6
Care and Maintenance
The body of this plane is ductile cast iron and comes treated with rust preventative.
Remove this using a rag dampened with mineral spirits. Clean all machined surfaces.
We recommend that you initially, then periodically, apply a light coat of paste wax
to seal out moisture and prevent rusting; this also has the added bonus of acting as
a lubricant for smoother planing. Wipe off any wood dust from the surfaces that
you will be waxing, apply a light wax coating, let dry, then buff with a clean soft
cloth. At the same time, the solvents in the wax will remove any harmful oils left
from your fingers that can lead to corrosion.
Note: Since the face of the fence and the bottom of the depth stop will come in
contact with the workpiece, it is important to keep these parts coated with paste
wax to prevent marring the workpiece.
Keep in mind that paste wax contains silicone that, if transferred to your workpiece,
could cause finishing problems such as "fish eyes". To avoid this problem, use
silicone-free products, such as Waxilit®sliding agent and glue release, or a tool
surface sealant and lubricant. Either is an excellent alternative to regular paste
wax. However, before treating a plane with a sealant, wipe off any fingerprints
with a cloth dampened with a small amount of light machine oil. Remove any
residual oil; then apply the sealant to the plane’s sole.
If storage conditions are damp or humid, the plane should, in addition to the
treatment outlined above, be wrapped in a cloth or stored in a plane sack. This
precaution will also guard against dings and scratches.
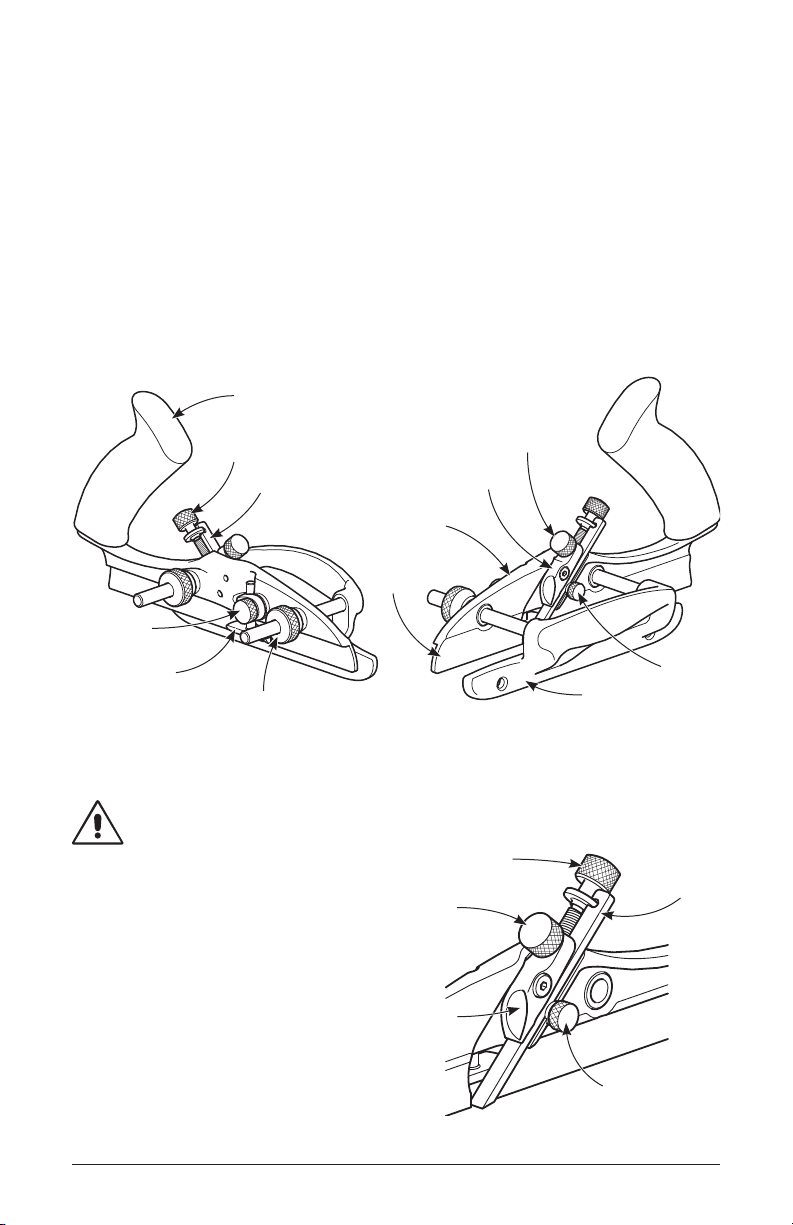
Every so often, take the plane apart to clean it. Remove the blade, the depth stop
and the fence from the body. Clean all parts with a cloth dampened with a dab of
light machine oil. For corroded plane bodies, we recommend you first remove the
rust with a fine rust eraser, then treat as described above.
The bright finish on the brass components can be maintained as above. If a patina
finish is preferred, simply leave the brass components unprotected until the desired
level of oxidation has occurred, then apply a sealant. If you want to make them
bright and shiny again, you can revitalize the surface with a brass polish.