Waters 2410 Manual



















Other manuals for 2410
2
Table of contents
Other Waters Measuring Instrument manuals
Popular Measuring Instrument manuals by other brands

Igema
Igema NA7-50 Installation and operating instructions

iBike
iBike iSport Setup and Instructions Summary

Agilent Technologies
Agilent Technologies E8362 user guide

Extech Instruments
Extech Instruments HD400 user guide

Valeport
Valeport DataLog x2 Installation and user guide

XTline
XTline XT130518 Original instruction manual

Interacoustics
Interacoustics AT235 Instructions for use

Dolby Laboratories
Dolby Laboratories DM100 user manual

HealTech Electronics
HealTech Electronics GIPRO X Supplementary manual
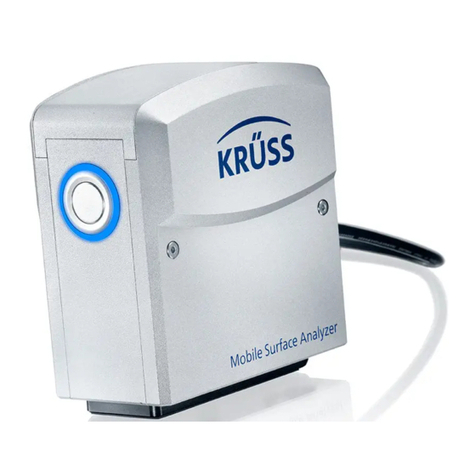
kruss
kruss Mobile Surface Analyzer user manual

IME
IME Nemo D4-L quick start guide

Beta industries
Beta industries BetaColor S2 XPress instruction manual

Tektronix
Tektronix KEITHLEY 2600B Series Reference manual

Measurement Computing
Measurement Computing USB-5200 Series user guide

PCB Piezotronics
PCB Piezotronics B353B17 Installation and operating manual

LOVATO ELECTRIC
LOVATO ELECTRIC DME D300 T2 instruction manual

SICK
SICK FLOWSIC100 Flare ADDENDUM TO OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS

Trans instruments
Trans instruments WalkLAB HP 9010 Operation manual






