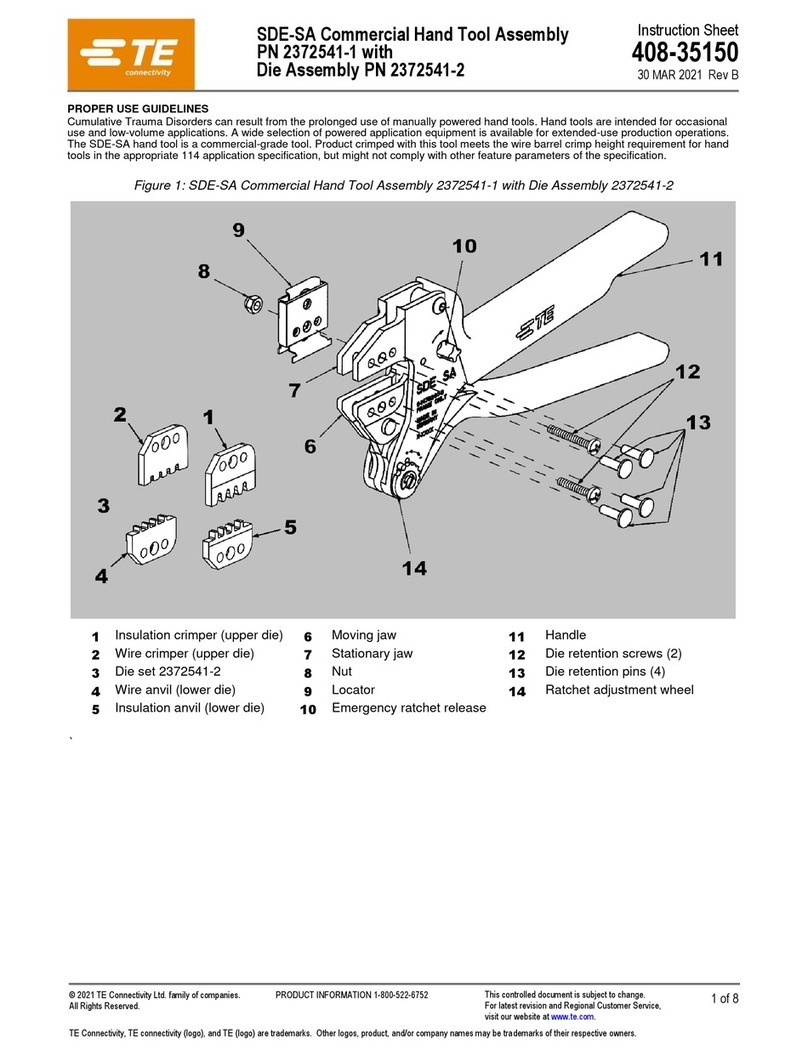
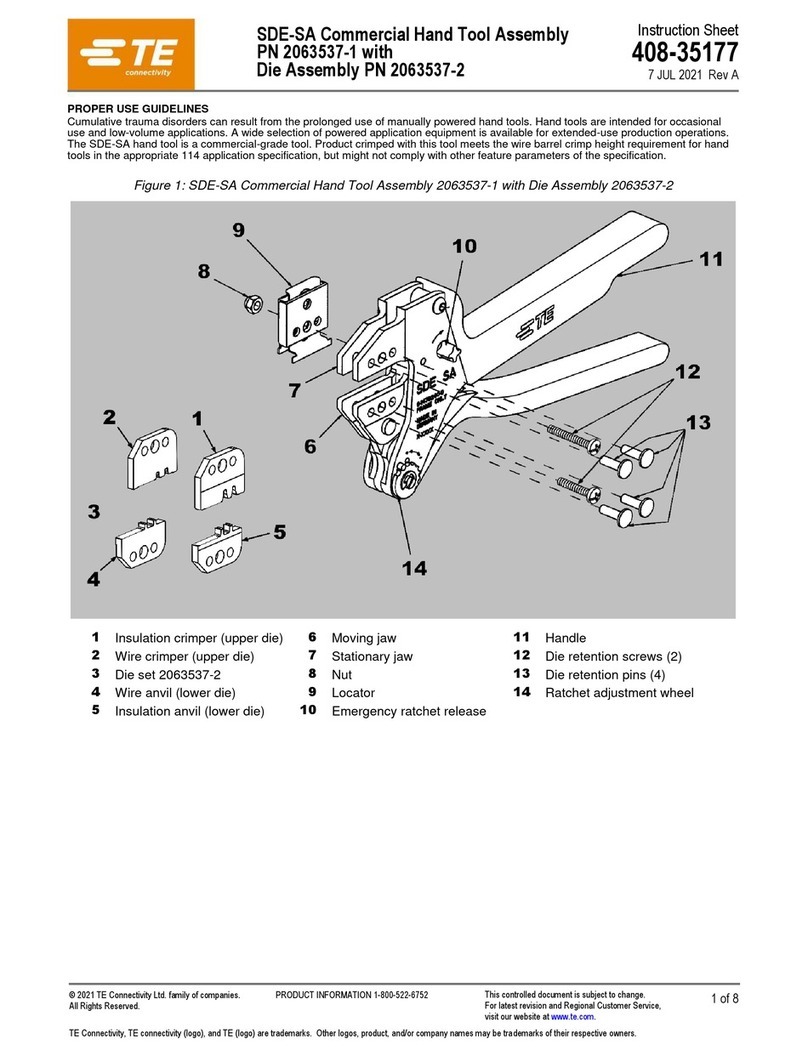
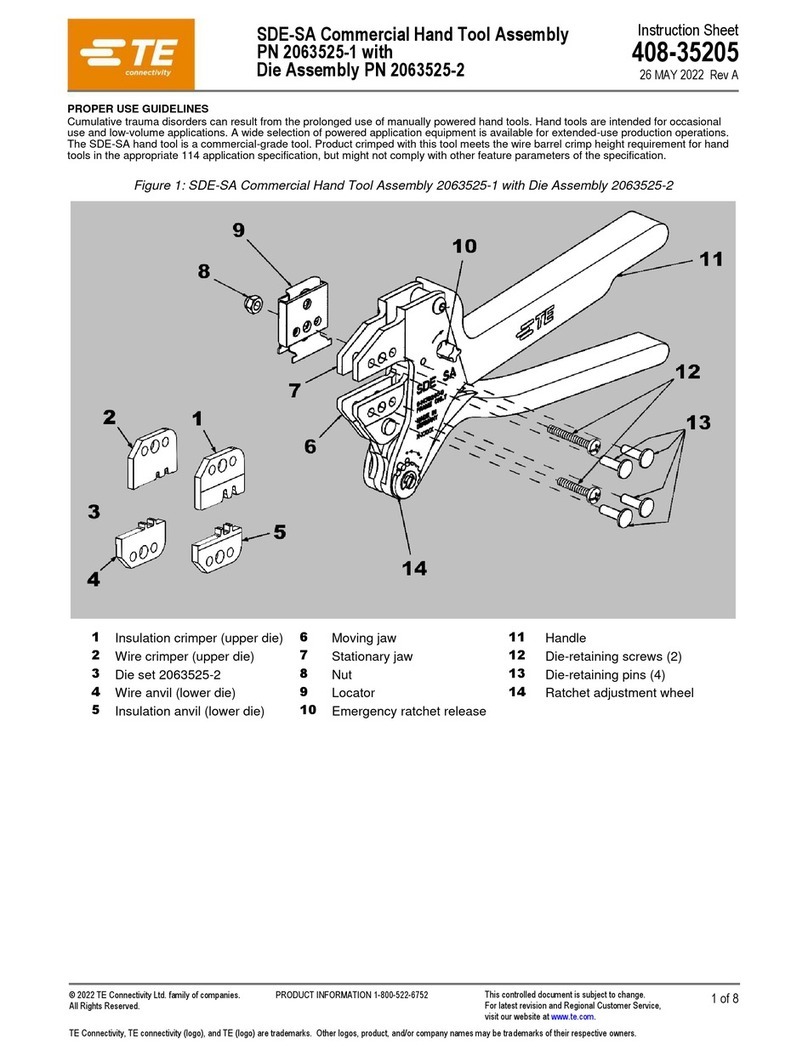
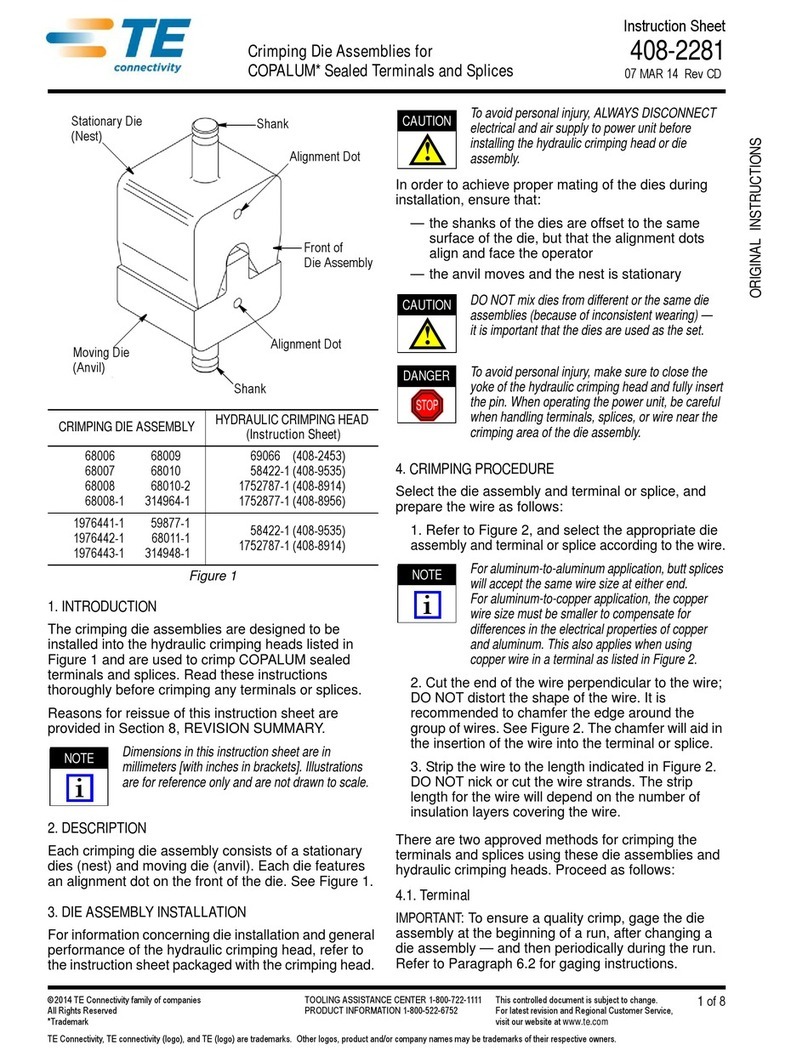
408-7484
3of 4
Rev B
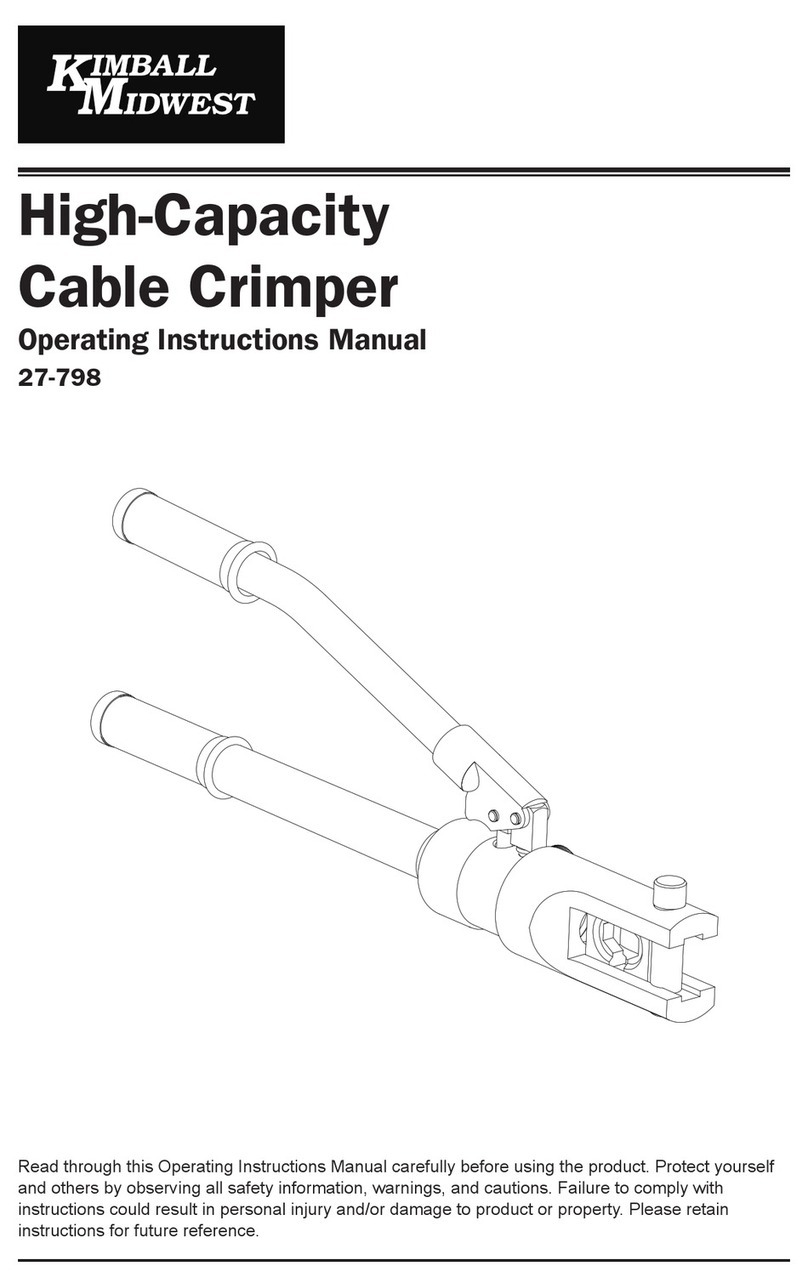
Make sure all pivot points and bearing surfaces are
protected with a thin coat of any good SAE 20 motor
oil. Do NOT oil excessively. When the tool is not in
use, keep the handles closed to prevent objects from
becoming lodged between the dies, and store the tool
in a clean, dry area.
5.2. Periodic Inspection
Regular inspection should be performed by quality
control personnel. A record of scheduled inspections
should remain with the tool and/or be supplied to the
supervisory personnel responsible for the tool. Though
recommendations call for at least one inspection a
month, the inspection frequency should be based on
the amount of use, ambient working conditions,
operator training and skill, and established company
standards. These inspections should be performed in
the following sequence:
A. Visual Inspection
1. Remove all lubrication and accumulated film by
immersing the tool (handles partially closed) into a
suitable degreaser that will not affect paint or plastic
material.
2. Make certain all retaining pins are in place and
are secured with the proper retaining rings. If
replacements are necessary, refer to Figure 5.
3. Close the tool handles until the ratchet releases,
and then allow the handles to open freely. If they do
not open quickly and fully, then the spring is
defective and must be replaced (see Section 6,
REPLACEMENT AND REPAIR).
4. Inspect the tool, with special emphasis on
checking for worn, cracked, or broken crimping
dies. If damage to any part of the head is evident,
return the tool for evaluation and repair (see Section
6, REPLACEMENT AND REPAIR).
B. Crimp Height Inspection
Crimp height inspection is performed through the
use of a micrometer with a modified anvil,
commonly referred to as a crimp height comparator.
TE does not market crimp height comparators.
Refer to Instruction Sheet 408-7424 for detailed
information on obtaining and using a crimp height
comparator.
Proceed as follows:
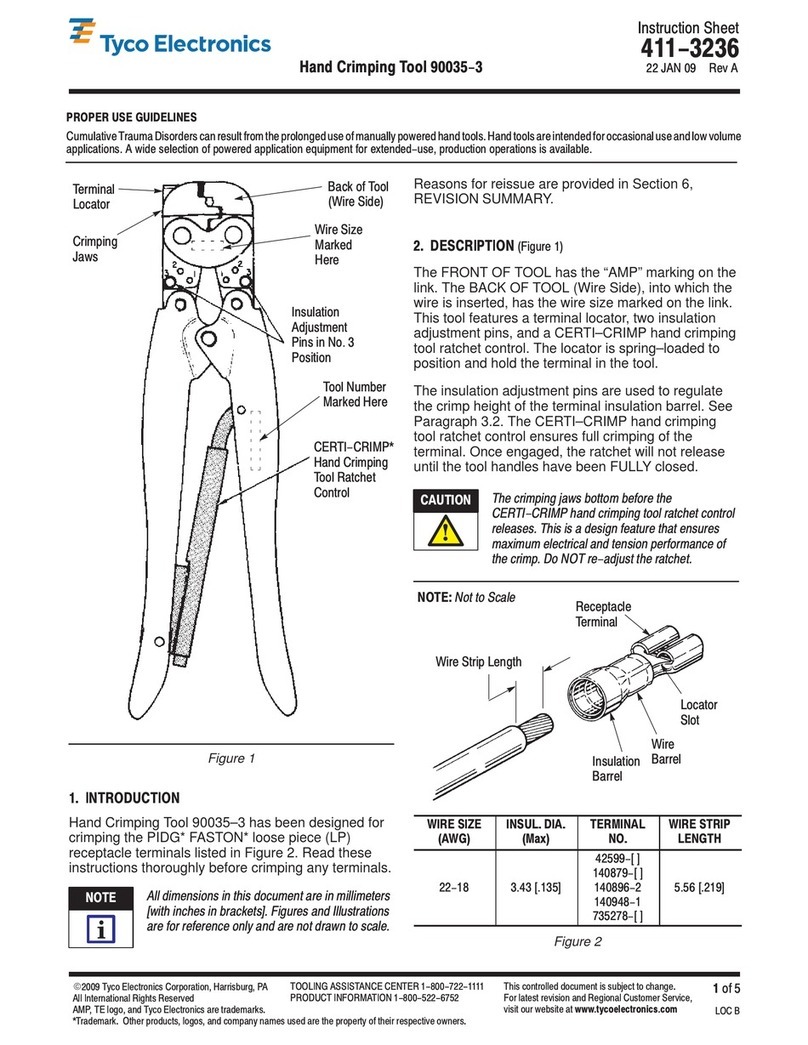
1. Refer to the chart in Figure 4 and select a contact
and a wire (maximum size) for each crimp section.
2. Refer to Section 3, CRIMPING PROCEDURE,
and crimp the contact(s) accordingly.
3. Using a crimp height comparator, measure the
wire barrel crimp height as shown in Figure 4. If the
crimp height conforms to that shown in the chart,
the tool is considered dimensionally correct. If not,
return the tool for evaluation and repair (refer to
Section 6, REPLACEMENT AND REPAIR).
Modified
Anvil
Position Point on
Center of Wire Barrel
Opposite Seam
“A”
±0.05
[±.002]
CONTACT
NUMBER
(LP)
WIRE SIZE
AWG (Max)
CRIMP SECT
(Wire Size
Marking)
CRIMP
HEIGHT
DIM. “A”
203802
203816 22 24 - 22 0.71 [.028]
20 20 0.86 [.034]
Figure 4
C. Ratchet Inspection
Obtain a 0.025-mm [.001-in.] shim that is suitable for
checking the clearance between the bottoming
surfaces of the crimping dies. Proceed as follows:
1. Select a contact and maximum size wire for the
hand tool.
2. Position the contact and wire between the
crimping dies, as described in Section 3,
CRIMPING PROCEDURE.
3. Holding the wire in place, squeeze the tool
handles together until the ratchet releases. Hold the
handles in this position, maintaining just enough
tension to keep the dies closed.
4. Check the clearance between the bottoming
surfaces of the crimping dies. If the clearance is
0.025 [.001] or less, the ratchet is satisfactory. If the
clearance exceeds 0.025 [.001], the ratchet is out of
adjustment and must be repaired.
If the tool conforms to these inspection procedures,
lubricate it with a thin coat of any good SAE 20 motor
oil and return it to service.