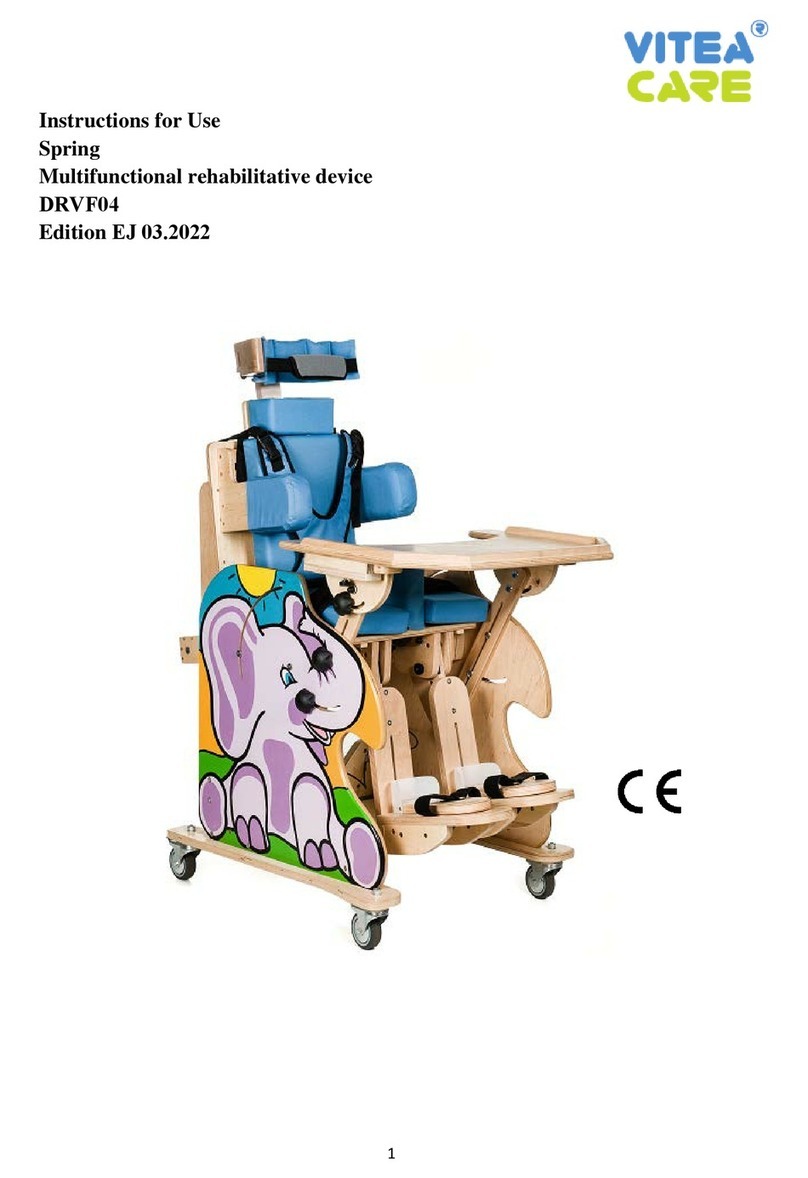
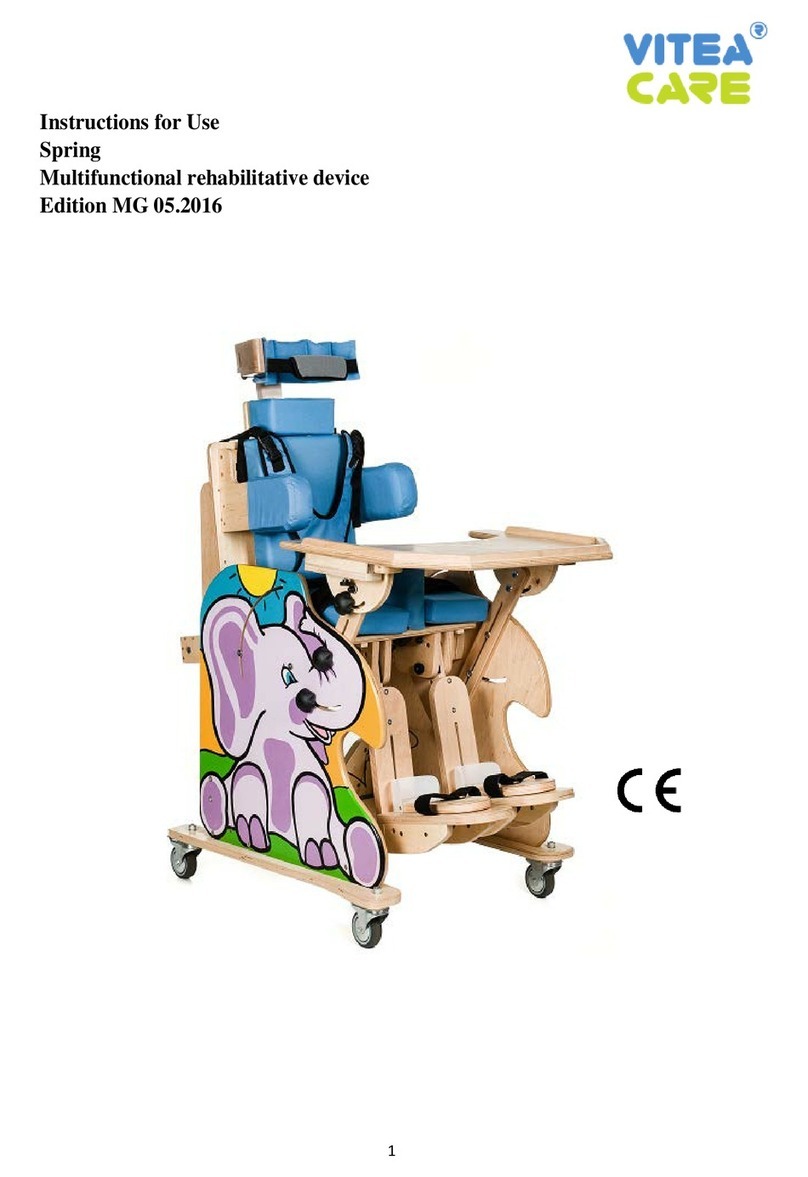
Vitea Care PARAPODIUM PD150 User manual

Dynamic Parapodium
Model PD150, PD 180, PD 200
User’s Manual
09.2016

CONTENTS
1.
MEDICAL INFORMATION .....................................................................................................
3
1.1 I
NTRODU TION
, K
EY
W
ORDS
, K
INESITHERAPY
.......................................................................................................... 3
1.2 D
ISTURBAN ES
O
F
F
UN TION
O
F
I
NTERNAL
O
RGANS
I
N
D
ISABLED
S
UBJE TS
D
UE
T
O
HRONI
S
ITTING
P
OSITION
A
ND
/O
R
B
ED
R
IDDING
............................................................................................................................................ 3
1.3 A
DVANTAGES
O
F
D
YNAMI
P
ARAPODIUM
................................................................................................................. 4
1.4 M
OST
OMMON
S
YSTEMI
D
ISTURBAN ES
L
IKELY
T
O
O
UR
I
N
P
ARAPLEGIA
.......................................................... 4
1.5 E
XEMPLARY
P
RELIMINARY
R
EHABILITATION
P
ROGRAMME
F
OR
T
HE
P
ERIOD
O
F
A
DAPTATION
O
F
T
HE
O
RGANISM
T
O
T
HE
D
EVI E
. ................................................................................................................................................................. 5
2.
USER’S MANUAL .................................................................................................................
6
2.1 G
ENERAL
P
RIN IPLES
O
F
S
AFETY
............................................................................................................................ 6
2.2 G
ENERAL INFORMATION
............................................................................................................................................ 7
2.3 P
REPARATION
O
F
T
HE
P
ARAPODIUM
T
O
U
SE
........................................................................................................... 9
2.4 U
SE
O
F
T
HE
P
ARAPODIUM
.....................................................................................................................................
10
2.5 T
RANSPORT OF THE DEVI E
....................................................................................................................................
12
2.6 S
TORING
,
LEANING
A
ND
M
AINTENAN E
O
F
T
HE
P
ARAPODIUM
. .............................................................................
13
2.7 S
AFETY PRE AUTIONS
............................................................................................................................................
13
2.8
ERTIFI ATES
..........................................................................................
B
ŁĄD
! N
IE ZDEFINIO ANO ZAKŁADKI
.
2.9 E
NVIRONMENTAL PROTE TION
................................................................................................................................
14
2.10 P
ERIODI AL SERVI ING
..........................................................................................................................................
14
2.11 W
ARRANTY
............................................................................................................................................................
15
2.12 W
ARRANTY INSTRU TIONS
.....................................................................................................................................
15
2

1. MEDICAL INFORMATION
“It is easier to achieve the intended aim after getting acquainted with the subject-matter of the undertaking – it
enables to predict possible consequences adequately and unifies the language of communication between the partners of
the dialogue reducing unnecessary, unpleasant experiences .
1.1 Introduction, Key ords, Kinesitherapy
Paraplegia and paraparesis can be of traumatic or pathologic origin and it most frequently occurs in the following
diseases:
•poliomyelitis anterior acuta (Heine–Medin disease, polio),
•spina bifida,
•syringomyelia
•paraplegia spondylica,
•paraplegia scoliotica,
•paraplegia neoplasmatica
•Duchenne’s dystrophy and others.
Application of the Dynamic Parapodium in rehabilitation is associated with the assumption that movement
(kinesitherapy) is a therapeutic method, providing a stimulus acting specifically on the organism which
considerably improves the patient’s quality of life.
“The motor process of learning to move (kinesitherapy) is a purposeful, dosed, methodicaly planned application of motor
patterns in order to maintain, support and restore the efficiency of the locomotor and nervous system, circulation, respiration
and metabolism. ( onradi E., Brenke R., Bewegungstherapie-Grundlagen, Ergebnisse, Trends. Ullstein – Mosby, Berlin,
1993)
Parapodium – a kind of orthosis (a technical construction used for the purpose of control of movements, providing aid to, or
total or partial reduction of load on the selected elements of the supportive and locomotor system of the body) stabilising,
equipped with the base of large surface area, used for subject with lower extremity and trunk paralysis, allowing to assume
upright position without additional support on crutches and sitting up.
Dynamic Parapodium = parapodium – orthosis system making active rehabilitation and movement (gait) possible.
Paraparesis (Latin paresis;) paresis affecting the lower extremities.
Paraplegia - (Latin paralysis s. Plegia;) palsy affecting the lower
extremities. Flaccid paralysis – damage of the peripheral motoneuron.
Spastic paralysis – damage of the central (interior) motoneuron.
Paresis - (Latin paresis) – reduced mobility or power of movement.
Paralysis, plegia - (Latin paralysis) – complete lack of movement.
1.2 Disturbances Of Function Of Internal Organs In Disabled Subjects Due To Chronic
Sitting Position And/Or Bed Ridding
onsiderable limitation of physical activity due to chronic supine or/and sitting position leads to the development of
interconnected pathological consequences, such as:
•Degenerative changes in the cardiovascular system,
•Orthostatic hypotensive syndrome,
•Venous stasis, deep venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism,
•Increased risk of coronary disease (lower serum level of high density lipoprotein cholesterol – HDL- ),
•Increase of body weight due to lowered basal metabolic rate and reduced daily energy
expenditure connected with the lack of physical activity, gas exchange abnormalities,
•Increased risk of atelestasis,
•pneumonia,
•reduced maximum oxygen consumption, which is an indicator of the general patient’s condition,
•hyperkalcemia,
•osteoporosis,
•glucose intolerance,
•miction (excretion of urine) and defecation (bowel movement) disturbances,
•increasing difficulty in everyday activities,
•upper extremity overload syndromes,
•muscular atrophy accompanied by contractures involving multiple joints,
•pathological long bone fractures,
•reduced ability to function independently,
•skin integrity disturbances,
•damage to peripheral nerves,
3

•increased level of stress associated with everyday activities,
•disturbances of sensory perception,
•social interaction and self-acceptation more difficult (depression),
•increased stigmatisation, stereotypy, discrimination and lack of acceptation among the active members of
the society,
•reduced effectiveness and possibility of rehabilitation, which leads to secondary aggravation of the
above disorders.
1.3 Advantages Of Dynamic Parapodium
1. Self-dependent standing up, i.e. assuming upright position and self-dependent sitting up with beneficial forced exercise
of the upper extremities, which, in turn, leads to:
•Elimination of muscular and articular contractures as well as spasticity,
•Adequate nutrient supply to the connective tissue,
•Healing of bedsores,
•Physiological load of the skeletal and articular system (locomotor system),
•Physiological function (and location in body cavities) of internal organs (peristaltics of the intestines – bowel
movements, normalisation of the mechanisms of micturition-neurogenic bladder) and others,
•Normalisation of function of the cardiovascular and respiratory system.
2. Self-dependent, completely safe and comfortable standing without the necessity to use hands for many hours (even if
the patient loses consciousness the upright position is maintained owing to continuous control of the centre of gravity of
the body).
3. Self-dependent, completely safe locomotion using the patient’s own muscular strength without the necessity of external
source of energy (external power supply) making full self-service and serving other people possible.
4. Wide range of rehabilitation together with ergotherapy.
5. Improving general condition as preparation for practising sports.
6. Preparation of the organism for use of other systems of orthoses of locomotion aid type helping the patient to walk in
the environment of healthy people.
However, it should be remembered that only assuming upright position itself is associated with additional exertion.
Advantages – the benefits associated with using such orthotic system as the Dynamic Parapodium place it In the
group of exceptionally valuable devices on the world scale.
1.4 Most Common Systemic Disturbances Likely To Occur In Paraplegia
ARNING. The prerequisite for starting rehabilitation of the patient making use of the Dynamic Parapodium is
previous consultation with the managing physician. After appropriate qualification of the patient, raising his
awareness concerning the possibility of occurrence of certain systemic dysfunctions and giving instructions
what the patient should do in case of such dysfunctions, an individual, preliminary therapeutic programme is
designed, whose aim is gradual adaptation of the organism to the device.
Danger. Neglecting the above recommendations may lead to natural reaction of the organism to the change of
position of many internal organs, unpleasant for the patient, requiring adaptation to the new conditions.
From our experience it follows that particular attention should be paid to:
1. Efficiency of the circulatory system (hypotonia – exertion hypotonia, orthostatic hypotonia), because in the cases of
high-located spinal cord damages the course of exercise may lead to paradoxical load on the cardiovascular system
(exertion hypotonia) with congestion of blood in the lower portion of the body and orthostatic hypotonia due to the effect
of gravity. Hypotonia together with reduced cardiac output and cerebral blood flow may cause nausea and vomiting,
vertigo, leading even to the loss of consciousness. Performing preliminary E G and, if necessary, also USG of the heart
is mandatory. Reduction of the risk of hypotonia is achieved by training – by lifting legs during exercise, regular
orthostatic training (e.g. backward head deflection, assuming upright position on a tilting table, walking aided by
orthoses), appropriate hydration, compression stockings, wide abdominal belt and physical fitness. If the above
mentioned symptoms occur, first aid involves tilting the patient back to facilitate venous return, increase cardiac output
and blood pressure.
2. Efficiency of the respiratory system. Spirometric assessment of respiratory efficiency is recommended. Prevention of
ventilation disturbances involves among others maintaining mechanical patency of the bronchial tree (positional
drainage, liquefaction of secretions, preventing bronchial spasms, etc.), increasing tidal volume by training muscles and
teaching the patient to assume appropriate position of the trunk.
4

3. Efficiency of the locomotor system. Frequent dysfunction of the locomotor system accompanying the underlying
disease prompt to analyse thoroughly the possible need of passive or dynamic correction, compensation, alleviation or
stabilisation of the particular elements of the system by means of appropriate orthoses (collars, etc.), e.g. the cranio-
cervical or thoracic segment of the vertebral column in the cases of subluxation symptoms or instability by means of
corsets or belts applied for the cases of scoliosis or muscular insufficiency, orthoses for the upper extremities in the
cases of contractures or special shoes or insoles – according to the individual needs of the patient. A very important
element of preparation, or even prerequisite, for the rehabilitation programme is taking into consideration the necessity
of massage and mobilisation in contractures, as well as increasing the muscular strength in the upper extremities.
4. Possibility of autonomic dysreflexia (sudden episodes of considerable elevation of arterial blond pressure which may
be life-threatening if not controlled immediately). Preventing of disturbances involves the elimination of potentially
harmful stimulation by
5. voiding the bladder immediately before exertion and during longer periods of exertion, as well as blood pressure
monitoring during the first sessions of exercise. In case of the episode, exercise should be discontinued and upright
position should be maintained until blood pressure returns to normal values.
6. Presence, or predisposition to, the formation of bedsores, which constitutes a common and important problem.
Prevention involves continuous control of body regions anatomically exposed to compression and application of
decompression measures (localisation, decompression and protection). The management of patients with bedsores
should not exclude rehabilitation by means of the Dynamic Parapodium.
7. Muscular spasms (due to hyperactivity resulting from loss of inhibitory control of motoneurons). Prevention is training,
which makes it possible to reduce both the frequency and magnitude of spasms. Pharmacological treatment is not
recommended, because it limits the possibility of training and may cause unfavourable side effects – depression,
vertigo, ataxia. In case of spasms the patient should be protected against injury to the lower extremities due to strong
contractions and rapid movements.
8. Thermoregulation problems. Limited ability to control body temperature may occur due to reduced perspiration and
inappropriate distribution of blood which leads in high temperature of the environment to the earlier occurrence of the
over-warming effect than in healthy subjects, associated with the risk of dehydration, elevation of body temperature,
heat stroke, or even circulatory collapse, whereas in cold environment it leads to excessive heat loss impairing the
cardiovascular control. Prevention involves optimal adjustment of the existing needs of rehabilitation to the efficiency of
the organism, with emphasis on regularity of training. In the cases of hypo- or hyperthermia, the exercise should be
discontinued and the environmental conditions (air temperature, relative air humidity), as well as the patient’s clothes,
intensity of the exercise and duration of the session adjusted according to the existing needs and possibilities.
arning
Absolute contraindications for use of the Dynamic Parapodium:
•Deep mental impairment ( unable to be controlled),
•onditions preceding cerebral stroke,
•onditions preceding myocardial infarction,
•Advanced osteoporosis with lower limb deformation (considerable deviation from the long axes of
the extremities),
•Disturbances of body balance (of a high degree),
•Articular contractures (knees, hip joints) over 30’,
•Very strong muscular spasticity in lower extremities,
1.5 Exemplary Preliminary Rehabilitation Programme For The Period Of Adaptation Of The
Organism To The Device.
The period of adaptation, which should last approximately seven weeks, has been divided into stages. The
principle is to go on to the next stages after mastering the skills required in the previous stage, providing the patient’s
condition is good enough to progress to more intensive exercise.
The exercise should always be done in the presence of an accompanying person!
The first stage
Daily training: up to 3 repetitions daily (the presence of an accompanying person mandatory during the exercises).
The aim of the exercise is to familiarise the patient with the device, making him feel safe while using the
parapodium, preliminary adaptation to maintaining upright position.
1. hanging the position from sitting to standing in the parapodium directly from a chair or bed, (the help of a
physiotherapist during the exercise is mandatory).
2. Maintaining upright position in the parapodium for the following periods of time: 30 sec.– first session, 1 min. – second
session in the parapodium. The duration of staying in the upright position is prolonged by one minute per day until the
period of 20 minutes. The proposed durations of the exercise on subsequent days of training are dependent on the
condition of the patient. If the basic duration has been successfully completed (without the episodes of fainting, vertigo,
5

fatigue) the exercise can be prolonged by one minute. In case of any adverse effects associated with upright position,
the exercise should be discontinued immediately. When the symptoms subside, the training should be resumed, starting
the stage from the beginning.
3. Leaving the parapodium and changing position to sitting on a chair, bed or wheelchair (the presence of an
accompanying person mandatory during this exercise).
The second stage
Daily training: up to 3 repetitions daily (the presence of an accompanying person during this exercise is
mandatory).
The aim of the exercise is training the ability to balance the body correctly in the parapodium (the ability to raise the
runners and the platforms from the background).
1. hanging the position from sitting to standing in the parapodium directly from a chair or bed, (the help of a
physiotherapist during the exercise is mandatory).
2. In standing position, with the handles of the parapodium held from the top, alternating deflections from the right to the
left (attempts to incline the body to the sides), rhythmical shifting of the centre of gravity, standing for 20 minutes.
3. Shifting the body balance for 1 min.; then standing for the rest of time. We add 1 minute daily of the balance-shifting
exercise. Between the balance-shifting exercises, lasting 1 minute each we use 1 minute break. This stage of training is
completed when we are able to do the 1-minute balance-shifting exercise ten times per session.
4. Leaving the parapodium and changing position to sitting on a chair, bed or wheelchair (the presence of an
accompanying person mandatory during this exercise).
The third stage
Daily training up to 3 repetitions a day (depending on the patient’s condition).
The aim of this exercise is a preliminary learning of walking.
1. hanging the position from sitting to standing in the parapodium directly from a chair or bed, (the help of a
physiotherapist during the exercise is mandatory).
2. In standing position, with the handles of the parapodium held from the top, alternating deflections from the right to the
left combined with raising the runners and the platforms from the background. During the brakes in the previous
exercise, inclining and turning the trunk in various directions, and/or active training of the upper extremities with various
loads.
3. Prolongation of the period of patient’s stay in the parapodium to 30 minutes guiding the parapodium by holding its
handles, with the help of an accompanying person. First attempts of self-dependent walking.
4. Leaving the parapodium and changing position to sitting on a chair, bed or wheelchair (the presence of an
accompanying person mandatory during this exercise).
The fourth stage
Daily training up to 3 repetitions daily (depending on the patient’s condition).
The aim of this exercise is learning to walk without the aid of an accompanying person.
1. hanging the position from sitting to standing in the parapodium directly from a chair or bed, (the help of a
physiotherapist during the exercise is mandatory).
2. Self-dependent walking with changes of directions – 20-30 minutes.
3. Leaving the parapodium and changing position to sitting on a chair, bed or wheelchair (the presence of an
accompanying person mandatory during this exercise).
In the subsequent weeks and months the load during the exercise is gradually increased, depending on the patient’s
condition. The patient learns to carry out everyday routines ( in the kitchen, bathroom, etc.). Gradual becoming
independent of the help of accompanying persons.
2. USER’S MANUAL
2.1 General Principles Of Safety
The greatest concern of mdh sp. z o.o. is improving the quality of life of the users of the device, ensuring safety to
the patients as well as to all individuals helping our patients and coming into contact with the device.
In order to ensure absolute safety to the users of the Dynamic Parapodium Model PD150, PD 180, PD 200 the
following recommendations should be strictly observed:
1. Before undertaking any attempts to use the device, read the details in the “Medical Manual” and the “User’s Manual”.
2. Make sure that you fully understand all information, recommendations and warnings contained in the “Medical Manual”
and the “User’s Manual”.
All the Manuals attached to the devices manufactured by mdh sp. z o.o. contain paragraphs marked with symbols
ATTENTION, ARNING and DANGER intended to attract the reader’s particular attention to their contents. The meaning of
the aforementioned symbols is as follows:
6

ATTENTION. This symbol is used to signal that particular attention to the content of the paragraph marked in
this way is needed.
ARNING. This symbol is used for the description of functions (activities), which performed incorrectly, i.e.
according to the Manual, may lead to the damage of the device.
DANGER. This symbol is used for the description of the functions (activities), which, performed incorrectly, i.e.
according to the instructions, may lead to life-threatening situations or serious injury to the user.
2.2 General information
The purpose of this manual.
The manual contains detailed information concerning the conditions of usage of the Dynamic Parapodium Model
PD150,PD 180, PD 200.
Dynamic Parapodium is only given on the basis of the physician’s opinion.
The instruction is directed to the users the user’s attendants therapists and physicians.
The Dynamic Parapodium Model PD150, PD 180, PD 200 is a mechanical device designed for disabled people
with paraplegia or paraparesis.
If the device is used by healthy people the manufacturer does not take any responsibility for any physical injuries or
damage of the device.
7

The parapodium consists of the following elements:
Diagram 1
Principles of Function of Dynamic Parapodium Model PD150, PD180, PD200.
Many years of experiments and observation of disabled people with paraplegia have proven, how difficult it is to
design a simple, easy to operate device for a large group of users characterised by a large diversity of physical condition of
the organism and complications involving the internal organs.
We assumed that the driving force for the device must be provided by the work of the parts of the body unaffected
by the disease, i.e. the upper part of the trunk and the hands. Our attempts in this field have been successful. We have
designed a device, which principles of function are presented below.
Unique design of the Dynamic Parapodium makes the device very sensitive to any alterations of its own gravity
centre. The position of the centre of gravity of the parapodium can be changes in two planes:
•The plane perpendicular to the axis of the runners, extending through the corset hanger joint (after positioning the
patient in the parapodium, this plane extends through the axis of their hip joints)
•The plane parallel to the axis of the runners and perpendicular to the axis extending through the corset hanger joint.
Alteration of the centre of gravity of the device together with the patient provides the driving force for the movement
of the parapodium.
The principles of movement of the Dynamic Parapodium Model PD150,PD180, PD200.
The driving force for the movement of the parapodium is provided by alteration of the centre of gravity of the
patient-parapodium system.
Alterations of the centre of gravity in the plane perpendicular to the intended direction of movement are obtained by
slight periodical movements of the upper part of the trunk. Even slight movements of the trunk to the sides are sufficient to
cause alternating lifting of the runners with platforms supporting the patient’s feet from the ground. Thanks to this the patient
is able to stand (to rest on) on one or the other leg like in typical walking.
8

Alterations of the centre of gravity in the parallel to the intended direction of movement are obtained by slight
bending of the patient’s trunk forth and back, possible owing to the special design of the lower joint and the corset hanger
joint.
Obtaining the movement of the parapodium is possible only thanks to the combination of these two types of
alterations of the gravity centre. It is important to move only this leg which is free from the body weight at the moment.
Thanks to efficient movement of handles (up-down, right-left) the patient can move in different directions.
DANGER
Even slight sideways movements of the upper part of the trunk, which causes lifting of the runners from the
ground, is sufficient to initiate the movement of the parapodium. The runners are equipped with lateral safety
supports. It is very difficult to make parapodium swing beyond the support provided by the lateral safety
supports by excessive movement. However, exceptionally fit patients are able, by periodical intensive
movements of the trunk forth and back co-ordinated with the movement of hands, to make the parapodium tilt
forth so much that it can fall down. It should be remembered that any attempt to overturn the parapodium on
purpose is contrary to the instructions for use of the device and may cause serious injury of the patient.
2.3 Preparation Of The Parapodium To Use
Detailed information on the preparation of the parapodium for use is contained in the “Assembly Instructions”
attached to the device.
Characteristic of the user of parapodium
Diagram 2.
9

Table 1.
PD 150
PD 180
PD 200
No.
Parameter (cm)
MIN.
MAX.
MIN.
MAX.
MIN.
MAX.
1.
Hip width
(S)
21
37
30
55
30
55
2.
Hip depth
(G)
13
25
16
30
19
33
3.
Height to the knees (D)
15
61
15
74
15
89
4.
Height to the troc
hanter (K)
55
85
70
105
85
120
5.
Weight
-
70
-
90
-
110
6.
ontracture of the knee (
°
) -
30
°
-
30
°
-
30
°
7.
lawfoot (
°
) -
15
°
-
15
°
-
15
°
8.
Width of footwear
-
11
-
11
-
11
9.
Length of footwear
-
30
32
34
10.
Total height
( E)
125
155
155
185
185
205
•Dynamic Parapodium Model PD150, PD180, PD 200, is to be used by patients with parameters
corresponding to those in Diagram 2 and table 1.
•The device must be assembled according to “Assembly Instruction ”.
•The height of the mounting, the width and depth of the corset, the height of the arm brackets and the
height of the knee holders as well as their span are adjusted individually for each patient and depend on
his height, the width and depth of the hips, height of the knees, etc.
ATTENTION
The distance of the corset hanger from the ground must be adjusted so that the patient, after fastening the
back belt, is in upright position and can remain so for a desired period of time without the aid of hands.
The patient must feel safe.
•The width and depth of the corset must be so adjusted that the patient feels kept (blocked) safely in the
region of the pelvic girdle, but without any discomfort and unpleasant compression.
•The position of knee holders must be so adjusted that the patient feels safe support for the leg, but
without hyperextension of knee joints. This ensures not only safety but also correct position of the body in
the parapodium, which makes walking much easier.
•The position of arm supports is adjusted to the patient’s needs. For individuals with strong arms it is
recommended to fix the supports as low as possible.
•The device must be checked thoroughly for the correctness of assembly and blockade of all mobile
elements.
•It should be checked whether the screw blocking the elements of the stabilising rod has been fixed tight
enough.
•losing and opening of the back flap and the correct functioning of the lock should be checked.
•It should be checked whether the pillow filling the space between the buttocks and the back flap is
correctly fixed (if used).
In the parapodium a three-point way of supporting the user enables a firm and safe grasp of the patient’s body
eliminating the occurrence of abrasions. The manufacturer allows to use only the device with the upholstery
completely on.
2.4 Use Of The Parapodium
ATTENTION
There are no contraindications for using the parapodium along with other individual orthopedic devices such as:
orthopedic footwear, orthopedic collars, corsets and orthosis. The decision whether to apply particular
orthopedic devices is always made by a physician.
ATTENTION
In case of hyperhidrosis and sensitive skin it is not recommended to use the device without underwear as a
protection against abrasions.
ATTENTION
Dynamic Parapodium is to be used indoors, in the range of temperatures between 10
0
and
45
0
.
.
10

ATTENTION
Dynamic Parapodium is to be used only on a flat, horizontal and hardened surface.
ATTENTION
Any attempt to overturn the parapodium on purpose more than the maximum lateral tilt (10’) is contrary to the
instructions for use of the device and may cause a threat to the patient’s life.
While using the parapodium the patient must not be loaded more than 5 kg over his normal weight.
Depending on patient’s individual parameters the device requires the space not less than 650 mm but not more
than 980 mm measured as the width of the device.
The use of the parapodium consists of three phases:
1. Getting-in phase.
2. Walking in the parapodium.
3. Leaving the parapodium.
Ad 1. Getting into the parapodium directly from a bed or chair.
In order to get into the parapodium the following activities should be done:
a) Bring the parapodium in front of the chair or bed, on which the patient is sitting,
b) Make sure that the chair will not move,
c) Unblock the lock and open the back belt of the corset,
d) Put the feet on the platforms,
e) Position the knees in the holders and fasten the belts around them,
f) Get hold of the corset with one hand, and of the arm support with the other and stand up to upright position
with the aid of the accompanying person,
g) Shift the hips to the front of the corset,
h) Pull the handle of the blockade of the lock, close the back belt and release the handle of the blockade,
i) heck if the blocking of the pelvic girdle region is correct, make sure that the hips are not compressed too
much.
j) Adjust the height of the lateral arm support,
k) heck the position of the patient’s centre of gravity in relation to the axis of corset hanger joints:
•if the patient is bent forward act according to “Assembly Instructions ”,
•if the patient is bent backward act according to “Assembly Instructions ”.
ARNING
During the attempts to stand up the patient must not get hold of or lean against the back flap of the corset.
Repeated leaning against the flap, which has to support the whole weight of the body then, may cause slight
deformations of the joint and, consequently, problems with closing the flap.
DANGER
Rising from the chair, etc. not protected from slipping back is dangerous for the patient and may lead to an
accident, resulting In contusion or injury.
During the attempts to stand up the patient must be helped by an accompanying person.
Non-compliance with the above recommendation may lead to his/her falling down, contusion or injury.
ATTENTION
While coming in and closing the back flap it should be remembered not to put a finger in when locking it.
Ad 2. Standing and walking phase including changing directions, etc.
DANGER
Before starting this phase of using the parapodium the user must get acquainted with the “Medical Manual”.
DANGER
A prerequisite for starting the process of rehabilitation using the Dynamic Parapodium is to contact the
physician managing the patient. After appropriate qualification of the patient, raising his awareness concerning
the probability of certain dysfunction of the organism, and giving instructions how to behave if such dysfunction
occur, an individual, initial therapeutic programme, aimed at gradual adaptation of the organism to the device,
must be designed. Non-compliance with the above recommendations may lead to the occurrence of
unpleasant natural reactions of the organism to the sudden change of position of most internal organs and
necessity to adapt to the new conditions.
11

Standing in the parapodium. The parapodium makes it possible for a disabled person to stand self-dependently and
comfortably without the aid of the hands for the period of many hours. Even if the patient faints, upright position is maintained
owing to continuous control of the child’s gravity centre.
alking in the parapodium. We start to learn walking by making periodic movements with the upper part of the trunk,
which leads to raising the runners and the platforms supporting the patient’s feet from the ground. It leads to the situation
when the patient’s weight is moved from left leg (runner) to the right one. Walking is possible only when: while moving the
body weight on the left leg we pull the handle on the right of the device and the other way round. Performing the next steps
can be achieved by regular alterations of the body weight from left leg to the right and simultaneously pulling the handle on
the other side.
DANGER
Even slight sideways movements of the upper part of the trunk, which causes lifting of the runners from the
ground, is sufficient to initiate the movement of the parapodium. The runners are equipped with lateral safety
supports. It is very difficult to make parapodium swing beyond the support provided by the lateral safety
supports by excessive movement. It should be remembered that any attempt to overturn the parapodium on
purpose is contrary to the instructions for use of the device and may cause serious injury of the patient.
ATTENTION
Even slight periodic movements of the trunk to the left and to the right (5÷10° from the vertical axis) leads to
lifting the runners from the ground, enabling walking thanks to slightly raising the handles of the parapodium
with hands.
1. Walking can be very difficult (or even impossible) if:
•The patient’s centre of gravity is positioned incorrectly in the parapodium; it may be caused by the mistake in
assembly of the parapodium, act according to “Assembly Instruction ”,
•Front runner ends converge – the parapodium is assembled incorrectly, act according to “Assembly Instruction ”,
•When the patient moves the trunk and lifts the runners from the ground, the front of the runners fall down –
“Assembly Instruction”.
2. The change of direction of movement is obtained by raising higher the handle on the side to which we want to turn.
3. In patients with injuries of the upper segments of the spinal cord and resultant tetraplegia it is very difficult to obtain the
effect of self-dependent walking. Such effect can, however, be obtained with a little help of the accompanying
person.
ATTENTION
During the use of the parapodium the patient’s hands should be on the handles. The accompanying person
while helping the patient must pay attention not to place his foot before the runner of the parapodium.
Ad 3. Sitting down and leaving the parapodium (sitting on a chair, bed, etc.).
When the standing and/or walking phase comes to an end, it is necessary for the patient to return to the chair
quickly and safely. Leaving the parapodium:
a) Unfasten the knee and feet holders,
b) Unlock the back flap of the corset and make the patient sit down on the chair,
c) Take out the patient’s feet from the platforms and put them on the wheelchair foot platforms,
d) lose the back flap of the corset,
e) Unblock the brake and move the wheelchair away.
DANGER
The patient can sit down on a chair, etc. only when it is protected from sliding back. While sitting the patient
should always be helped by an accompanying person. Non-compliance with the above recommendations
may lead to falling down, contusion or injury.
2.5 Transport of the device
In order to transport the device it is recommended to initiate balancing movement as the patient would perform. In
case of carrying it through the door or stairs the parapodium should be kept by handles from the back, on the side of the
entry to the device.
While transporting the device for long distances it is recommended to disassemble it into two parts according to
pict.4.
In order to disassemble the device follow these instructions:
a) Unscrew the screws with two pads (pos.3, pict.4),
b) Take off the corset assembly (pos.1, pict.4) from the basis assembly (pos.2, pict.4).
12

In order to reassembly the parapodium follow these instructions:
a) Put the corset assembly back (pos.1, pict.4) on the basis assembly (pos.2, pict.4),
b) Adjust the previous height of the mounting of the corset assembly (1),
c) Screw the screws with two pads again (pos.3, pict.4),
d) heck the condition of equal dimensions X and Y (X=Y).
Y
X
Pict.3
2.6 Storing, Cleaning And Maintenance Of The Parapodium.
The Dynamic Parapodium is a mechanical device, which framework is made of steel coated with lacquer and
chromium according to PN-93/ -81515 and PN-83/H-97006. The soft elements are made of foam-filled leather (ecological
leather) or velour upholstery.
Parapodium, as any medical device, should be cleaned regularly and used according to the manufacturer’s
instructions.
Recommendations concerning storing
The device should be stored in a dry, air-conditioned room, in which the relative humidity is not higher than 80%.
Recommendations concerning cleaning and maintenance:
•Lacquer coated surfaces should be cleaned with a damp piece of cloth. Adding mild detergents used to clean
household appliances is acceptable.
•Leather upholstery should be cleaned and conserved with special agents used to clean leather clothing
•Velour upholstery should be washed at 40° with water containing mild detergents used to wash underwear and
coloured clothing.
•Metal surfaces should be cleaned with alcohol. The case of cutting the metal layer should be reported to the
service point and a safety layer should be put on. Moreover, any trace of corrosion should also be reported.
In case of using the parapodium In hospitals and clinics by many patients and their regulations do not contradict it
is recommended to disinfect the handles (with alcohol) before giving the device to another patient. It is not allowed
to the patient to have contact with the upholstery unless different upholstery is being used for each patient.
2.7 Safety precautions
•The device must not be overturned, thrown or dragged with the patient or without him.
•Beside the fact that the device was made of non-flammable materials you should pay attention while closing to the
fire sources.
•Occurrence of corrosion points does not influence the safety but lowers the aesthetic. The manufacturer does not
allow to use a corroded device. The upper layer guarantees safety for 24 months against corrosion.
13

•The users of the device must not be under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
•The predicted time of using the device is 4 years. After this period it can be used only after a positive control
performed by the manufacturer.
•The device may cause decolouration of the floor due to rubber elements during normal exploitation.
2.8 Environmental protection
The device excluding the upholstery is made of steel and undergoes recycling In 95%.
After delivery the service is to collect the packaging. All elements made of polythene may be totally recycled.
2.9 Periodical servicing
Table 2 constitutes a periodical servicing card, which includes inspections of the device that need to be performed
periodically. Inspections and technical maintenance should be performed according to the schedule specified in the card.
Table 2.
INTERVAL
ELEMENT
INSPE TION
METHOD OF REPAIR
heck visually the state of
parapodium, if there are any visible
If any damages are
Dynamic
damages, such as fissures,
found, replace
Parapodium
deformations or any other visible
damaged elements with
damages, which can affe
ct device
new ones.
usage or safety of the user.
Measure height of rubber veneer
Minimum permissible height
–
5
mm
Internal feet **
Replace
PD0325 4 pieces
6 months *
Measure height of rubber veneer
Minimum permissibl
e height
–
2mm
External feet **
PD0326 2 pieces
Replace
PD0327 2 pieces
heck if all regulation screws, nuts Follow "Assembly and
and bolts are fastened
Adjustment Instruction"
ATTENTION
Lower
If any fissures, cuts or
permanent
articulation shock
deformations of lower articulation
Replace
absorber
shock absorbers are found
–
12 months * PD0442 4 pieces replace
orset’s shock
If any fissures, cuts or permanent
absorber
deformations of corset’s shock
Rep
lace
PD0361 4 pieces absorbers are found – replace
*time of intense usage - 2h/day
** if used on hard and rough surfaces (e.g. concrete floor) check every 2 months
In case of the malfunction of the parapodium it should not be used and the service should immediately be informed.
The name and the address of the authorised service is on the Warranty hart.
14

2.10 arranty
The Warranty hart is a separate document attached to every new product.
2.11 arranty instructions
Failure to comply with the procedures presented below will result in the loss of warranty.
•In case of any damage, the use of the device should be discontinued until the moment of repair.
•No unauthorised repairs are permitted.
•No original parts of the device can be replaced with self-made or commercially available spare parts.
The only person authorised to maintain the assembly and all the repairs to the device is the person authorized by
the manufacturer.
mdh Sp. z o.o. hopes that the present manual will meet all your expectations and needs in the field of usage of Dynamic
Parapodium Model PD150, PD180, PD200. However, if you think that any modifications or supplements to the above
instructions are needed, please share your opinion with us, and we will consider introducing the appropriate changes.
It is a great challenge for mdh sp. z o.o. to create a perfect dynamic orthosis that could serve all disabled people with
paraplegia, irrespective of the severity of the disorder. It is our aim for the next few years to enable each disabled person to
stand up and walk. Therefore, we would like to invite all the users of the Dynamic Parapodium Model PD150,Pd180, PD 200
to co-operate with us, in order to improve the existing device and to develop new, more advanced orthoses.
ATTENTION: The models of Dynamic Parapodium delivered to you may slightly differ from the devices on the pictures
because mdh sp. z o.o. constantly improves them.
3. Symbols
onfirmation of compliance with EU
standards
Manufacturer
Date of production
Read the user's manual
Warning
atalog number
Serial number
Protect from humidity
Protect from sunlight
Permitted user weight.
Use inside buildings
The possibility of fingers jamming.
Temperature of storage and use
15

MANUFACTURER
mdh Sp. z o.o
90-349 Łódź
22/24 Tymienieckiego Street
tel.: (+48 42) 674 83 96
tel.: (+48 42) 676 32 54
fax.: (+48 42) 299 69 24
www.viteacare.com
„Dynamic Parapodium Model PD150, PD180, PD200. User’s Manual“ is a property of mdh Sp. z o.o.
All rights reserved.
Attention: The devices presented in this manual are protected by appropriate international patents. The
manufacturer reserves the right to introduce technical and trade changes in the manual.
16
This manual suits for next models
2
Table of contents
Other Vitea Care Medical Equipment manuals
Popular Medical Equipment manuals by other brands

Getinge
Getinge Arjohuntleigh Nimbus 3 Professional Instructions for use

Mettler Electronics
Mettler Electronics Sonicator 730 Maintenance manual

Pressalit Care
Pressalit Care R1100 Mounting instruction

Denas MS
Denas MS DENAS-T operating manual

bort medical
bort medical ActiveColor quick guide

AccuVein
AccuVein AV400 user manual