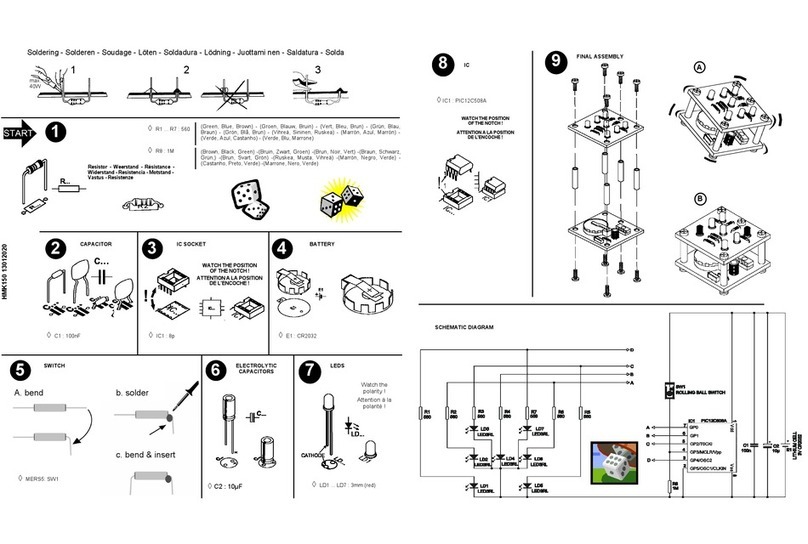
- 5 -
DO NOT BLINDLY FOLLOW THE ORDER OF THE
COMPONENTS ON THE TAPE. ALWAYS CHECK THEIR
VALUE ON THE PARTS LIST!
1. Assembly (Skipping this can lead to troubles ! )
Ok, so we have your attention. These hints will help you to make this project successful. Read them carefully.
1.1 Make sure you have the right tools:
• A good quality soldering iron (25-40W) with a small tip.
• Wipe it often on a wet sponge or cloth, to keep it clean; then apply solder to the tip, to give it a wet look. This is called ‘thinning’ and
will protect the tip, and enables you to make good connections. When solder rolls off the tip, it needs cleaning.
• Thin raisin-core solder. Do not use any fl ux or grease.
• A diagonal cutter to trim excess wires. To avoid injury when cutting excess leads, hold the lead so they cannot
fl y towards the eyes.
• Needle nose pliers, for bending leads, or to hold components in place.
• Small blade and Phillips screwdrivers. A basic range is fi ne.
For some projects, a basic multi-meter is required, or might be handy.
1.2 Assembly Hints :
• Make sure the skill level matches your experience, to avoid disappointments.
• Follow the instructions carefully. Read and understand the entire step before you perform each operation.
• Perform the assembly in the correct order as stated in this manual.
• Position all parts on the PCB (Printed Circuit Board) as shown on the drawings.
• Values on the circuit diagram are subject to changes, the values in this assembly guide are correct*.
• Use the check-boxes to mark your progress.
• Please read the included information on safety and customer service.
* Typographical inaccuracies excluded. Always look for possible last minute manual updates, indicated as ‘NOTE’ on a separate leafl et.
1.3 Soldering Hints :
1. Mount the component against the PCB surface and carefully solder the leads.
2. Make sure the solder joints are cone-shaped and shiny.
3. Trim excess leads as close as possible to the solder joint.