3
2. POSITIONING THE CHILD
With• NESSIEinplaceatoorlevelchildrencanbe
positioned for therapy and play.
Adjustments
• to the width of NESSIE can be done by simply
moving NESSIE’s “arms” until the required position is achieved.
Children
• can be placed securely into many positions along NESSIE’sproled
contours, with the most common options shown below:
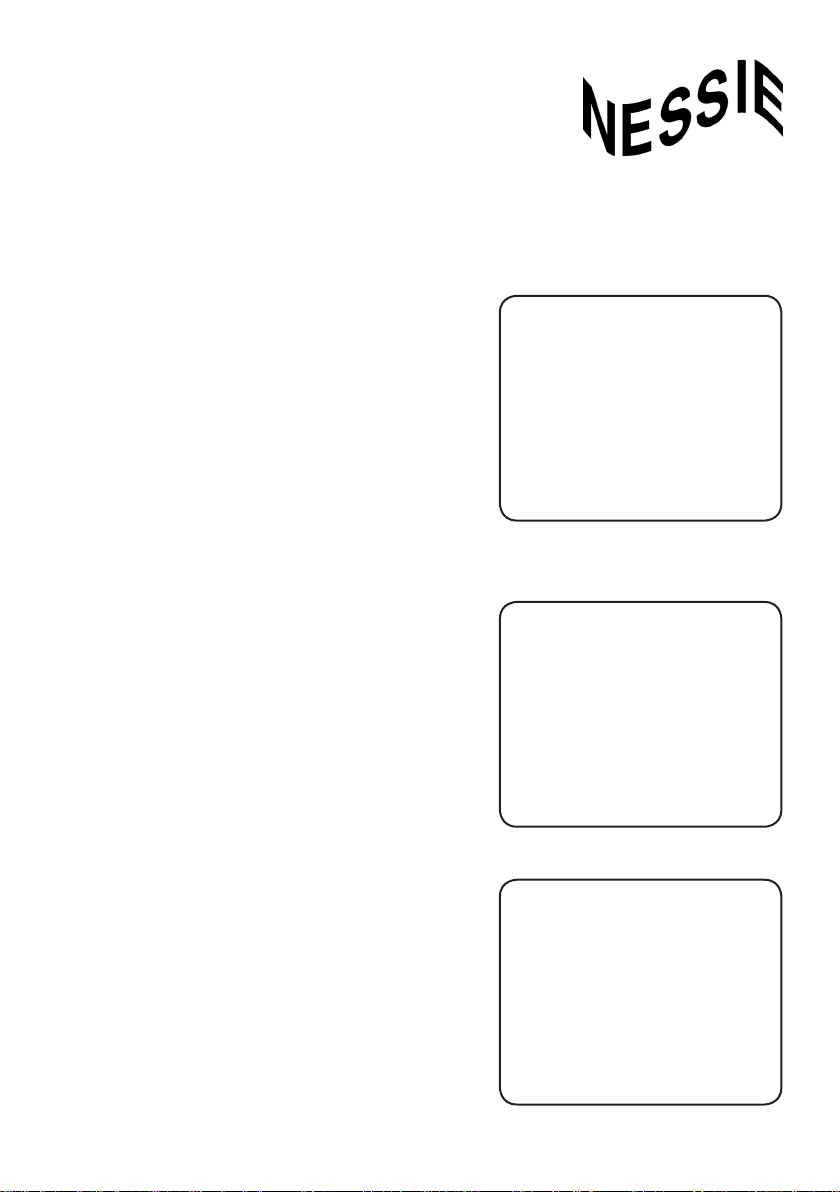
Supine ‘Lying on your back’ (Fig.2a)
Placing• children into Supine is the most stable
position.
Supine
• position supports physical development
through strengthening neck, tummy, shoulder
andhipexorsaschildrenhavetolifthead,
arms and legs up against gravity.
The
• hipsinexionreducesthechanceof
extensor thrust.
Supports
• sensory development as this is the
position in which it is easiest for children to focus their eyes.
Encourages
• hand / feet exploration and hands to mid line.
Prone ‘Tummy Time’ (Fig.2b)
Tummy• Time supports physical development
by strengthening neck, shoulders, arms and
back, and is an important foundation for the
transition to sitting via side lying / side sitting.
Is
• the precursor for rolling, and is a position
supported by all child development workers.
e.g. health visitors and physiotherapists.
Long Sitting (Fig.2c)
Important• part of child development,
encouraging head control, hands to midline
and reaching for toys.
NESSIE’s
• unique ‘BUMPS’ encourage
transverse weight bearing through arms and
shoulders.
Fig.2a
Fig.2c
Fig.2b