TechnipFMC Smith Meter microLoad.net User manual

MANUAL
Electronic Preset Delivery System
Bulletin MN06150 Issue/Rev 0.7 (9/18)
Installation Manual
Smith Meter®microLoad.net™

Caution
The default or operating values used in this manual and in the program of the Smith Meter®microLoad.net™are for
factory testing only and should not be construed as default or operating values for your metering system. Each metering
application.
Disclaimer
TechnipFMC Measurement Solutions, Inc. hereby disclaims any and all responsibility for damages, including but
not limited to consequential damages, arising out of or related to the inputting of incorrect or improper program or
default values entered in connection with the microLoad.net.

Receipt of Equipment
When the equipment is received the outside packing case should be checked immediately for any shipping damage.
remove the unit from its packing case and inspect for damaged or missing parts.
If damage has occurred during shipment or parts are missing, a written report should be submitted to
the Customer Service Department, TechnipFMC Measurement Solutions, Inc., 1602 Wagner Avenue, Erie, Penn-
sylvania 16510.
Prior to installation, the unit should be stored in its original packing case and protected from adverse weather
conditions and abuse.
Caution
This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used
in accordance with this Instruction Manual, may cause interference to radio communications. It has not
been tested to comply with the limits for a Class A computing device pursuant to Subpart J of Part 15
of FCC Rules, which are designed to provide reasonable protection against such interference when
operated in a commercial environment. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause
interference, in which case the user, at his own expense, will be required to take whatever measures may
be required to correct the interference.
Warning
These preset devices must be used with fail-safe backup equipment to prevent accidental runaway delivery
of product. Failure to provide backup equipment could result in personal injury, property loss and equipment
damage.
Warning
On initial power-up of a new unit or after installation of a new computer board, there are several alarms that will be
triggered, which cannot be cleared until the microLoad.net is programmed.

Section I – Introduction.......................................................................................................................................... 6
Section II – Pre-Installation Considerations .........................................................................................................7
Mechanical ............................................................................................................................................................8
Electrical ...............................................................................................................................................................8
Section III – Installation ........................................................................................................................................10
Mechanical ..........................................................................................................................................................10
Electrical .............................................................................................................................................................10
Start-Up .............................................................................................................................................................. 11
Section IV – Diagrams...........................................................................................................................................12
Pulse Inputs ........................................................................................................................................................16
Wiring Diagrams..................................................................................................................................................17
Analog Inputs ......................................................................................................................................................26
Communications .................................................................................................................................................27
Promass Coriolis Meter Communications ...........................................................................................................
Digital Inputs .......................................................................................................................................................
Digital Outputs.....................................................................................................................................................
Instrument Power Wiring.....................................................................................................................................
Sample Application Wiring ..................................................................................................................................
Interposing Relays ..............................................................................................................................................
Section V – Appendix A – ATEX Installation .......................................................................................................44
Section VI – Related Publications........................................................................................................................45
Table of Contents

Tables and Figures
Tables
Table 1. Typical Wire Sizes....................................................................................................................................8
..................................................................................8
..................................................................................8
Table 4. Wiring Checklist .....................................................................................................................................10
Table 5. MNET Board Terminal Assignments.......................................................................................................15
..........................................................................................16
Table 7. Promass Modeling for Single Pulse Wiring ............................................................................................21
Table 8. Promass Modeling for Dual Pulse Wiring...............................................................................................21
Table 9. Wiring Termination for T-568B and T-568A ............................................................................................
Figures
Figure 1. I/O Block Diagram ....................................................................................................................................7
Figure 2. microLoad.net Dimensions.....................................................................................................................12
..........................................................................................................................
Figure 4. MNET Board...........................................................................................................................................14
Figure 5. Wiring Diagram, Prime 4 ........................................................................................................................17
Figure 6. Wiring Diagram, PEX-P Transmitter Single Pulse..................................................................................18
Figure 7. Wiring Diagram, PPS Transmitters ........................................................................................................19
Figure 8. Wiring Diagram, PA-6 Transmitters........................................................................................................ 20
Figure 9. Wiring Diagram, Promass Coriolis Meter ...............................................................................................22
Figure 10. Wiring Diagram, Universal Pulse Transmitter (UPT)..............................................................................
Figure 11. Wiring Diagram, Open Collector Output.................................................................................................24
Figure 12. Wiring Diagram, Typical Metered Injector ..............................................................................................25
............................................................................................26
Figure 14. General Wiring for Serial Communications ............................................................................................27
Figure 15. Multiple microLoad.net Serial Communications .....................................................................................28
.........................................................................................................................29
Figure 17. RS-485 Shared Printing .........................................................................................................................
Figure 18. microLoad.net Ethernet Communications ..............................................................................................
Figure 19. Additive Injector Communications..........................................................................................................
Figure 20. Lubrizol EIA-485 Additive Injector Communications ..............................................................................
Figure 21. Promass Coriolis Meter Communications ..............................................................................................
Figure 22. DC Digital Inputs ....................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
Figure 24. AC Digital Outputs..................................................................................................................................
Figure 25. MACF Board / Instrument Power Wiring ................................................................................................
Figure 26. Sample Application Worksheet...............................................................................................................40
Figure 27. Sample Application AC Wiring................................................................................................................41
Figure 28. Sample Application DC & Signal Wiring.................................................................................................42
Figure 29. Sample Application Power Wiring ..........................................................................................................

Section I – Introduction
Introduction
This manual is to be used for the installation of the Smith Meter®microLoad.net™Electronic Preset Controller with
“Pre-Installation Considerations” describes the areas that must be considered prior to the installation of the
microLoad.net.
“Installation” describes the areas that have to be considered when installing the microLoad.net.
“Diagrams” covers dimensional outline drawings, wiring schematics, typical interconnect diagrams etc.
“Related Publications” lists the literature that is associated with the microLoad.net.

Section II – Pre-Installation Considerations
Supervisory Computer
Supervisory Computer,
SCADA, Printers, Card
Readers, Smart Additive
Injectors, Mass Meters,
Shared Printing
Pumps, Digital Valves,
Alarm Relays, Stop Relay,
Piston Injector, Metered
Injector, Additive Pumps,
General Purpose
External To talizer
Pulse Output
AC Digital Output
AC Digital Output
AC Digital Output
AC Digital Output
DC Digital Output
DC Digital Output
Ethernet
EIA-232/EIA-485
EIA-232/EIA-485
EIA-232/EIA-485
Security Switch,
Permissives, High
Flow Switches,
Remote Start, Remote
Stop,Transaction
Reset, Printer Tr ay
Switch, Piston Injector
Feedback, General
Purpose
DC Digital Input
DC Digital Input
DC Digital Input
Temperature, Pressure, or
Density
Temperature
Flow Meter
Pulse Input
Pulse Input
RTD
4-20 ma
Figure 1. I/O Block Diagram
The Smith Meter®microLoad.net™is a micro-processor based single arm, single product electronic preset instrument

Section II – Pre-Installation Considerations
An important pre-installation consideration is the se-
lection of the ancillary equipment to be used with the
microLoad.net and how that equipment is interfaced.
(Table 6, page 16) which will assist in the assignment
of devices to the microLoad.net’s various I/O positions.
The Worksheet lists the available I/O points versus
possible devices or functions which may be applied.
By checking the appropriate boxes on the Worksheet
I/O map of your application is established. A sample
application starts on page 40.
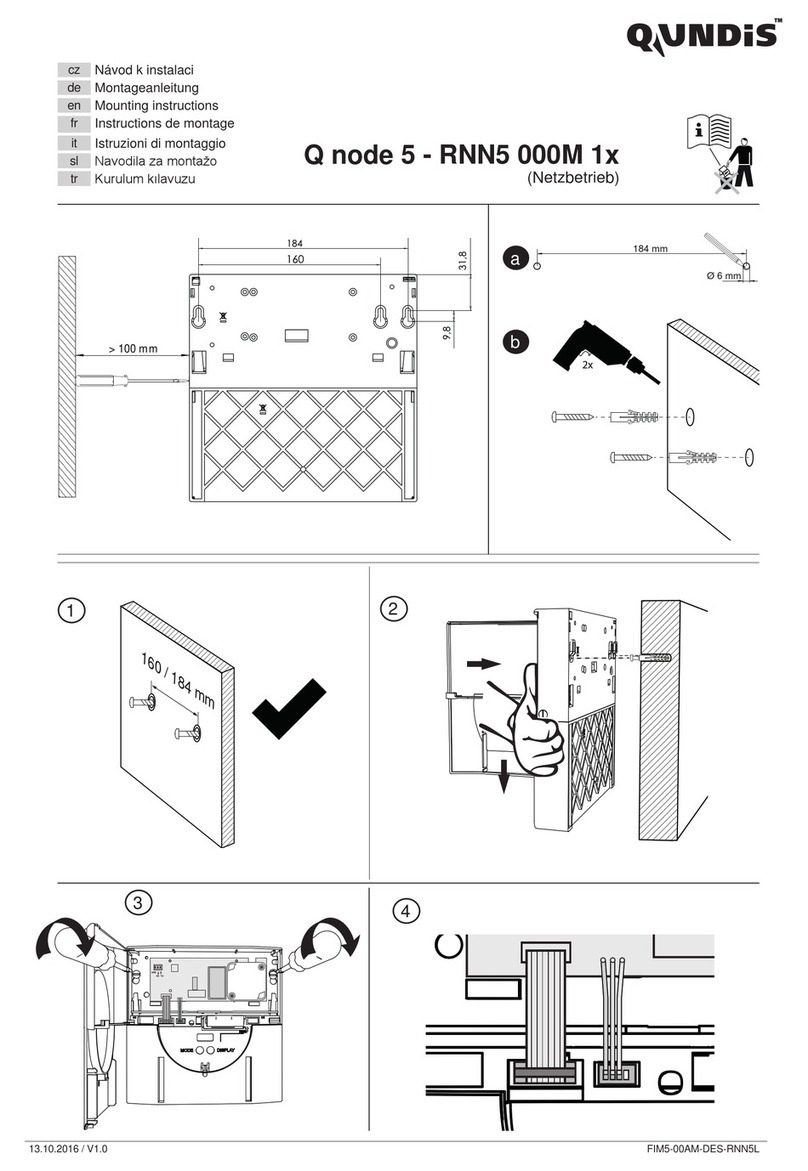
Mechanical
In addition to the following, all previous warnings and
cautions should be reviewed before installation.
1. A solid vertical or slanted surface should be used
for mounting the explosion-proof microLoad.net
housing.
2. The location and the height of microLoad.net should
be selected to permit easy viewing of the display
and to provide convenient access to the keypad
by all users. See Figure 2 for dimensions of the
microLoad.net.
cover. For service, wiring and removal of parts the cover
must removed.
4. Conduit entry to the explosion-proof microLoad.net
is both through the bottom and sides. There are two
the unit.
5. Inwarm climates,microLoad.net shouldbe shadedfrom
direct sunlight. The maximum external temperature
of the microLoad.net housing must not exceed 140°F
(60°C) to ensure that the internal temperature limit is not
exceeded.
Electrical
Note: See Appendix A for information regarding ATEX electrical
installation.
1. All DC wiring must be routed into microLoad.net
through the conduit entries located in the bottom of
the housing. Do not route DC and AC wiring through
the same conduit entry.
2. The DC signal wires must be multi-conductor
shielded cable of 18 to 24 AWG minimum stranded
copper.
at a minimum. Direct Ethernet connections between
computer and microLoad.net require a crossover
-
ration is used where the microLoad.net units are
networked through a hub or switch.
Note: The following recommendations are based on our knowledge
of the electrical codes. The local electrical codes should be reviewed
to ensure that these recommendations follow the local code. Also
installation manuals of all the equipment being wired into the micro-
Load.net should be reviewed for transmission distances and wire
recommendations.
Table 1. Typical Wire Sizes
Equipment Number & Gauge
of Wire
Belden
Number or
Equivalent
Transmitters
4 / 18 Ga.
4 / 20 Ga.
9418
8404
Temp. Probes
Density and
Pressure
ransmitters 4 / 22 Ga.
8729
OR
9940
EIA-485 Comm 4 / 24 Ga. 9842
Table 2. Maximum Cable Length and Baud Rate (EIA-232)
Baud Rate Feet Meters
250 75
19,200 500 150
9,600 1,000
4,800 2,000 610
2,400 4,000 1,220
1,200 4,000 1,220
Table 3. Maximum Cable Length and Baud Rate (EIA-485)
Baud Rates Feet Meters
4,000 1,220
4. All AC wiring must be routed into microLoad.net
through the conduit entries located in the side of
the housing. Connectors sized for a maximum of 14
gauge wire, consult the local electrical codes for the
minimum AC wire size required for your application.
Do not route AC and DC wiring through the same
conduit entry.
5. All AC wiring should be stranded copper and must
comply with federal, state and local codes and
6. Two separate AC circuits must be provided from
the breaker panel. One circuit will supply isolated
power to the microLoad.net electronics (instrument
power). The second circuit will supply power to the
external devices.
7. For proper operation, the microLoad.net must be

earth grounded. The grounding point should be as
close to the unit as possible. To ensure proper earth
a) The resistance between the earth ground lug in
the microLoad.net and the grounding point must
not exceed 2 Ω.
copper stake that extends into the water table.
Where this is not practical, a ground plane may
be used.
Note: Electrical conduit, piping, and structural steel are
not considered proper grounding points for equipment using
electronics.
c) No other devices, except the microLoad.net
and ancillary equipment such as load printers,
should be connected to any point in the ground-
ing circuit.
Section II – Pre-Installation Considerations
8. All user wiring is terminated at compression-type
screw terminal strips. These terminal strips may be
removed from the microLoad.net MACF and MNET
circuit boards to facilitate ease of wiring. Once wir-
ing is complete, the terminal strips are then “plugged
into” their respective positions on the circuit boards.
9. If external relay permissives are used in series with
microLoad.net AC digital outputs, an RC network
must be placed in parallel with the permissive to
prevent a false turn-on of the microLoad.net digital
capacitor and a 680 Ωresistor (Electrocube part
10. Interposing relays must be installed between the
pump controller, alarming device, and the micro-
Load.net permissive sense relays. Permissive
sense inputs are DC voltage.

Mechanical
1. Mount the microLoad.net using four (4) 5/16 - 18
bolts. See Figure 2 for mounting hole layout.
2. Attach the required conduit runs to the microLoad.
net. Be sure to plug all unused conduit entries.
cover/keypad/display. This is done by removing six
(6) cap screws, which hold the cover to the micro-
Load.net enclosure. Carefully pull the cover away
from the enclosure and unplug factory-installed
cables by removing the terminal blocks at the MNET
circuit board. Note the position of these connections
for reinstallation later.
4. Care must be taken in handling the microLoad.net
enclosure and cover to avoid scratching the ground
Electrical
1. AC circuits must be isolated from DC circuits and
brought into the unit through their respective conduit
openings.
ATEX / IECEx
Cable entry must be in accordance to EN/IEC
For wiring systems utilizing cable glands, the gland
cable end must be securely installed and, depend-
ing on the cable type, be properly protected from
mechanical damage.
sealing device must be used immediately at the
entrance of the enclosure.
Any unused entry must be suitably blocked with an
applications.
For North American Zone applications, the plug must
be listed metal close up type.
The maximum ambient temperature for the enclo-
sure is 60°C.
Equipment bonding shall be provided at the external
grounding facility terminal, external connection is not
required when using metallic conduit or armored ca-
Cover to body fasteners must be either DIN 912
-
less steel), or DIN 912-A2-70 (18-8 stainless steel).
Keypad is protected by an intrinsic safe barrier, the
enclosure must be grounded as per national electri-
cal code regulations, for example NEC/CEC etc.
Battery back-up option (if equipped) use only ap-
proved AAA NiMH (1.2V/Cell Nominal) rechargeable
batteries meeting IEC 61951-2 requirements, IEC
Section III – Installation
capacity of 1.5 Ah at a 1 h discharge rate.
Caution: To prevent ignition of hazardous atmo-
spheres, disconnect from supply circuit before
opening, keep tightly closed when circuits are in
operation.
Warning: Contains internal battery-powered circuit,
to prevent ignition of hazardous atmospheres, do
not open enclosure unless area is known to be
non-hazardous.
Note: Refer to page 42 for certication and marking information.
2. All signal and DC wiring should be connected before
connecting AC wiring.
tight.
4. All exposed shields must be properly insulated to
prevent short circuits to other terminals or to the
chassis. The shield at the device (e.g., tempera-
ture device, transmitter, etc.) must be cut back to
continuous. If splices are required, they must be
soldered and properly insulated.
If other communicating devices are used with the
microLoad.net, refer to the manual for that unit for
shielding information. Shields for other communi-
cating equipment should not be terminated in the
microLoad.net.
Note: Shields must not be terminated at the earth ground lugs.
in the microLoad.net to permit easy removal of the
be removed and laid back out of the way so that the
boards can be replaced without removing individual
wires.
6. There is an earth ground lug provided in the unit.
The wire from the lug should be connected to the
proper grounding point. See Pre-Installation Con-
siderations, page 4.
Note: CENELEC approved microLoad.nets require that the
customer install ferrules (Aderendhulsen) per DIN 46 228 on
the grounding wires prior to installation into the grounding lugs.
7. Typical electrical installation diagrams are provided
in the following sections to show the microLoad.net
and ancillary equipment. Before wiring the ancillary
equipment, refer to its installation manual. Use the
installation diagrams in conjunction with the following
checklist to make all necessary connections to your
microLoad.net.
8. Reconnect all terminal blocks to their respective
positions on the MACF and MNET boards. These
terminals blocks are not “keyed”, therefore take
extreme care to be certain that terminal blocks are
returned to the correct position and are in the correct
orientation.

Section III – Installation
Table 4. Wiring Checklist
Install Pulse Input Wiring (from Meters and Metered
Injectors)
Install Pulse Outputs Wiring
Install Analog Input Wiring (RTD and 4-20ma)
Install Communications Wiring
Install Digital Input Wiring (DC)
Install Digital Output Wiring (DC)
Install Digital Output Wiring (AC)
Install Earth Ground
Install Instrument Power Wiring
Cable entries must be in accordance to EN/IEC 60079-1
For wiring systems utilizing cable glands the gland
The cable end must be securely installed and depending
on the cable type be properly protected from mechanical
damage.
-
ing device must be used immediately at the entrance
of the enclosure. Any unused entry must be suitably
and IECEx applications. For North American Zone
applications, the plug must be listed 'metal close-up
type.
The maximum ambient temperature for the enclosure
Equipment bonding shall be provided at the external
grounding facility terminal, external connection is not
required when using metallic conduit or armoured
Cover to body fasteners must be either DIN 912 grade
or DIN 912-A2-70 (18-8 stainless steel).
Keypad is protected by an intrinsic safe barrier, the
enclosure must be grounded as per national electrical
code regulations, for example NEC/CEC etc.
Battery back-up option (if equipped) use only approved
AAA NiMH (1.2V/Cell Nominal) rechargeable batteries
meeting IEC 61951-2 requirements, IEC IEC Designa-
a 1 h discharge rate.
Warning: Contains internal battery-powered circuit.
To prevent ignition of hazardous atmospheres, do not open
enclosure unless area is known to be non-hazardous.
To reduce the risk of ignition of hazardous atmospheres,
within 18 inches of the enclosure. Substitution of com-
ponents may impair intrinsic safety. To prevent ignition of
hazardous atmospheres and to prevent electrical shock,
disconnect from supply circuits before opening, keep
tightly closed when circuits are in operation.
Start-Up
instrument power to the unit. The displays should light,
indicating that the microLoad.net is ready for Start-Up.
to match the inputs and outputs to which it has been
connected. The Reference Manual (MN06148) provides
of the inputs to the microLoad.net. Next, apply external
device power and check the operation of output devices.
The microLoad.net is now ready for use. The Operations
Manual (MN06149) describes the procedures used in
the day to day use of the instrument.

Section IV – Diagrams
Figure 2. microLoad.net Dimensions
2.50
(64)
5.70
(145)
3.69
(94)
7.36
(187)
9.65
(245)
2.50
(64)
2.50
(64)
3.69
(94)
8.63
(219)
4.75
(121)
Two (2) 3/4" NPT Conduit Connection
1/2" NPT Conduit Connection
1/2" NPT Conduit Connection
Mounting
Hole
Layout
2.38
(60)
5.75
(146)
Inches (mm)

Section IV – Diagrams
Figure 3. Opening microLoad.net

Section IV – Diagrams
Figure 4. MNET Board
Switch “S2” Functions
Note: Factory setting for all S2 switches is OFF
Switch 3 Switch 4 Function
OFF OFF
ON OFF Forces IP address to 192.168.0.1
OFF ON Forces IP address to 10.0.0.1
ON ON Enables DCHP
Switch “S1” Functions (RS-485 termination)
Position 1 Position 2 Position 3 Position 4 Position 5 Position 6
COM1 COM1 COM2 COM2
Note: Factory settings for all positions of “S1” is OFF

Section IV – Diagrams
Table 5. MNET Board Terminal Assignments
Connector: CN1
1COM2232Tx 485Tx-
2COM2485Tx+
3COM2232Rx 485Rx+
4COM2485Rx-
5Common
6COM3232Tx 485Tx-
7COM3485Tx+
8COM3232Rx 485Rx+
9COM3485Rx-
10 Common
Terminal #Description232 485
Connector: CN2
1COM1232Tx 485Tx-
2COM1485Tx+
3COM1232Rx 485Rx+
4COM1485Rx-
5Common
Terminal #Description 232485
Connector: CN3
1RTD +
2SIG +
3SIG -
4RTD -
5Shield
Terminal #Description
Connector: CN4
1Input (DC) #1 +
2Input (DC) #1 -
3Input (DC) #2 +
4Input (DC) #2 -
5Input (DC) #3 +
6Input (DC) #3 -
7Pulse Out +
8Pulse Out-
Terminal #Description
Connector: CN5
1Meter Pulse Input/Channel A +
2Meter Pulse Input/Channel A-
3Factory Use Only - Do not connect
4Factory Use Only - Do not connect
5Shield
6Meter Pulse Input/Channel B/Metered Inj +
7Meter Pulse Input/Channel B/Metered Inj-
8Factory Use Only - Do not connect
9Factory Use Only - Do not connect
10 Shield
11 Output (DC) #1 +
12 Output (DC) #1 -
13 Output (DC) #2 +
14 Output (DC) #2 -
Terminal #Description
Connector: CN6
1Factory Cable to MACF (DC PW R +)
2Factory Cable to MACF (Common)
3Factory Cable to MACF (+12 Vdc Transmitter) power
4Factory Cable to MACF (Common)
5Factory Cable to MACF (Earth/Enclosure Gnd)
Terminal #Description
Connector: CN7
1AC Output Common
2N.C.
3Output (AC) #6
4Output (AC) #5
5Output (AC) #4
6Output (AC) #3
Terminal #Description
Connector: CN8
RJ-45 Ethernet Port
14-20 mA input +
2Return - (Common).
Connector: CN9
Terminal #Description
Connector: CN15
Factory Cable to MACF (CN1)
Note: Electronically connected to common

Section IV – Diagrams
Table 6. microLoad.net I/O Conguration Worksheet

Section IV – Diagrams
Figure 5. Wiring Diagram PRIME 4
PRIME 4 Wire Codes:
Note: Pulse Inputs
• If EPLD (U24 chip) is Rev. 0, dual pulse will not function under 25 Hz. Only single pulse will count from 25 Hz
down to 3 Hz. Above 25 Hz, dual pulse will function as normal.
• If EPLD (U24 chip) is Rev. 1 or higher, dual pulse will function from 3 Hz and higher.
• Pulse doubling will not function for input pulses below 25 Hz.
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5 Shield
4
3
2 A-
1 A+
CN5
5
4 Gnd
3 +12Vdc
2
1
CN6
WHITE
BLACK
RED
YELLOW
PRIME 4PRIME 4
YELLOW
RED
BLACK
WHITE
CN6
1
2
3 +12Vdc
4 Gnd
5
CN5
1 A+
2 A-
3
4
5 Shield
6 B+
7 B-
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
MNET Board
MNET Board
Prime 4, Single PulsePrime 4, Dual Pulse

Section IV – Diagrams
Figure 6. Wiring Diagram, PEX-P Transmitter Single Pulse
PEX-P Wire Codes:
Note: Pulse Inputs
• If EPLD (U24 chip) is Rev. 0, dual pulse will not function under 25 Hz. Only single pulse will count from 25 Hz
down to 3 Hz. Above 25 Hz, dual pulse will function as normal.
• If EPLD (U24 chip) is Rev. 1 or higher, dual pulse will function from 3 Hz and higher.
• Pulse doubling will not function for input pulses below 25 Hz.
PEX-P
RED
BLACK
WHITE
CN6
1
2
3 +12Vdc
4 Gnd
5
CN5
1 A+
2 A-
3
4
5 Shield
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
MNET Board
PEX-P, Dual Pulse

Section IV – Diagrams
Figure 7. Wiring Diagram, PPS Transmitters
PPS Terminal Connections:
1. Common
4. B Bar
5. Signal A
6. A Bar
Note: Pulse Inputs
• If EPLD (U24 chip) is Rev. 0, dual pulse will not function under 25 Hz. Only single pulse will count from 25 Hz
down to 3 Hz. Above 25 Hz, dual pulse will function as normal.
• If EPLD (U24 chip) is Rev. 1 or higher, dual pulse will function from 3 Hz and higher.
• Pulse doubling will not function for input pulses below 25 Hz.
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5 Shield
4
3
2 A-
1 A+
CN5
5
4 Gnd
3 +12Vdc
2
1
CN6
PPS MNET Board
PPS, Single Pulse
6
5
4
3
2
1
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5 Shield
4
3
2 A-
1 A+
CN5
5
4 Gnd
3 +12Vdc
2
1
CN6
PPS MNET Board
PPS, Dual Pulse
6
5
4
3
2
1

Section IV – Diagrams
Figure 8. Wiring Diagram, PA-6
PA-6 Terminal Connections
Note: Pulse Inputs
• If EPLD (U24 chip) is Rev. 0, dual pulse will not function under 25 Hz. Only single pulse will count from 25 Hz
down to 3 Hz. Above 25 Hz, dual pulse will function as normal.
• If EPLD (U24 chip) is Rev. 1 or higher, dual pulse will function from 3 Hz and higher.
• Pulse doubling will not function for input pulses below 25 Hz.
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5 Shield
4
3
2 A-
1 A+
CN5
5
4 Gnd
3 +12Vdc
2
1
CN6
PA-6
MNET Board
PA-6, Single Pulse
5
3
1
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5 Shield
4
3
2 A-
1 A+
CN5
5
4 Gnd
3 +12Vdc
2
1
CN6
PA-6
MNET Board
PA-6, Dual Pulse
5
3
1
PA-6
5
3
1
Table of contents
Other TechnipFMC Control Unit manuals
Popular Control Unit manuals by other brands
DeZurik
DeZurik KSL-LA manual

Ross
Ross Vision 4800DR-332-02 installation guide

Circutor
Circutor CBS-4 Series instruction manual

Renschler
Renschler Picolario2 single quick start guide

Sierra Wireless
Sierra Wireless AirPrime EM7565 Hardware integration guide

Sioux Tools
Sioux Tools 1785 Service and operation manual