teach robots when developing robots;
Fault diagnosis and maintenance;
General operation of robot installation.
Risk assessment must be performed before the robot arm is powered on for the
first time. Part of the risk assessment performed by the integrator is the necessity
to identify the correct security configuration settings and additional protections
for emergency stop buttons and / or for specific robot applications.

6
The following list identifies the significant risks that integrators must consider.
Please note that there may be other significant hazards from certain robotic
devices.
Finger is clamped between joint 4 and joint 5;
Sharp edges and sharp spots on the tool or the tool connector may
cause damage to human skin;
The obstacles sharp edges and sharp spots, which is closed by the
robot trajectory, may be dangerous to human skin;
Sprains orfractures due to impact between the robot payload and a
solid surface;
Consequences due to loosening of bolts used to secure robotic arms
or tools;
Items fall off the tool. For example, due to insufficient clamping or
accidentally power down;
Operating error due to different emergency stop button allocation
and types.
2.4 Safety Operations
2.4.1 Emergency Stop
Emergency stop takes precedence over all the other robot control operations.
Pressing emergency stop will cause all controlled hazards to stop, removing the
motor power from the robot drive. It will remain in effect until reset manually.
Activate emergency stop button to immediately stop the robot from any motion.
The user must perform a restoration procedure, resetting the emergency stop
button and pressing the "Power On" button on demonstrator, to resume normal
operation. Emergency stop shall not be used as a risk reduction measure, but as a
secondary protective device.
Emergency stop must not be used for normal program stop; constantly pressing
may result in additional unnecessary wear on the robot.
2.4.2 Movement without Drive Power
In rare cases, it may be necessary to move one or multiple robot joints in the event
of a robot power failure or an emergency situation that does not require power,
which can force the robot joints to move with the following method:

7
Manual brake release: Remove the M3 screws that secure the joint cover and
remove the joint cover. Press the plunger in the small electromagnet to release the
brake.
Manually moving the robot arm is limited to
emergency situation and may damage joints.
If manual release the break, gravity may cause
the robot arm to fall. Always hold the robot arm,
tools and work-pieces when releasing the break.
Image 2.4.2 Manual break release schemata

8
2.5 The Risk of Collision
There is still a collision detection blind zone during the actual operation of the
robot. Users must pay attention to the risk of collision detection failure under
special working conditions. Typical three types of operating conditions are as
follows.
Scenario 1: When the robot tool flange is outside the range of about 900mm from
the center of the robot base, if the robot moves along the direction of the red
arrow in Figure 2.4.2.1 and Figure 2.4.2.2, the robot is less sensitive to external
forces in the moving direction. The risk of pinching is more likely to occur; when
the robot moves along the direction of the green arrow in Figure 2.4.2.1 and
Figure 2.4.2.2, if the robot collides with the external environment, the external
force generated by the collision is more sensitive.
Image 2.4.2.1 Scenario 1: robot front view

9
Image 2.4.2.2 Scenario 1: robot top view
Scenario 2: Centering on the Z-direction of the robot base coordinate system, the
radius is about 500mm. If the contact point is within this range, and the contact
force direction is perpendicular to the plane of the joints of the joints 2 and joint 3,
the collision detection function is difficult to detect collisions between the robot
and the outside world. As the red arrow shown in Figure 2.4.2.3 in Figure 2.4.2.4;
if the force direction between the robot and the outside is consistent with the Z
direction of the robot base, the robot is more sensitive to the external force
generated by the collision, as the green arrow shown in Figure 2.4.2.3.
Image 2.4.2.3 Scenario 2: robot front view

10
Image 2.4.2.4 Scenario 2: robot front view
Scenario 3: When the robot collides with the outside world, and if the collision
point is located in the spherical range with a radius of about 500mm centered on
the robot base, the robot is more difficult to detect the collision regardless of the
pose and state of the robot. It is more prone to the risk of pinching, as the arrow
shown in Figure 2.4.2.5 and in Figure 2.4.2.6; when the collision point is outside
the range, and does not meet the conditions of the collision detection zone
described in scenario 1 and scenario 2. At the time, the robot is more likely to
detect collisions with the outside world, as the green arrow shown in Figure
2.4.2.5 and in Figure 2.4.2.6.
Image 2.4.2.5 Scenario 3: robot side view

11
Image 2.4.2.6 Scenario 3: robot front view
For all the above described scenarios, if the robot moves in a direction that is
insensitive to external collision detection, considering the limitation of the
cooperation between the robot and the outside world, the running speed at this
time should be reduced as much as possible.

12
3Production Introduction
3.1 Overview
The collaborative robot system consists of the following parts:
GCR20-1100 robot
Control box
Demonstrator
Cables
Software
Optional accessories
Image 3.1.1 Robot system schemata
System critical parameters
Degree of freedom:6
Operational temperature:0℃~25℃
Load(TCP): 20kg
IP Code:Robot IP54
Control box IP30
Repeatability:±0.05mm
Operation hours:35000h
Workspace:1100mm
Installation orientation :Vertical,
Horizontal and Upside down

13
3.2 Robot
3.2.1 Introduction
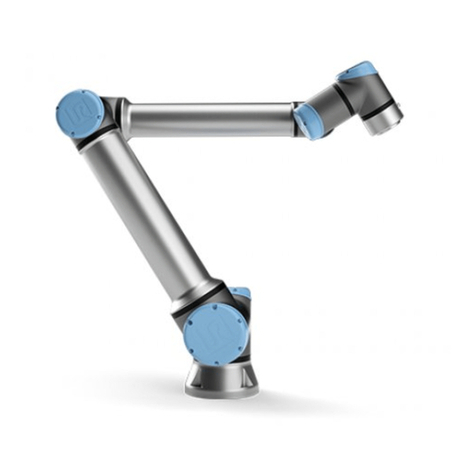
The SIASUN collaborative robot GCR20-1100 consists of 6 modular joints.
The total length of robotic arm is 1260.5mm, workspace radius 1100mm, with
traction teaching, visual guidance, collision detection and other functions. Each
joint of the robot is equipped with a position sensor to detect the joint operation
position and equipped with a reliable brake to stop it in time. Robot can be
installed in any direction.
The robot consists of the following components:
J1 J2
J3
J4 J5
J6
①
②
Figure 3.2.1 SIASUN GCR20-1100 Robot
Base module ②Joint module
Base module
The base is located at the bottom of the robot (J1). The robot cable is connected to
the control box via the base module port board to supply power and data to the
robot.
Joint module
The robot consists of 6 independent drive modules, which are die-case in
aluminum.
Electrical System
The electrical system consists of all the electrical components that powering and
controlling each joint motor (including drives, connectors, cables and etc.).

14
3.2.2 Base Input Panel Description
Image3.2.22 Base module schemata
The base input panel is located at the bottom of the robot and contains several
functional ports. Used to connect cables, supply power to robots, transmit data,
and connect gas lines. Base input panel includes the following functional ports:
1. AIR (φ4)
2. Thread hole
3. Expansion port(RS 485)、 Communication power supply.
port
Design
Limit
Vacuum value
AIR1
Max pressure
7bar
0.95bar
①
②
③

15
3.2.3 Tool Flange
The flange is on the end of robot, which follow GB/T14468.1-50-4-M6 or ISO
9409-1-50-4-M6 standard. There are mounting thread holes and pin holes for
tools installation on the flange. The expansion I / O port on the flange can be used
for connecting tools.
①②③④⑤⑥
Image3.2.3Tool flange schemata
①
Expansion I/O port 1
②
Thread hole
③
Air fitting(1×φ4mm)
④
Point recording button
⑤
Status indicator LED
⑥
Traction teaching button

16
The indicator light described as follow:
Description
Color
Image demo
1.Robot power on
2.Standby
Constant
blue
Error detected
Flashing
red
1.Running program
2.Robot 0 position
3.Manually move to any point
4.Collection detected
Constant
green
Traction teach
Flashing
green
Robot power on
Flashing
white
Table of contents
Other SIASUN Robotics manuals