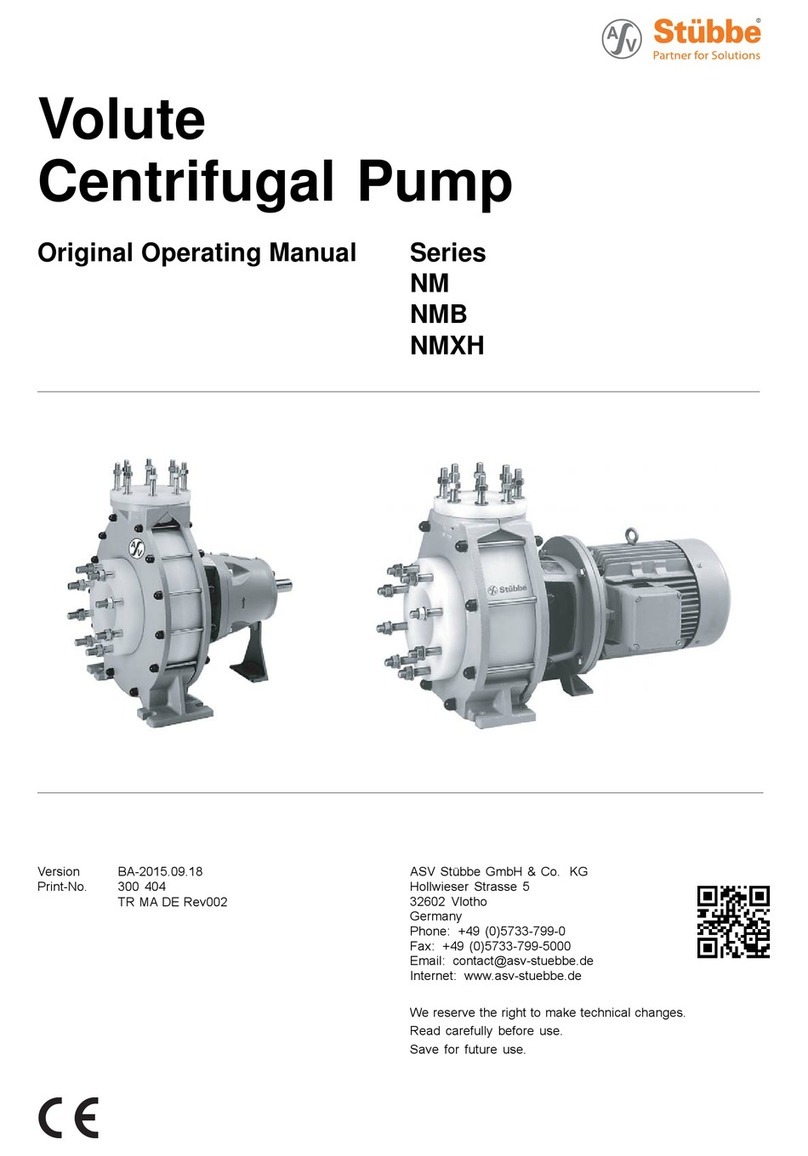
Stübbe ETL Series Installation instructions

Plastic
Sump Pump
Original operating manual Series ETL
Version BA-2018.08.22 EN
Print-No. 300 106
TR MA DE Rev003
STÜBBE GmbH & Co. KG
Hollwieser Straße 5
32602 Vlotho
Germany
Phone: +49 (0) 5733-799-0
Fax: +49 (0) 5733-799-5000
E-mail: co[email protected]
Internet: www.stuebbe.com
Subject to technical modifications.
Read carefully before use.
Save for future use.

Table of contents
Table of contents
1 About this document ............................... 4
1.1 Target groups ................................. 4
1.2 Other applicable documents ................ 4
1.3 Warnings and symbols ....................... 5
2 Safety ................................................. 6
2.1 Intended use .................................. 6
2.2 General safety instructions .................. 6
2.2.1 Product safety ................................ 6
2.2.2 Obligations of the operating company ...... 6
2.2.3 Obligations of personnel ..................... 7
2.3 Specific hazards .............................. 7
2.3.1 Hazardous pumped liquids .................. 7
3 Layout and function ................................ 8
3.1 Marking ....................................... 8
3.1.1 Name plate ................................... 8
3.2 Description .................................... 8
3.3 Assembly ..................................... 8
4 Transport, storage and disposal .................. 9
4.1 Transport ...................................... 9
4.1.1 Unpacking and inspection on delivery .. .. .. 9
4.1.2 Lifting ......................................... 9
4.2 Storage ....................................... 10
4.3 Disposal ....................................... 10
5 Setup and connection .............................. 11
5.1 Preparing for installation ..................... 11
5.1.1 Check operating conditions ................. 11
5.1.2 Preparing the installation site ............... 11
5.1.3 Surface preparation .......................... 11
5.2 Setting up ..................................... 11
5.3 Planning pipelines ............................ 11
5.3.1 Specifying supports and flange
connections ................................... 11
5.3.2 Specifying nominal widths ................... 12
5.3.3 Designing pipelines .......................... 12
5.3.4 Optimizing changes of cross section and
direction ....................................... 12
5.3.5 Providing safety and control devices
(recommended) .............................. 12
5.4 Connecting the pipes ........................ 12
5.4.1 Keeping the piping clean .................... 12
5.4.2 Installing the pressure pipe .................. 12
5.4.3 Inspection for stress-free pipe
connections ................................... 12
5.5 Electrical connection ......................... 13
5.5.1 Connecting the motor ........................ 13
5.5.2 Check direction of rotation ................... 13
5.6 Performing the hydrostatic test .............. 13
6Operation............................................ 14
6.1 Preparing for commissioning ................ 14
6.1.1 Check downtimes ............................ 14
6.1.2 Filling and bleeding .......................... 14
6.2 Commissioning ............................... 14
6.2.1 Switching on .................................. 14
6.2.2 Switching off .................................. 14
6.3 Shutting down the pump ..................... 15
6.4 Restoring the pump to service .............. 15
6.5 Operating the stand-by pump ............... 15
7 Maintenance ......................................... 16
7.1 Inspections ................................... 16
7.2 Servicing ...................................... 16
7.2.1 Maintenance in accordance with maintenance
schedule ...................................... 16
7.2.2 Cleaning the pump ........................... 16
7.3 Dismounting .................................. 17
7.3.1 Preparations for dismounting ................ 17
7.3.2 Dismounting hydraulic system ... ....... .... 17
7.3.3 Dismounting coupling and intermediate
ring ............................................ 18
7.3.4 Dismounting V-rings ......................... 18
7.3.5 Dismounting shaft bearing ................... 18
7.4 Replacement parts and return .............. 18
7.5 Installing ...................................... 19
8 Troubleshooting .................................... 20
9 Appendix ............................................. 22
9.1 Replacement parts ........................... 22
9.1.1 Part numbers and designations ....... .. .. .. 22
9.1.2 Drawing ETL 20-100 to 65-200 ............. 23
9.1.3 Drawing ETL 80-200 ......................... 24
9.2 Technical specifications ...................... 25
9.2.1 Ambient conditions ........................... 25
9.2.2 Flange tightening torques ................... 25
9.2.3 Sole plate tightening torques ... ...... ....... 25
9.2.4 Tightening torques of casing screws .... .. .. 25
9.2.5 Switching frequency ......................... 25
9.2.6 Volumetric flow of liquid medium - minimum
flow rate ....................................... 25
9.2.7 Sound pressure level ........................ 26
9.2.8 Installation dimensions and filling
heights ........................................ 28
9.3 Maintenance schedule ....................... 29
9.4 Lubrication .................................... 30
9.4.1 Lubricating points ............................ 30
9.4.2 Lubricant ...................................... 30
9.5 Declaration of conformity in accordance with
EC machinery directive ...................... 31
2 ETL BA-2018.08.22 EN 300 106

Table of contents
List of figures
Fig. 1 Name plate (example) ....................... 8
Fig. 2 Assembly ..................................... 8
Fig. 4 Replacement parts ETL 20-100 to
65-200 ........................................ 23
Fig. 5 Replacement parts ETL 80-200 ............. 24
Fig. 6 Installation dimensions and filling
heights ........................................ 28
Fig. 7 Lubricating points ............................ 30
List of tables
Tab. 1 Other application documents, purpose and
where found .................................. 4
Tab. 2 Warnings and symbols ....................... 5
Tab.3 Measurestobetakenifthepumpisshut
down .......................................... 15
Tab. 4 Measures depending on the behavior of the
pumped liquid ................................ 15
Tab. 5 Fault/number assignment ................... 20
Tab. 6 Troubleshooting list .......................... 21
Tab. 7 Designation of components according to part
numbers ...................................... 22
Tab. 8 Ambient conditions ........................... 25
Tab. 9 Flange tightening torques ................... 25
Tab. 10 Sole plate tightening torques ................ 25
Tab. 11 Tightening torques of casing screws ........ 25
Tab. 12 Switching frequency ......................... 25
Tab. 13 Volumetric flow of liquid medium ............ 25
Tab. 14 Noise level for 2-pole motors
0.25 kW to 1.5 kW ........................... 26
Tab. 15 Noise level for 2-pole motors
2.2 kW to 45 kW .............................. 26
Tab. 16 Noise level for 4-pole motors
0.18 kW to 1.5 kW ........................... 26
Tab. 17 Noise level for 4-pole motors
2.2 kW to 11 kW .............................. 27
Tab. 18 Installation dimensions (minimum
dimensions) ................................... 28
Tab. 19 Maintenance schedule ....................... 29
Tab. 20 Lubricant ...................................... 30
Tab. 21 Lubricant quantities .......................... 30
300 106 BA-2018.08.22 EN ETL 3

About this document
1 About this document
This manual:
• is part of the equipment
• applies to all series referred to
• describes safe and proper operation during all operating
phases
1.1 Target groups
Operating company
• Responsibilities:
– Always keep this manual accessible where the device
is used on the system.
– Ensure that employees read and observe this docu-
ment, particularly the safety instructions and warnings,
and the documents which also apply.
– Observe any additional country-specific rules and reg-
ulations that relate to the system.
Qualified personnel, fitter
• Mechanics qualification:
– Qualified employees with additional training for fitting
therespectivepipework
• Electrical qualification:
– Qualified electrician
• Transport qualification:
– Qualified transport specialist
• Responsibility:
– Read, observe and follow this manual and the other
applicable documents, especially all safety instructions
and warnings.
1.2 Other applicable documents
Document/purpose/ Where found
Installation drawing
• Dimensions when installed, fitting
dimensions, etc.
Documentation
included
Resistance lists
• Resistance of materials used to
chemicals
•www.stuebbe.com/pdf_resistance/
300051.pdf
CE declaration of conformity
• Conformity with standards
(→9.5 Declara-
tion of conform-
ity in accorda-
ncewithECm-
achinery directi-
ve, Page 31).
Data sheet (300 134)
• Technical specifications, operating
conditions, dimensions
•www.stuebbe.com/
pdf_datasheets/300134.pdf
Spare parts list
• Ordering spare parts
Documentation
included
Sectional drawing
• Sectional drawing, part numbers,
component designations
Documentation
included
Supplier documentation
• Technical documentation for parts
supplied by subcontractors
Documentation
included
Tab. 1 Other application documents, purpose
and where found
4 ETL BA-2018.08.22 EN 300 106

About this document
1.3 Warnings and symbols
Symbol Meaning
• Immediate acute risk
• Death, serious bodily harm
• Potentially acute risk
• Death, serious bodily harm
• Potentially hazardous situation
• Minor injury
• Potentially hazardous situation
• Material damage
Safety warning sign
Take note of all information
highlighted by the safety warning
sign and follow the instructions to
avoid injury or death.
Instruction
1., 2., ... Multiple-step instructions
Precondition
→Cross reference
Information, notes
Tab. 2 Warnings and symbols
300 106 BA-2018.08.22 EN ETL 5

Safety
2 Safety
The manufacturer accepts no liability for damage caused
by disregarding any of the documentation.
2.1 Intended use
• Only use the pump with suitable media (→resistance lists).
• Do not use pump for combustible or explosive fluids.
• Adhere to the operating limits and size-dependent mini-
mum flow rates.
• Avoid cavitation:
– Open the suction-side fitting and do not use it to regu-
late the flow.
– Do not open the pressure-side fitting beyond the
agreed operating point.
• Avoid overheating:
– Do not operate the pump while the pressure-side fitting
is closed.
– Note minimum flow (→Data sheet).
• Avoid damage to the motor:
– Do not open the pressure-side fitting beyond the
agreed operating point.
– Note the maximum permissible number of times the
motor can be switched on per hour (→manufacturer's
specifications).
• Consult with the manufacturer regarding any other use of
the device.
• If pumps are delivered without motors, then final assembly
as a pump assembly must take place in accordance with
the provisions of the Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC.
• Use the pump only as part of a large system/tool.
Prevention of obvious misuse (examples)
• Observe pump limits of use regarding temperature, pres-
sure, flow and speed (→data sheet).
• The power consumption of the pump increases as the spe-
cific gravity of the pumped fluid increases. Adheretothe
permissible specific gravity in order to eliminate the pos-
sibility that the pump, coupling and motor become over-
loaded (→data sheet).
A lower specific gravity is permissible. Adapt the auxiliary
systems accordingly.
• When conveying fluids containing solids, observe the limit
values for proportions of solid particles and particle size
(→Data sheet, technical description).
• When using auxiliary plant systems:
– Ensure compatibility of the operating medium with the
product medium.
– Ensure constant supply of the relevant operating
medium.
• Pumps used with water as the pumped liquid must not be
used for foodstuffs or drinking water. Use for food or drink-
ing water only if specified in the data sheet.
• The type of installation should be selected only in accor-
dance with these operating instructions. For example, the
following are not allowed:
– Hanging base plate pumps in the pipe
– Overhead installation
– Installation in the immediate vicinity of extreme heat or
cold sources
– Installation too close to a wall
2.2 General safety instructions
Observe the following regulations before carrying out any
work.
2.2.1 Product safety
The pump has been built according to state-of-the-art technol-
ogy and the recognized technical safety regulations. Never-
theless, operation of the pump can still put the life and health
of the user or third parties at risk or damage the pump or other
property.
• Operate the pump only if it is in perfect technical condition
and use it only as intended, staying aware of safety and
risks, and in adherence to the instructions in this manual.
• Keep this manual and all other applicable documents com-
plete, legible and accessible to personnel at all times.
• Refrain from any procedures and actions that would pose
a risk to personnel or third parties.
• In the event of any safety-relevant faults, shut down the
pump immediately and have the fault corrected by appro-
priate personnel.
• In addition to the entire documentation for the product,
comply with statutory or other safety and accident-preven-
tion regulations and the applicable standards and guide-
lines in the country where the pump is operated.
2.2.2 Obligations of the operating company
Safety-conscious working
• Operate the pump only if it is in perfect technical condition
and use it only as intended, staying aware of safety and
risks, and in adherence to the instructions in this manual.
• Ensure that the following safety aspects are observed and
monitored:
– Intended use
– Statutory or other safety and accident-prevention reg-
ulations
– Safety regulations governing the handling of haz-
ardous substances
– Applicable standards and guidelines in the country
where the pump is operated
– Applicable guidelines of the operator
• Make personal protective equipment available.
6 ETL BA-2018.08.22 EN 300 106

Safety
Qualified personnel
• Make sure all personnel tasked with work on the pump
have read and understood this manual and all other appli-
cable documents, especially the safety, maintenance and
repair information, before they start any work.
• Organize responsibilities, areas of competence and the
supervision of personnel.
• Ensure that all work is carried out by specialist technicians
only:
– Installation, repair and maintenance work
– Transportation
– Work on the electrical system
• Make sure that trainee personnel only work on the pump
under supervision of specialist technicians.
Safety equipment
• Provide the following safety equipment and verify its func-
tionality:
– For hot, cold and moving parts: pump safety guarding
provided by the customer
– For pumps without capability to run dry: Dry run pro-
tection
– For potential electrostatic charging: provide suitable
grounding
Warranty
• Obtain the manufacturer's approval prior to carrying out
any modifications, repairs or alterations during the warranty
period.
• Only use genuine parts or parts that have been approved
by the manufacturer.
2.2.3 Obligations of personnel
• All directions given on the pump must be followed (and kept
legible), e.g. the arrow indicating the sense of rotation and
the markings for fluid connections.
• Pump, coupling guard and components:
– Do not step on them or use as a climbing aid
– Do not use them to support boards, ramps or beams
– Do not use them as a fixing point for winches or sup-
ports
– Do not use them for storing paper or similar materials
– Do not use the hot pump or motor components as a
heating point
– Do not de-ice the pump using gas burners or similar
tools
• Do not remove the safety guarding for hot, cold or moving
parts during operation.
• Use personal protective equipment if necessary.
• Only carry out work on the pump while it is not running.
• Before all installation and maintenance work, disconnect
the motor from the mains and secure it against being
switched back on again.
• Never reach into the suction or discharge flange.
• Following all work on the pump, refit safety devices in
accordance with the instructions and bring into service.
• Do not make any modifications to the device.
2.3 Specific hazards
2.3.1 Hazardous pumped liquids
• When handling hazardous fluids, observe the safety regu-
lations for the handling of hazardous substances.
• Use personal protective equipment when carrying out any
work on the pump.
• Collect leaking pumped liquid and residues in a safe man-
ner and damage them in accordance with environmental
regulations.
300 106 BA-2018.08.22 EN ETL 7

Layout and function
3 Layout and function
3.1 Marking
3.1.1 Name plate
Typ:
Ser. NO.:
ID. NO.:
M. Seal:
Imp. Ø: m3/h H: m
Q:
Mat.:
Hollwieser Str. 5
D-32602 Vlotho
1
2
3
4
5
6
87
Fig. 1 Name plate (example)
1Pumptype
2 Serial number
3 Ident. number
4 Housing / sealing material
5 Shaft seal information
6 Impeller diameter [mm]
7 Differential head
8Flow
3.2 Description
Non self-priming, vertical centrifugal pump
Useinopenorclosedunpressuredcontainersorpits/trenches.
Thepumpisdry-runningsafe.
3.3 Assembly
2
1
3
4
5
6
8
7
9
10
11
12
13
Fig. 2 Assembly
1 V-ring seal
2 Discharge flange
3 Volute casing
4 Strainer (optional)
5Suctioncup
6Impeller
7Protectiontube
8Shaft
9 Immersion tube
10 Sole plate
11 Shaft bearing
12 Coupling
13 Motor
8 ETL BA-2018.08.22 EN 300 106

Transport, storage and disposal
4 Transport, storage and disposal
4.1 Transport
The user/owner is responsible for the transport of the
pump.
Weight specifications (→documents for the particular
order)
4.1.1 Unpacking and inspection on delivery
1. Unpack the pump/pump assembly upon delivery and
inspect it for transport damage.
2. Check completeness and accuracy of delivery.
3. Ensure that the information on the name plate agrees with
the order/design data.
4. Report any transportation damage to the manufacturer
immediately.
5. Dispose of packaging material according to local regula-
tions.
Retain the transport frame for horizontal storage (recom-
mended).
4.1.2 Lifting
DANGER
Death or limbs crushed as a result transported items
falling over!
Use lifting gear appropriate for the total weight to be trans-
ported.
Attach lifting gear in accordance with the following dia-
grams.
Never use the lifting eye of the motor as the attachment
point for lifting the entire pump (the lifting eye of the motor
may be used for securing a pumpassemblywithahigh
center of gravity against being knocked over).
Do not stand under suspended loads.
1. Attach lifting gear in accordance with the above diagram.
2. Lift the pump/pump assembly appropriately.
300 106 BA-2018.08.22 EN ETL 9

Transport, storage and disposal
4.2 Storage
DANGER
Death or limbs crushed as a result of the pump overturn-
ing!
For vertical storage:
– Place pump on a horizontal underground and secure
against overturning.
NOTE
Material damage due to inappropriate storage!
Store the pump properly.
1. Seal all openings with blind flanges, blind plugs or plastic
covers.
2. Make sure the storage room meets the following condi-
tions:
–Dry
– Frost-free
– Vibration-free
–UVprotected
3. For horizontal storage:
– Protect pump against sagging by means of proper sup-
port.
4. Rotate the pump shaft twice a month.
5. Make sure the shaft and bearing change their rotational
position in the process.
4.3 Disposal
Plastic parts can be contaminated by poisonous or radioac-
tive pumped liquids to such an extent that cleaning will be
insufficient.
WARNING
Risk of poisoning and environmental damage by the
pumped liquid or oil!
Use personal protective equipment when carrying out any
work on the pump.
Prior to the disposal of the pump:
– Collect and damage any escaping pumped liquid or oil
in accordance with local regulations.
– Neutralize residues of pumped liquid in the pump.
Remove plastic parts and damage them in accordance with
local regulations.
Dispose of the pump in accordance with local regulations.
10 ETL BA-2018.08.22 EN 300 106

Setup and connection
5 Setup and connection
NOTE
Material damage due to distortion or passage of electrical
current in the bearing!
Do not make any structural modifications to the pump
assembly or pump casing.
Do not carry out any welding work on the pump assembly
or pump casing.
NOTE
Material damage caused by dirt!
Do not remove the transport seals until immediately before
installing the pump.
Do not remove any covers or transport and sealing covers
until immediately before connecting the pipes to the pump.
5.1 Preparing for installation
5.1.1 Check operating conditions
1. Ensure the required operating conditions are met:
– Resistance of body and seal material to the medium
(→resistance lists).
– Required ambient conditions
(→9.2.1 Ambient conditions, Page 25).
2. Ensure necessary dimensions for tank cut-out (→data
sheet).
3. Ensure safe aeration and venting of the container in all
operating phases.
4. Ensure required installation dimensions and filling lev-
els (→9.2.8 Installation dimensions and filling heights,
Page 28).
– Minimum distances
– Maximum filling height
– Minimum filling height
5.1.2 Preparing the installation site
Ensure the installation site meets the following conditions:
– Pump is freely accessible from all sides
– Sufficient space for the installation/removal of the pipes
and for maintenance and repair work, especially for the
removal and installation of the pump and the motor
– Pump not exposed to external vibration (damage to
bearings)
– No corrosive exposure
– Frost protection
5.1.3 Surface preparation
Aids, tools, materials:
– Spirit level
1. Make sure the surface meets the following conditions:
– Level and horizontal
– Clean (no oil, dust or other impurities)
– Capable of bearing the weight of the pump assembly
and all operating forces
– Stability of the pump ensured
– Resonance-free
2. Clean containers, basins or pits carefully and protect from
further contamination, e.g. by installing overflow wall in
front of the container or pit inlet.
5.2 Setting up
1. Remove the suction-side cover if present.
2. Lift pump/pump assembly (→4.1 Transport, Page 9).
3. Place pump/pump assembly on the contact surface of the
container/pit.
4. Attach sole plate to the contact surface.
– Pump must not be mechanically under stress as a
result of being attached
5. Screw on the sole plate (→9.2.3 Sole plate tightening
torques, Page 25).
5.3 Planning pipelines
Water hammer may damage the pump or the system. Plan
the pipes and fittings as far as possible to prevent water
hammer occurring.
5.3.1 Specifying supports and flange connections
NOTE
Material damage due to excessive forces and torques on
the pump.
Ensure pipe connection without stress.
1. Plan pipes safely:
– No pulling or thrusting forces
– No bending moments
– Adjust for changes in length due to temperature
changes (compensators, expansion shanks)
2. Support pipes in front of the pump.
3. Ensure the pipe supports have permanent low-friction
properties and do not seize up due to corrosion.
300 106 BA-2018.08.22 EN ETL 11

Setup and connection
5.3.2 Specifying nominal widths
Keep the flow resistance in the pipes as low as possible.
1. Make sure the suction extension is not smaller than the
nominal width of the suction branch.
2. Make sure the nominal pressure line width is not smaller
than the nominal discharge flange width.
– Ensure the flow velocity is less than 3 m/s.
5.3.3 Designing pipelines
Plan pipes safely:
– No pulling or thrusting forces
– No bending moments
– Adjust for changes in length due to temperature
changes (compensators, expansion shanks)
5.3.4 Optimizing changes of cross section and
direction
1. Avoid radii of curvature of less than 1.5 times the nominal
pipe diameter.
2. Avoid abrupt changes of cross-section along the piping.
5.3.5 Providing safety and control devices
(recommended)
Avoid reverse running
1. Install a non-return valve between the discharge flange and
stop valve, to ensure that the medium does not flow back
after the pump is switched off.
2. In order to enable venting, include vent connection
between discharge flanges and non-return valve.
Make provisions for isolating and shutting off the pipes
For maintenance and repair work.
Provide shut-off devices in the pressure pipe.
Allow measurements of the operating conditions
1. Provide a pressure gauge in the pressure line for pressure
measurement.
2. Provide pressure measurement on the pump side.
5.4 Connecting the pipes
NOTE
Material damage due to excessive forces and torques on
the pump.
Ensure pipe connection without stress.
5.4.1 Keeping the piping clean
NOTE
Material damage due to impurities in the pump!
Make sure no impurities can enter the pump.
1. Clean all piping parts and fittings prior to assembly.
2. Flush all pipes carefully with neutral medium.
3. Ensure no flange seals protrude inwards.
4. Remove any blind flanges, plugs, protective foils and/or
protective paint from the flanges.
5.4.2 Installing the pressure pipe
1. Remove the transport and sealing covers from the pump.
2. Fit the pressure line stress-free and sealed
(→9.2.2 Flange tightening torques, Page 25).
3. Ensure no seals protrude inwards.
5.4.3 Inspection for stress-free pipe connections
Piping installed and cooled down
1. Disconnect the pipe connecting flanges from the pump.
2. Check whether the pipes can be moved freely in all direc-
tions within the expected range of expansion:
– Nominal width < 150 mm: by hand
– Nominal width > 150 mm: with a small lever
3. Make sure the flange surfaces are parallel.
4. Reconnect the pipe connecting flanges to the pump.
5. If present, check support foot for stress.
12 ETL BA-2018.08.22 EN 300 106
Setup and connection
5.5 Electrical connection
DANGER
Risk of electrocution!
All electrical work must be carried out only by qualified elec-
tricians.
Before all work on the electrical system, disconnect the
motor from the mains and secure against being switched
back on again.
5.5.1 Connecting the motor
Follow the instructions of the motor manufacturer.
1. Connect the motor according to the connection diagram.
2. Make sure no danger arises due to electric power.
3. Install an EMERGENCY STOP switch.
5.5.2 Check direction of rotation
DANGER
Danger to life from rotating parts.
Use personal protective equipment when carrying out any
work on the pump.
Maintain an adequate distance from rotating parts.
1. Switch on motor for max. 2 seconds and switch it off again
immediately.
2. Check whether the sense of rotation of the motor matches
the direction of rotation on the fan impeller.
3. If the sense of rotation is different: Change over any two
phases.
5.6 Performing the hydrostatic test
Only necessary if the entire system needs to be tested
under pressure.
NOTE
Material damage due to bursting of pump casing.
Testing pressure must not exceed the permissible pump
pressure (→documents for the particular order).
Make sure the testing pressure does not exceed the per-
missible pump pressure.
– If necessary, do not perform pressure test on the pump.
300 106 BA-2018.08.22 EN ETL 13
Operation
6Operation
6.1 Preparing for commissioning
6.1.1 Check downtimes
Check downtimes (→6.4 Restoring the pump to service,
Page 15).
6.1.2 Filling and bleeding
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous pumped
liquids!
Use protective equipment for any work on the pump.
Collect leaking liquid safely and damage fitting in accor-
dance with local regulations.
1. Close the pressure-side fitting.
2. Fill pump and, if present, suction pipe with fluid.
Ensure minimum filling height when doing so (→Tab.
18 Installation dimensions (minimum dimensions),
28 Page).
3. Verify that no pipe connections are leaking.
6.2 Commissioning
6.2.1 Switching on
Pump set up and connected properly
Motor set up and connected properly
All connections stress-free and sealed
All safety equipment installed and tested for functionality
Pump prepared, filled and vented correctly
Container is filled sufficiently up to minimum height
“Z” (→9.2.8 Installation dimensions and filling heights,
Page 28).
DANGER
Risk of injury due to running pump!
Do not touch the pump when it is running.
Do not carry out any work on the pump when it is running.
Allow the pump to cool down completely before starting any
work.
DANGER
Risk of injury and poisoning due to pumped liquid spray-
ing out!
Use personal protective equipment when carrying out any
work on the pump.
NOTE
Risk of cavitation if suction flow is restricted!
Open the suction-side fitting and do not use it to regulate
the flow.
Do not open the pressure-side fitting beyond the operating
point.
NOTE
Material damage due to overheating.
Do not operate the pump for long periods with the pressure-
side fitting closed.
Observe minimum flow (→order data sheet).
1. Open the suction-side fitting.
2. Close the pressure-side fitting.
3. Switch on the motor and check it for smooth running.
4. Once the motor has reached its nominal speed, open
the pressure-side fitting slowly until the operating point is
reached.
5. Make sure temperature change is smaller than 5 K/min for
pumps with hot fluids.
6. After the initial stress due to the pressure and operating
temperature, check that the pump is not leaking.
6.2.2 Switching off
Pressure-side fitting closed (recommended)
WARNING
Risk of injury due to hot pump parts!
Use personal protective equipment when carrying out any
work on the pump.
1. Switch off motor.
2. Check all connecting bolts and tighten them if necessary
(only after initial commissioning).
14 ETL BA-2018.08.22 EN 300 106

Operation
6.3 Shutting down the pump
DANGER
Risk of injury due to running pump!
Do not touch the pump when it is running.
Do not carry out any work on the pump when it is running.
Before all installation and maintenance work, disconnect
the motor from the mains and secure it against being
switched back on again.
DANGER
Risk of electrocution!
All electrical work must be carried out only by qualified elec-
tricians.
Before all work on the electrical system, disconnect the
motor from the mains and secure against being switched
back on again.
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous pumped
liquids!
Use protective equipment for any work on the pump.
Collect leaking liquid safely and damage fitting in accor-
dance with local regulations.
Take the following measures whenever the pump is shut
down:
Pump is Action
shut down Take measures appropriate for
the fluid (→Tab . 4 M easur es
depending on the behavior of
the pumped liquid, 15 Page).
…emptied Close suction and pressure-side
fitting.
…dismounted Isolate the motor from its power
supply and secure it against
unauthorized switch-on.
…put into
storage
Note measures for storage.
Tab. 3 Measures to be taken if the pump is shut down
Duration of shutdown (depending
on process)
Behavior of the
pumped liquid
Short Long
Crystallized or
polymerized,
solids
sedimenting
Flush the
pump.
Flush the
pump.
Solidifying/
freezing,
non-corrosive
Heat up or
empty the
pump and
containers.
Empty the
pump and
containers.
Solidifying/
freezing,
corrosive
Heat up or
empty the
pump and
containers.
Empty the
pump and
containers.
Remains liquid,
non-corrosive
––
Remains liquid,
corrosive
–Empty the
pump and
containers.
Tab. 4 Measures depending on the behavior
of the pumped liquid
6.4 Restoring the pump to service
1. Complete all steps as for commissioning
(→6.2 Commissioning, Page 14).
2. If the pump is shut down for over 1 year, replace elastomer
seals (O-rings, shaft sealing rings).
6.5 Operating the stand-by pump
Stand-by pump filled and bled
Operate the stand-by pump at least once a week.
Open pressure-side fitting far enough so that the stand-by
pump operating temperature is achieved and heating is
even (→6.2.1 Switching on, Page 14).
300 106 BA-2018.08.22 EN ETL 15

Maintenance
7 Maintenance
Trained service technicians are available for fitting and
repair work. Submit evidence of conveyed medium on
request (DIN safety data sheet or safety certificate).
7.1 Inspections
The inspection intervals depend on the operational strain
on the pump.
DANGER
Risk of injury due to running pump!
Do not touch the pump when it is running.
Do not carry out any work on the pump when it is running.
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous pumped
liquids!
Use protective equipment for any work on the pump.
1. Check at appropriate intervals:
– Adherence to the minimum flow rate
– Normal operating conditions unchanged
– Filling level of the container
2. For trouble-free operation, always ensure the following:
–Noleaks
–Nocavitation
– Free and clean filters
– No unusual running noises or vibrations
– No inadmissible leaks on the shaft seal
7.2 Servicing
Operating life of antifriction bearings when operated within
the permissible range: >2 years.
Intermittent operation, high temperatures, low viscosities
and aggressive ambient and process conditions reduce the
service life of antifriction bearings.
Plain bearings are subject to natural wear and tear which
is heavily dependent on the respective operating condi-
tions. It is therefore not possible to make general state-
ments about the operating life.
DANGER
Risk of injury due to running pump!
Do not touch the pump when it is running.
Do not carry out any work on the pump when it is running.
Before all installation and maintenance work, disconnect
the motor from the mains and secure it against being
switched back on again.
DANGER
Risk of electrocution!
All electrical work must be carried out only by qualified elec-
tricians.
Before all work on the electrical system, disconnect the
motor from the mains and secure against being switched
back on again.
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous or hot fluid!
Use protective equipment for any work on the pump.
Allow the pump to cool down completely before commenc-
ing any work.
Make sure the pump is depressurized.
Empty the pump, safely collect the pumped liquid and dam-
age it in accordance with environmental rules and require-
ments.
7.2.1 Maintenance in accordance with main-
tenance schedule
Perform maintenance work in accordance with the mainte-
nance schedule (→9.3 Maintenance schedule, Page 29).
7.2.2 Cleaning the pump
NOTE
High water pressure or spray water can damage bearings!
Do not clean bearing areas with a water or steam jet.
Clean large-scale grime from the pump.
16 ETL BA-2018.08.22 EN 300 106

Maintenance
7.3 Dismounting
DANGER
Risk of injury due to running pump!
Do not touch the pump when it is running.
Do not carry out any work on the pump when it is running.
Before all installation and maintenance work, disconnect
the motor from the mains and secure it against being
switched back on again.
DANGER
Risk of electrocution!
All electrical work must be carried out only by qualified elec-
tricians.
Before all work on the electrical system, disconnect the
motor from the mains and secure against being switched
back on again.
DANGER
Death or limbs crushed as a result of the pump overturn-
ing!
Place pump on a horizontal underground and secure
against overturning.
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous or hot fluid!
Use protective equipment for any work on the pump.
Allow the pump to cool down completely before commenc-
ing any work.
Make sure the pump is depressurized.
Empty the pump, safely collect the pumped liquid and dam-
age it in accordance with environmental rules and require-
ments.
WARNING
Risk of injury due to heavy components!
Pay attention to the component weight. Lift and transport
heavy components using suitable lifting gear.
Set down components safely and secure them against
overturning or rolling away.
WARNING
Risk of injury during disassembly!
Secure the pressure-side gate valve against accidental
opening.
Depressurize the blocking pressure system, if available.
Wear protective gloves, components can become very
sharp-edged due to wear or damage.
Remove spring-loaded components carefully (e.g.
mechanical seal, stressed bearing, valves etc.), as com-
ponents can be ejected by the spring stress.
Observe the manufacturer's specifications (e.g. for the
motor, coupling, mechanical seal, blocking pressure sys-
tem, cardan shaft, drives, belt drive etc.).
NOTE
Material damage due to incorrect dismounting/installation
of the pump.
Only specialist mechanics should complete dismounting/
installation work.
7.3.1 Preparations for dismounting
Pump is depressurized
Pump completely empty, flushed and decontaminated
Electrical connections disconnected and motor secured
against switch-on
Pump cooled down
Pressure gauge lines, pressure gauge and fixtures dis-
mounted
When dismounting, observe the following:
– Mark the precise orientation and position of all compo-
nents before dismounting them.
– Dismount components concentrically without canting.
–Dismountpump(→sectional drawing).
7.3.2 Dismounting hydraulic system
1. Undo the pressure pipe screw connection between spiral
casing and sole plate.
2. Screw out the hexagon screws or stud bolts (901.2 or
902.1) from the spiral casing (102).
3. Pull the spiral casing (102) to the bottom.
– Do not tilt the spiral casing
– Do not damage the centering and impeller
4. Remove the impeller cap (260) including O-ring (412.4).
5. Screw out the hexagon nut (920.1), remove spring ring
(934.0) and disc (550).
6. Screw out the impeller (230) from the shaft (211).
7. Remove the key (940.2) and O-ring (412.3).
300 106 BA-2018.08.22 EN ETL 17

Maintenance
7.3.3 Dismounting coupling and intermediate ring
1. Screw out screws on the motor flange, remove motor (801)
and motor-side coupling half (840.1).
2. Screw out screws (901.3) and remove motor bell housing
(341).
3. Remove intermediate ring.
4. Undo stud bolt (840.2) and remove pump-side coupling
half.
7.3.4 Dismounting V-rings
1. Screw out nuts (920.4) and screws (554.3) and remove
motor (801).
2. Dismounting hydraulic system (→7.3.2 Dismounting
hydraulic system, Page 17).
3. Remove the housing cover (161).
4. Remove shaft protection tube (714).
5. Screw out fastening screws (901.7).
6. Remove the suspension pipe (713) including reinforcement
plate (893.2) from the drive assembly group.
7. Remove intermediate ring (509) and V-ring.
8. Remove sealing washer (444).
9. Pull off the sealing flange (490) from the bearing bracket
mounting (330).
10. Remove V-ring in the bearing cover (360.2).
7.3.5 Dismounting shaft bearing
1. Remove V-rings step 1 to 9 (→7.3.4 Dismounting V-rings,
Page 18).
2. Press out the spring dowel sleeves (531) in the shaft sleeve
area (523.1).
3. Remove the shaft sleeve (523.1) from the shaft.
4. Screw out socket head cap screws (914.4).
5. Remove bearing cover (360.2).
6. Bend the stem of the securing plate (931.1) to one side and
undo the shaft nut (921.1).
7. Press the shaft assembly group (211) including distance
sleeve (525) and the shaft bearing (321.1) out of the bear-
ing support towards the hydraulics side.
8. Screw out headless setscrews (904.1).
9. Remove the sleeve (525) from the shaft.
10. Press out shaft bearing (321.1) and labyrinth disc (555).
11. Remove the circlip (932.2) from the bearing support.
12. Press the bearing (321.1) including the top labyrinth disk
(555) out of the bearing support (330).
7.4 Replacement parts and return
1. Have the following information ready to hand when order-
ing spare parts (→type plate).
–Devicetype
– ID number
– Nominal pressure and diameter
– Body and seal material
2. Please complete and enclose the document of compliance
for returns
(→www.stuebbe.com/en/service/download).
3. Use only spare parts from Stübbe.
18 ETL BA-2018.08.22 EN 300 106

Maintenance
7.5 Installing
Install components concentrically and without tilting in
accordance with the markings applied.
WARNING
Risk of injury due to heavy components!
Pay attention to the component weight. Lift and transport
heavy components using suitable lifting gear.
Set down components safely and secure them against
overturning or rolling away.
WARNING
Risk of injury during assembly!
Install spring-loaded components carefully (e.g. mechani-
cal seal, stressed bearing, valves etc.), as components can
be ejected by the spring stress.
Observe the manufacturer's specifications (e.g. for the
motor, coupling, mechanical seal, blocking pressure sys-
tem, cardan shaft, drives, belt drive etc.).
NOTE
Material damage due to incorrect dismounting/installation
of the pump.
Only specialist mechanics should complete dismounting/
installation work.
NOTE
Material damage due to unsuitable components!
Always replace lost or damaged screws with screws of the
same strength where required.
Only replace seals with seals of the same material.
NOTE
Material damage, fragile components.
Install ceramic parts of the plain bearing and magnets of the
magnetic coupling with care, do not strike them or knock
them.
1. When installing please observe:
– Replace worn parts with genuine spare parts.
– Replace seals, inserting them in such a way that they
are unable to rotate.
– Do not apply synthetic or mineral oil, grease or cleaning
agents to elastomer components.
– Adhere to the prescribed tightening torques
(→9.2.4 Tightening torques of casing screws,
Page 25).
2. Installing the pump:
– in reverse order to the dismounting
(→7.3 Dismounting, Page 17).
–→sectional drawing
3. Installing the pump in the system (→5 Setup and connec-
tion, Page 11).
300 106 BA-2018.08.22 EN ETL 19

Troubleshooting
8 Troubleshooting
If faults occur which are not specified in the following table or
cannot be traced back to the specified causes, please consult
the manufacturer.
Possible faults are identified by a fault number in the table
below. This number identifies the respective cause and rem-
edy in the troubleshooting list.
Fault Number
Pump not pumping 1
Pumpingrateinsufficient 2
Pumping rate excessive 3
Pumping pressure insufficient 4
Pumping pressure excessive 5
Pump running roughly 6
Pump leaks 7
Excessive motor power uptake 8
Tab. 5 Fault/number assignment
Fault number
1234 5678
Cause Remedy
X–––––––
Pressure pipe closed by fitting Open the fitting.
XX –X–X––Pump or suction strainer blocked or
encrusted
Clean intake/suction pipe, pump or
suction strainer.
X–––––––
Transport and sealing cover still in place Remove the transport and sealing cover.
—X—X—X——Back pressure of the system is too high,
pump selected is too small.
Consult the manufacturer.
–X–X–X––Suction head too large: NPSHpump is larger
than NPSHsystem
Increase pump inlet pressure.
Consult the manufacturer.
X––––X––Intake/suction pipe and pump not correctly
vented or not completely filled
Completely fill and vent pump and/or
pipe.
XX –X–X––Air is sucked in Check the filling level of the container.
XX –X–X––Proportion of gas too high: pump is
cavitating
Consult the manufacturer.
–X–X–X––Temperature of fluid is too high: pump is
cavitating
Increase pump inlet pressure.
Lower temperature.
Contact the manufacturer.
–X–X–––XViscosity or specific gravity of the pumped
liquid outside the range specified for the
pump
Consult the manufacturer.
XX –X––––Geodetic differential head and/or pipe flow
resistances too high
Remove sediments from the pump
and/or pressure pipe.
Install a larger impeller and consult the
manufacturer.
–X–– XX––Pressure-side fitting not opened wide
enough
Open the pressure-side fitting.
XX –– XX––Pressure pipe blocked Clean the pressure pipe.
20 ETL BA-2018.08.22 EN 300 106
Other manuals for ETL Series
1
This manual suits for next models
13
Table of contents
Other Stübbe Water Pump manuals
Popular Water Pump manuals by other brands

SMITH & LOVELESS
SMITH & LOVELESS Sonic Start Streamline Installation & operation instructions

Pentair Pool Products
Pentair Pool Products LA01N INSTALLATION AND PARTS LIST

Berkeley
Berkeley BVM2-30/2 Installation and operating manual

Raider
Raider Green Tools RD-WP32 user manual

CASELLA CEL
CASELLA CEL TUFF Standard Operator's manual

BUSCH
BUSCH R5 ATEX instruction manual