10
STM-2085
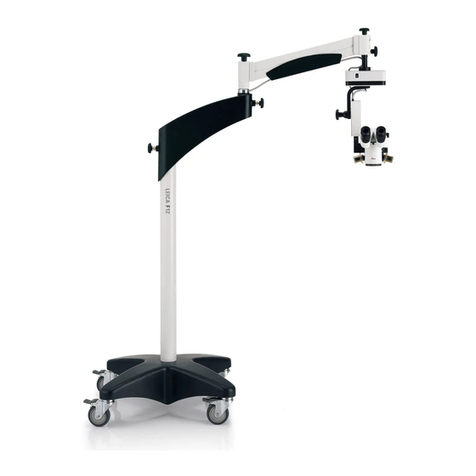
3-8 Adjusting the condenser (Fig.8, 9)
The condenser and the objective are coaxial. It
has been adjusted before leaving factory, so the
user needn’t to adjust them by self.
The highest position of the condenser has been
adjusted before leaving factory, so the user
needn’t to adjust them by self.
Turn the condenser focus knob① to move the
condenser up and down. Raise the condenser
when using the high magnification objective, and
descend it when using the low magnification one.
Centering the Condenser:
1. Adjust the condenser focus knob① to the
highest position.
2. Focus the specimen with 10× objective.
3. Rotate field iris diaphragm ring④until the
image of field iris diaphragm can be observed.
4. Adjust the condenser focusing knob① to
focus the image of field iris diaphragm.
5. Rotate the centering screw③by Allen
wrench to center the field iris diaphragm.
6. Gradually open the field iris diaphragm until
the image of the field iris diaphragm inscribed
with the field of viewing. That means the
condenser is centered correctly.
7. Slightly increase the field iris diaphragm in
reality operation to make the image
circumscribed with the field.
Adjusting Aperture Iris Diaphragm
The aperture iris diaphragm is designed for the
adjustment of the numerical aperture, not for the
brightness. Generally, setting the aperture iris
diaphragm to 70- 80% of the N.A. of the objective
in use will provide an image with good contrast. If
you want to observe the image of the aperture
iris diaphragm, remove one eyepiece and look
through the tube. You will see a dark circle
encroaching on the bottom of the tube.
Adjusting the Field Iris Diaphragm
When using, turn the ring④to reduce the field
iris diaphragm, look into the field, if the
diaphragm image is faintness, and do the follow
steps: first, turn the condenser focus knob, shift
the condenser holder to the position where the
observed image of the field of view is sharp; then
open the field diaphragm, let the image full of
the field of view, reduce the mixed light,
improving the quality of the image.
①②③
Fig.8
④
Fig.9