V-Tap VoIP Manual EN v2.7 Oct 2018 © 2017-2018 Vidicode 4
1Introduction
The V-Tap VoIP is a hardware and software solution for the recording of
telephone calls that are transported over an IP network. The supplied
hardware unit sniffs the digital data coming from external IP telephones
and can copy the data back to the network or stores the data directly
onto an SD card. In both cases the data is wrapped into a special Tunnel-
format that can be received by the Call Recorder Apresa (running on
Linux) or by the Call Recorder VoIP software (running on a Windows PC).
The external Apresa recorder or CR-VoIP software can both interpret the
Tunnel-format and make playable audio files from it, together with the
original date, time and call number information (meta data).
The build-in switch function allows 4 Ethernet connections (100 Mbps).
This makes it possible to connect 3 external IP phones and one
connection to the network. For a desktop solution, it is also possible to
connect a PC or other network peripherals.
An IP phone can also be a Softphone running on a PC. This is achieved
by simply wiring the PC’s network through the V-Tap VoIP switch.
In the case that no SD card is inserted, the sniffed data is sent life over
the network to the Apresa recorder or CR-VoIP software.
With an SD card inserted, the sniffed data is stored as files on the card.
Depending on whether a Tunnel has been defined or not, the files are
sent over the network or can be read later by the CR-VoIP software.
By using the SD card (FAT32 formatted), the V-Tap VoIP can operate
completely stand alone and can store data for months or even years,
depending on the capacity of the card.
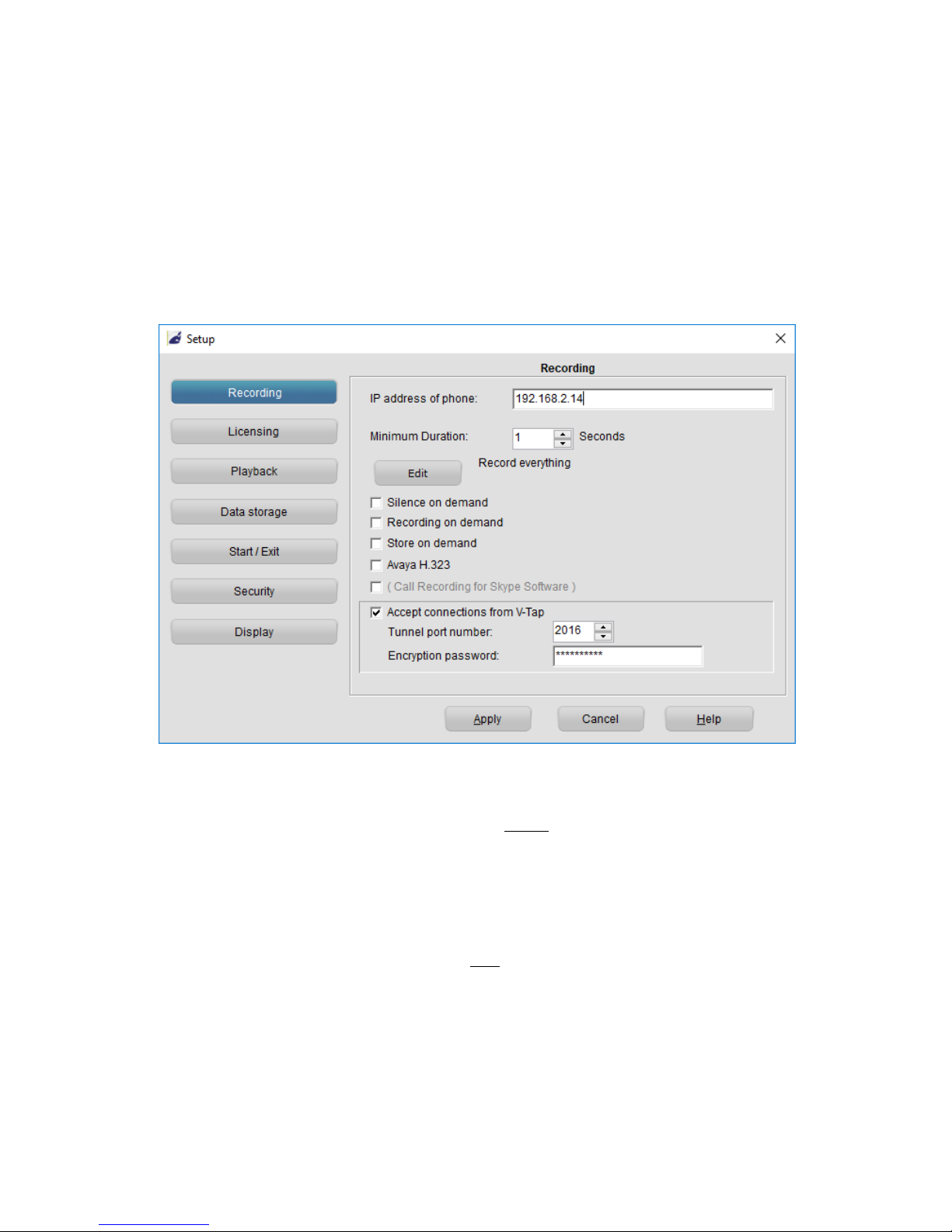
The internal settings of the V-Tap VoIP can be accessed through a web
interface by any browser.
The V-Tap VoIP is a member of a family of compatible products that can
be used to create all sorts of Call Recording solutions. There are V-Taps
for Analog and ISDN telephony, there is an App for mobile recording
and all these products communicate with the Apresa Corporate
recording solution or Apresa cloud-based recording.
NOTE: The V-Tap VoIP needs to be powered through USB, otherwise
the device cannot record from external IP phones.