Teletronics International EzBridge 5800 User manual

EzBridge 5800
User Manual
500mW

No part of this documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work
(such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) without written permission from the copyright owner.
All the other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Statement of Conditions
We may make improvements or changes in the product described in this documentation at any time. The information
regarding to the product in this manual are subject to change without notice.
We assumes no responsibility for errors contained herein or for direct, indirect, special, incidental, or consequential
damages with the furnishing, performance, or use of this manual or equipment supplied with it, even if the suppliers
have been advised of the possibility of such damages.
Electronic Emission Notices
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
(1)This device may not cause harmful interference.
(2)This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
FCC Information
The Federal Communication Commission Radio Frequency Interference Statement includes the following paragraph:
The equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B Digital Device, pursuant to part 15 of
the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment usage generates radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communication. However, there is no grantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to
correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
•Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
•Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
•Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
•Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
The equipment is for home or office use.
Important Note
FCC RF Radiation Exposure Statement: This equipment complies with FCC RF radiation exposure limits set forth for
an uncontrolled environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with a minimum distance of 20cm
between the antenna and your body and must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or
transmitter.
Caution: Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the
user's authority to operate the equipment.

Table of Contents
Introduction……………….……………………………...…..……………...4
1.1 Features …………………………………….......…………….………4
1.2 Specifications ……………………………...………………….………4
1.3 Product Kit ……………………………...……………………..………7
1.4 System Requirements…………………...………………….………..7
1.5 Assembly Diagram …………………………………………………...8
1.6 Default Factory Software Settings ………………………………….8
EzBridge 802.11B Basics …………...…….……………….….………..…9
2.1 Ports ……………………………………………………….……..……9
2.2 LEDs ……………………………………………………….…..……...9
2.3 Installation …………………………………………..……........……..10
Preparation for Installation …………………………………..…...……..…..10
Hardware Installation ………………………………………….......………...10
Configuring Windows for IP Networking ……………………….…...….11
2.4 If you are using Windows 98/Me …………………………...….……11
2.5 If you are using Windows 2000 ……………………………….....….12
2.6 If you are using Windows XP ………………………..………….…...14
Web Configuration Interface ……………………..……………….……....17
3.1 Client Bridge Mode …………………………..……………………….17
Info Page …………….………………………..……………….………18
Configruation Page ….………………………..……………………...19
Stations Page …………………………………..………….…………..22
Admin Page ……………………………………..………….…….……23
3.2 AP Mode …………………………………………..………….….…….26
Info Page …………………………………………..…………………..27
Assoc Page ………………………………………..…………….…….27
Configuration Page ………………………………..……………….…28
MAC Filter Page ……………………………………..………………..30
Advanced Page ………………………………………..……………...31
Encryption Page ………………………………………..……………..32
Admin Page ……………………………………………..……….…….34
Appendix A – Warranty Policy ………………………………..……….…..37
Appendix B – RMA Policy ……………………………………..……….…..38
Appendix C – Regulatory Information ………………………..………….39
Appendix D – Contact Information ……………………………..…….…..41
Appendix E – Important Outdoor Installation Guide …………..………42
Appendix F – Model Info and Compatible Cards ………………..……..43
Appendix F – Troubleshooting ………………………………………..…..44
Appendix G – Glossary …………………………………………………..…45

Introduction
The 802.11b EzBridge 5800 aims to fill in the gap between regular 2.4 GHz and that of 5.8 GHz equipment. It
combines the ease and reliable 802.11b equipment with that of the less crowded 5.8 GHz frequency band. It is the
perfect solution to quickly add more equipment in saturated 2.4 GHz environment. The EzBridge 5800 is a cost
effective solution that is easy to install and operate. To get the most out of this product, please read this manual
carefully.
1.1 Features
•802.11b Wi-Fi compliant
•Quick and easy to install
•Works with any device that has an Ethernet port
•LED indicators show unit operating status
•FCC Certified for use with YDI amplifiers and outdoor antennas with the Diamond WLAN Card
•Web-based configuration screen of EzBridge 5800 enables fast and easy setup
•Supports RTS threshold control for better throughput
•Wireless data encryption with 64 and 128 bits encryption for security
•One-year warranty
1.2 Specifications
EzBridge and PCMCIA Card
Data Rates Supported
1, 2, 5.5, and 11 Mbps
Network Standard
IEEE 802.11b
Uplink
10BaseT Ethernet
Frequency Band
2.4 to 2.497 GHz (subject to local regulations)
Network Architecture Types
Infrastructure
Wireless Medium
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS)
Media Access Protocol
Carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance
(CSMA/CA)
Modulation
•DBPSK @1 Mbps
•DQPSK @ 2 Mbps
•CCK @ 5.5 and 11 Mbps
Operating Channels
•11 channels (US, Canada))
•13 channels (ETSI)
•4 channels (France)
•14 channels (Japan)

Receive Sensitivity
•1 Mbps: –94 dBm
•2 Mbps: –91 dBm
•5.5 Mbps: –87 dBm
•11 Mbps: –84 dBm
Available Transmit Power Settings
100 mW / 200 mW
Range
(typical @ 99-mW transmit power
setting, including 1.95 dBi diversity
dipole antenna)
Indoor:
•50 m (164 ft) @ 11 Mbps
•110 m (360 ft) @ 1 Mbps
Outdoor:
•240 m (787 ft) @ 11 Mbps
•600 m (1968 ft) @ 1 Mbps
EMC Certification
FCC 47CFR15 subpart C (15.247) and Class B device
ETSI 300-328/301-489-17 (General EMC requirement for RF
equipment)
Antenna
Two soldered dipole antennas
Security
IEEE 802.11 WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
Encryption Key Length
64-bit, 128-bit
Filter
MAC Address Filtering
Status Indicators
LED Light provide status of: Power, Wireless LAN, and Ethernet.
Automatic Configuration Support
DHCP client
Remote Configuration Support
HTTP for configuration
TFTP for firmware upgrade
Dimensions WxHxD (mm/inch)
161mm x 30mm x 119mm (6.3 ‘’x1.2 ‘’x4.7’’)
Weight
195g (6.87oz)
Environmental
•Operating temperature: 0 oCto 40 oC(32 oCto 104 oC)
•Storage temperature: -20 oFto 70 oF(-4 oFto 158 oF)
•Humidity: 10 to 90% (non-condensing)
Input Power Requirements
DC 5V 2A
One year

Warranty
UDC 5800HM
Frequency Band to Ant 5725 - 5850 MHz
Frequency Band to Radio 2400 - 2500 MHz
Local Oscillator Frequency 3328 MHz
Frequency Stability ± 2.5 ppm
Output Power 500 mWatt (+ 27 dBm)
Input Power 0.5 mW ~ 25 mW
(-3 dBm to 14 dBm)
RX Conversion Gain 10 dB
TX Conversion Gain up to 14 dB
Noise Figure 4 dB
RF Connector N-Type, female, 50 Ohm
Power Consumption TX: 1.3A @ 9VDC
RX: 0.72 A @ 9VDC
Operating Temperature -40 °C to + 70 °C
2.4/5.8 GHz Channel Conversion Table
802.11 Channel 2400 MHz 5800 MHz
1 2412 5740
2 2417 5745
3 2422 5750
4 2427 5755
5 2432 5760
6 2437 5765
7 2442 5770
8 2447 5775
9 2452 5780
10 2457 5785
11 2462 5790

1.3 Product Kit
The EzBridge 5800 Kit contains the following items:
•One EzBridge 802.11b PCB
•One UDC 5800
•Two Power Extractor (One 7.5 VDC and One 9 VDC)
•One Power Adapter 48VDC
•Nema-4 Enclosure w/ Waterproof CAT5 Jack and Plug.
•One PoE w/ Ground
•Mounting Kit
•Two Ethernet Cable (One Straight and One Cross Over)
•One User Manual
Note: If any item listed above is damaged or missing, please contact your dealer immediately.
1.4 System Requirements
•PC (desktop or notebook) with Ethernet interface.
•TCP/IP protocol must be installed on all PCs. (Refer to User Manual for additional information)
•Network cables. Use standard 10/100BaseT network (UTP) cables with RJ45 connectors.
•All wireless devices must be compliant with the IEEE 802.11B specifications.
•Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.0 or later or Netscape Navigator 4.7 or later.

1.5 Assembly Diagram
*Part pictures will vary, please use it only as a general guide line.
1.6 Default Factory Software Settings
AP (Unit on the side with the 2 Pigtail Antenna Adapter)
IP Address: 192.168.1.90
SSID: snmp_11b_ap
Channel: 1
Client Bridge
IP Address: 192.168.1.99
SSID: blank
Channel: 11

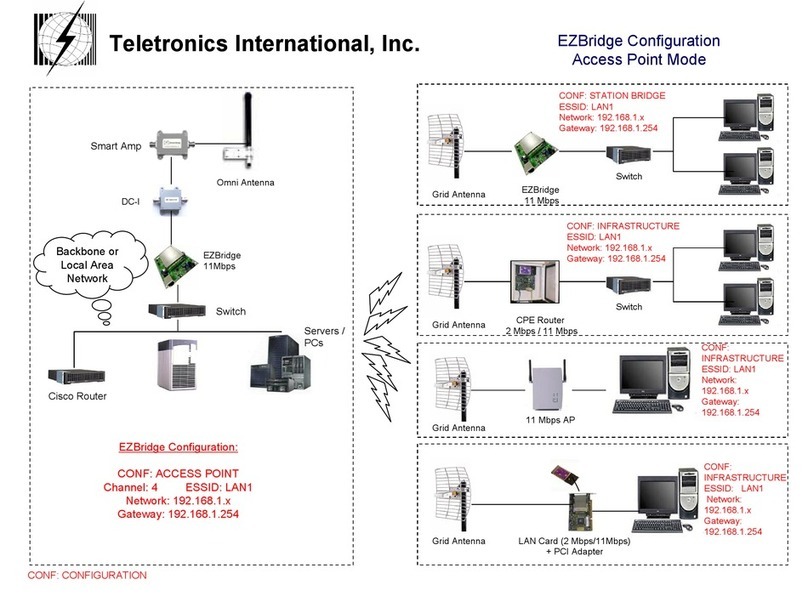
EzBridge 802.11B Basics
This section is consisted of three parts. You will learn the guise of the hardware, including the ports and LEDs, and the
installation ofAccess Point.
2.1 Ports
The ports are on the rear panel of the device. Please see the following picture – the rear view of theAccess Point to
learn more details about your device.
Antenna Connection
When the Access Point begins to work, you may adjust the angle of the antenna or reposition yourAccess Point to
obtain a better performance.
LAN Connection
Use Ethernet straight LAN cable to connect your PC, hub/switch or broadband router/modem to this port.
DC 5V Power Input
Use the power adapter which is only supplied with your Access Point.
Set to Default Button
When you press this button, the Access Point will reboot and reset current settings to factory default settings.
2.2 LEDs
The 802.11b EzBridge includes three types of LED indicators. Please check the following picture – the front view of the
Access Point and table to obtain the information on the LED indicators on your Access Point.

LED Status Function
On Power on.
Power Off No power.
Blinking Blinking: Wireless LAN is transmitting.
On On: Wireless LAN connection is active.
WLAN
Off Off: Wireless LAN connection is not active.
Blinking Blinking: Wired LAN is transmitting.
On On: Wired LAN is active.
Ethernet Off Off: Wired LAN is not active.
2.3 Installation
Preparation for Installation
Before the permanent install of the EzBridge 5800 the unit must be preconfigured within reach of a computer/laptop.
The configuration of the EzBridge 5800 is no different than setting up a regular EzBridge. Please ensure that all the
items listed in “1.4 System Requirements” are prepared, and then choose the place with the consideration of power
outlet and network connection to do the permanent install.
Hardware Installation
Follow the procedures below to fully install your EzBridge 5800:
1. Select proper location.
2. Mount the EzBridge by following the mounting instruction included in the EzBridge Kit.
3. Connect the Ethernet port on the NEMA4 box to the ODU side of the PoE. Then connect the NET side to the
internal Network. After both are connected connect the power adapter to the power jack on the PoE to power
on the EzBridge 5800. You may want to do a quick on on the LEDs to ensure the unit is getting power.
4. Now the hardware installation is complete, and you may proceed to the next chapter –“Configuring Windows
for IP Networking” for instruction on setting up network configurations.

Configuring Windows for IP Networking
To establish a communication between your PCs and the EzBridge 5800, you will need to set up a static IP address for
your computer first. This section helps you configure the network settings for your operating system. Please follow the
procedures below to complete the settings:
2.4 Windows 98/Me
1. Click Start on the taskbar and choose Control Panel from the submenu of Settings.
2. Select Network to open the Network dialog box, and then under the Configuration tab, select the TCP/IP
protocol for your network card.
3. Click Properties to open the TCP/IP Properties dialog box.
4. Click the IP Address tab and choose Specify an IP address. For example, type in 192.168.1.X in the IP
Address (where X is any free IP number from 1-254, excluding 99) area and 255.255.255.0 in the Subnet Mask
area. To ensure the system is now using the IP address you specify, restart the computer.

Note: Again the IP address must be in the format of 192.168.1.x. Where the value of X should be ranged from 1 to 254
excluding 99.
5. Click OK, and then restart the system.
2.5 Windows 2000
1. Click Start on the taskbar and choose Network and Dial-up Connection from the submenu of Settings.
2. Double-click the Local Area Connection open the Local Area Connection Properties box.
3. Select the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) for your network card, and then click Properties to open the Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box.
4. Under the General tab, choose Use the following IP address, and then specify an IP address. For example,
type in 192.168.1.X in the IP Address (where X is any free IP number from 1-254, excluding 99) area and
255.255.255.0 in the Subnet Mask area.

Note: Again the IP address must be in the format of 192.168.1.x. Where the value of X should be ranged from 1 to 254
excluding 99.
5. Click OK.
2.6 Windows XP
1. Click Start on the taskbar and choose Network from the submenu of Control Panel.
2. Right-click the Local Area Connection icon and then choose Properties from the menu. You should see the
Local Area Connection Properties dialog box shown below.

3. Select the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) for your network card, and then click Properties.
4. In the opened dialog box, choose Use the following IP address
5. Under the General tab, choose Use the following IP address, and then specify an IP address. For example,
type in 192.168.1.X in the IP Address (where X is any free IP number from 1-254, excluding 99) area and
255.255.255.0 in the Subnet Mask area.

Note: Again the IP address must be in the format of 192.168.1.x. Where the value of X should be ranged from 1 to 254,
excluding 99.
Click OK.

Web Configuration Interface
3.1 Client Bridge Mode
Default IPAddress in Client Bridge Mode: 192.168.1.99
To access the web control interface please open up a browser window and type in the factory default IP address in the
URL.
Then press Enter on your keyboard, you will see the login prompt window appear similar like the one shown below.
There is no default User name or Password. Leave User Name and Password field blank and then click OK.
Note: You may set a new password by clicking the Admin tab after you enter the Web Configuration page

Info
Firmware Revision
Current firmware revision loaded on the EzBridge.
Connected to SSID
SSID in which the EzBridge is associated to.
Using Channel
If the EzBridge is associated with anAP or Bridge it will display the channel used.
MAC address of Access Point
The associatedAP’s MAC address.
Current transmission rate (Mbits/s)
Displays the current maximum transmission rate established by the wireless link.
Current communications quality (%)
The communications quality is calculated in a ratio percentage based on the signal strength and noise.
MAC address of the wireless card
The MAC address of the wireless card plugged inside the EzBridge.
Current IP address
IP address assign on the unit.

Configuration

Operation Mode
Ad-hoc: An 802.11 networking framework in which devices or stations communicate directly with each other, without
the use of an access point (AP). Use this mode if there is no wireless infrastructure or where services are not required.
Infrastructure: An 802.11 networking framework in which devices communicate with each other by first going through
an Access Point (AP). This mode is the default factory setting.
SSID
Network Name is also known as SSID, which stands for Service Set Identifier. Any client in Infrastructure mode has to
indicate the SSID of an Access Point to start accessing the service from behind such as internet access.
Channel
Channels are important to understand because they affect the overall capacity of your Wireless LAN.A channel
represents a narrow band of radio frequency. A radio frequency modulates within a band of frequencies; as a result,
there is a limited amount of bandwidth within any given range to carry data. It is important that the frequencies do not
overlap or else the throughput would be significantly lowered as the network sorts and reassembles the data packets
sent over the air.
These are the only 3 channels out of the 11 available that do not overlap with one another. To avoid interference within
the network with multipleAPs, set each AP to use one of the 3 channels (e.g. Channel 1) and then the otherAP to be
one of the other 2 channels (i.e. Channel 6 or Channel 11) within the range of the wireless radio. This simple method
will reduce interference and improve network reliability.
802.11b/g Wireless Channel Frequency Range: 2.4 GHz – 2.497 GHz
802.11b/g Non-overlapping Channel Frequency Ranges
•Channel 1 = 2.401 GHz – 2.423 GHz
•Channel 6 = 2.426 GHz – 2.448 GHz
•Channel 11 = 2.451 GHz – 2.473 GHz
Americas: Wireless Channels 1 – 11
Asia: Wireless Channels 1 – 14
Europe: Wireless Channels 1 – 13
Transmission Rate
This option indicates the transmission rate of the bridge. Specify the rate according to the speed of your wireless
network from the list. Most of the time the default setting Best (automatic) should be selected for best performance.
You may want to adjust the setting manually If your link quality and signal strength is usually low or high to get the best
performance.
WEP enabled
Short for Wired Equivalent Privacy, a security protocol for wireless local area networks (WLANs) defined in the 802.11b
standard. WEP is designed to provide the same level of security as that of a wired LAN. This option will enable the
WEP security authenticator.
WEP Key Length
64 bit (10 Hex Digit)
WEP Key type Example
64-bit WEP with 5 characters
Key1= 2e3f4
Key2= 5y7js
Key3= 24fg7
Key4= 98jui

64-bit WEP with 10 hexadecimal digits
('0-9', 'A-F')
Key1= 0x123456789A
Key2= 0x23456789AB
Key3= 0x3456789ABC
Key4= 0x456789ABCD
128 bit (26 Hex Digit)
WEP Key type Example
128-bit WEP with 13 characters
Key1= 2e3f4w345ytre
Key2= 5y7jse8r4i038
Key3= 24fg70okx3fr7
Key4= 98jui2wss35u4
128-bit WEP with 26 hexadecimal digits
('0-9', 'A-F')
Key1= 0x112233445566778899AABBCDEF
Key2= 0x2233445566778899AABBCCDDEE
Key3= 0x3344556677889900AABBCCDDFF
Key4= 0x44556677889900AABBCCDDEEFF
*Hexadecimal digits have to preceded by '0x'
WEP Key 1 – 4
Follow the example above to setup either character or hexadecimal key according to the key length.
WEP key to use
Select one pre-defined WEP key to use for authentication.
Deny unencrypted data
When the WEP authentication is enabled any unencrypted data will be blocked from getting pass this unit from the
receiving side.
Shared key Authentication
Shared key authentication supports authentication of stations as either a member of those who know a shared secret
key or a member of those who do not. Shared key authentication is not secure and is not recommended for use. It
verifies that an authentication-initiating station has knowledge of a shared secret. This is similar to pre-shared key
authentication for Internet Protocol security (IPSec). The 802.11 standard currently assumes that the shared secret is
delivered to the participating wireless clients by means of a more secure channel that is independent of IEEE 802.11.
In practice, a user manually types this secret for the wireless AP and the wireless client.
Shared key authentication uses the following process:
1. The authentication-initiating wireless client sends a frame consisting of an identity assertion and a request for
authentication.
2. The authenticating wireless node responds to the authentication-initiating wireless node with challenge text.
3. The authentication-initiating wireless node replies to the authenticating wireless node with the challenge text
that is encrypted using WEP and an encryption key that is derived from the shared key authentication secret.
4. The authentication result is positive if the authenticating wireless node determines that the decrypted
challenge text matches the challenge text originally sent in the second frame. The authenticating wireless node
sends the authentication result.
Because the shared key authentication secret must be manually distributed and typed, this method of authentication
does not scale appropriately in large infrastructure network mode, such as corporate campuses.
Table of contents
Other Teletronics International Network Hardware manuals

Teletronics International
Teletronics International TT 4900 User manual

Teletronics International
Teletronics International TT 2400 User manual

Teletronics International
Teletronics International TT2400 Instruction manual

Teletronics International
Teletronics International EZ Bridge 802.11G User manual

Teletronics International
Teletronics International TT5800 Instruction manual

Teletronics International
Teletronics International TT 900 User manual
Teletronics International
Teletronics International EzBridge Instruction sheet