ADEEPT Ultimate Kit for Arduino MEGA 2560 User manual


Preface
Adeept is a technical service team of open source software and hardware.
Dedicated to applying the Internet and the latest industrial technology in open
source area, we strive to provide best hardware support and software service for
general makers and electronic enthusiasts around the world. We aim to create
infinite possibilities with sharing. No matter what field you are in, we can lead you
into the electronic world and bring your ideas into reality.
This is an entry-level learning kit for Arduino. Some common electronic
components and sensors are included. Through the learning, you will get a better
understanding of Arduino, and be able to make fascinating works based on
Arduino.
If you have any problems for learning, please contact us at support@adeept.com.
We will do our best to help you solve the problem.

Component List







Content
About Arduino.......................................................................................................................... - 1 -
Lesson 1 Blinking LED........................................................................................................... - 2 -
Lesson 2 Active Buzzer......................................................................................................... - 7 -
Lesson 3 Controlling an LED with a button.................................................................. - 11 -
Lesson 4 Controlling Relay ................................................................................................ - 16 -
Lesson 5 Serial Port............................................................................................................. - 19 -
Lesson 6 LED Flowing Lights ............................................................................................ - 24 -
Lesson 7 LED bar graph display ...................................................................................... - 27 -
Lesson 8 Breathing LED..................................................................................................... - 31 -
Lesson 9 Controlling a RGB LED by PWM..................................................................... - 35 -
Lesson 10 Play the Music................................................................................................... - 38 -
Lesson 11 LCD1602 display.............................................................................................. - 41 -
Lesson 12 A Simple Voltmeter......................................................................................... - 45 -
Lesson 13 7-segment display........................................................................................... - 48 -
Lesson 14 A simple counter.............................................................................................. - 52 -
Lesson 15 Controlling Servo motor................................................................................ - 55 -
Lesson 16 Using a thermistor to measure the temperature.................................. - 58 -
Lesson 17 IR Remoter Controller.................................................................................... - 61 -
Lesson 18 Temperature & humidity sensor DHT-11................................................. - 65 -
Lesson 19 Ultrasonic distance sensor............................................................................ - 69 -

Lesson 20 3-axis Accelerometer—ADXL345................................................................ - 72 -
Lesson 21 4x4 matrix keyboard ...................................................................................... - 78 -
Lesson 22 Controlling DC motor...................................................................................... - 82 -
Lesson 23 Joy stick.............................................................................................................. - 88 -
Lesson 24 Tilt Switch........................................................................................................... - 91 -
Lesson 25 Dot-matrix display........................................................................................... - 94 -
Lesson 26 Controlling Stepper Motor............................................................................. - 99 -
Lesson 27 Photoresistor................................................................................................... - 102 -
Lesson 28 Automatically Tracking Light Source....................................................... - 105 -
Lesson 29 Frequency meter ........................................................................................... - 107 -
Lesson 30 Intrusion Detection based on the PIR..................................................... - 112 -
Lesson 31 Control a relay with IR remoter controller............................................ - 115 -
Lesson 32 Control a RGB LED with IR remoter controller .................................... - 117 -
Lesson 33 Control a stepper motor with IR remoter controller.......................... - 119 -

- 1 -
About Arduino
What is Arduino?
Arduino is an open-source electronics platform based on easy-to-use
hardware and software. It's intended for anyone making interactive projects.
ARDUINO BOARD
Arduino senses the environment by receiving inputs from many sensors, and
affects its surroundings by controlling lights, motors, and other actuators.
ARDUINO SOFTWARE
You can tell your Arduino what to do by writing code in the Arduino
programming language and using the Arduino development environment.
Before the development of Arduino program, the first thing you have to do is to
install Arduino IDE software. The software provides you with the basic
development environment that is required for developing Arduino program.
You need the following URL to download Arduino IDE:
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software
For different operating system platforms, the way of using Arduino IDE is
different. Please refer to the following links:
Windows User:http://www.arduino.cc/en/Guide/Windows
Mac OS X User:http://www.arduino.cc/en/Guide/MacOSX
Linux User:http://playground.arduino.cc/Learning/Linux
For more detailed information about Arduino IDE, please refer to the following
link:
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Guide/HomePage

- 2 -
Lesson 1 Blinking LED
Overview
In this tutorial, we will start the journey of learning Arduino MEGA 2560. In the
first lesson, we will learn how to make a LED blinking.
Requirement
- 1* Arduino MEGA 2560
- 1* USB Cable
- 1* 220ΩResistor
- 1* LED
- 1* Breadboard
- 2* Jumper Wires
Principle
In this lesson, we will program the Arduino's GPIO output high(+5V) and low
level(0V), and then make the LED which is connected to the Arduino’s GPIO
flicker with a certain frequency.
1. What is the LED?
The LED is the abbreviation of light emitting diode. It is usually made of
gallium arsenide, gallium phosphide semiconductor materials. The LED has
two electrodes, a positive electrode and a negative electrode, it will light only
when a forward current passes, and it can be red, blue, green or yellow light,
etc. The color of light depends on the materials it was made.
In general, the drive current for LED is 5-20mA. Therefore, in reality it usually
needs an extra resistor for current limitation so as to protect the LED.

- 3 -
2. What is the resistor?
The main function of the resistor is to limit current. In the circuit, the character
‘R’represents resistor, and the unit of resistor is ohm(Ω).
The band resistor is used in this experiment. A band resistor is one whose
surface is coated with some particular color through which the resistance can
be identified directly.
There are two methods for connecting LED to Arduino’s GPIO:
①
As shown in the schematic diagram above, the anode of LED is connected to
Arduino’s GPIO via a resistor, and the cathode of LED is connected to the
ground(GND). When the GPIO output high level, the LED is on; when the GPIO
output low level, the LED is off.
The size of the current-limiting resistor is calculated as follows: 5~20mA
current is required to make an LED on, and the output voltage of the Arduino
MEGA 2560’s GPIO is 5V, so we can get the resistance:
R = U / I = 5V / (5~20mA) = 250Ω~1KΩ
Since the LED has a certain resistance, thus we choose a 220ohm resistor.
②
As shown in the schematic diagram above, the anode of LED is connected to
VCC(+5V), and the cathode of LED is connected to the Arduino’s GPIO. When
the GPIO output low level, the LED is on; when the GPIO output high level, the
LED is off.
The experiment is based on method ①, we select Arduino's D8 pin to control
the LED. When the Arduino’s D8 pin is programmed to output high level, then
the LED will be on, next delay for the amount of time, and then programmed
the D8 pin to low level to make the LED off. Continue to perform the above
process, you can get a blinking LED.

- 4 -
3. Key functions:
●setup()
The setup() function is called when a sketch starts. Use it to initialize variables,
pin modes, start using libraries, etc. The setup function will only run once,
after each powerup or reset of the Arduino board.
●loop()
After creating a setup() function, which initializes and sets the initial values,
the loop() function does precisely what its name suggests, and loops
consecutively, allowing your program to change and respond. Use it to actively
control the Arduino board.
●pinMode()
Configures the specified pin to behave either as an input or an output.
As of Arduino 1.0.1, it is possible to enable the internal pullup resistors with
the mode INPUT_PULLUP. Additionally, the INPUT mode explicitly disables the
internal pullups.
●digitalWrite()
Write a HIGH or a LOW value to a digital pin.
If the pin has been configured as an OUTPUT with pinMode(), its voltage will be
set to the corresponding value: 5V (or 3.3V on 3.3V boards) for HIGH, 0V
(ground) for LOW.
If the pin is configured as an INPUT, digitalWrite() will enable (HIGH) or disable
(LOW) the internal pullup on the input pin. It is recommended to set the
pinMode() to INPUT_PULLUP to enable the internal pull-up resistor.
●delay()
Pauses the program for the amount of time (in miliseconds) specified as
parameter. (There are 1000 milliseconds in a second.)
Procedures
1. Build the circuit

- 5 -
2. Program
/***********************************************************
File name: 01_blinkingLed.ino
Description: Lit LED, let LED blinks.
Website: www.adeept.com
E-mail: [email protected]
Author: Tom
Date: 2015/12/27
***********************************************************/
int ledPin=8;//definition digital 8 pins as pin to control the LED
void setup()
{
pinMode(ledPin,OUTPUT); //Set the digital 8 port mode, OUTPUT:
Output mode
}
void loop()
{
digitalWrite(ledPin,HIGH); //HIGH is set to about 5V PIN8
delay(1000); //Set the delay time, 1000 = 1S
digitalWrite(ledPin,LOW); //LOW is set to about 5V PIN8
delay(1000); //Set the delay time, 1000 = 1S
}
3. Compile the program and upload to Arduino MEGA 2560 board
Now, you can see the LED is blinking.

- 6 -

- 7 -
Lesson 2 Active Buzzer
Overview
In this lesson, we will learn how to program the Arduino to make an active
buzzer sound.
Requirement
- 1* Arduino MEGA 2560
- 1* USB cable
- 1* Active buzzer
- 1* 1 kΩResistor
- 1* NPN Transistor (S8050)
- 1* Breadboard
- Several Jumper Wires
Principle
A buzzer or beeper is an audio signaling device. As a type of electronic buzzer
with integrated structure, which use DC power supply, are widely used in
computers, printers, photocopiers, alarms, electronic toys, automotive
electronic equipments, telephones, timers and other electronic products for
voice devices. Buzzers can be categorized as active and passive buzzers (See
the following pictures).
When you place the pins of buzzers upward, you can see that two buzzers are
different, the buzzer that green circuit board exposed is the passive buzzer.
In this study, the buzzer we used is active buzzer. Active buzzer will sound as
long as the power supply. We can program to make the Arduino output
alternating high and low level, so that the buzzer sounds.

- 8 -
A slightly larger current is needed to make a buzzer sound. However, the
output current of Arduino’s GPIO is weak, so we need a transistor to drive the
buzzer.
The main function of transistor is blowing up the voltage or current. The
transistor can also be used to control the circuit conduction or deadline. And
the transistor is divided into two kinds, one kind is NPN, for instance, the
S8050 we provided; another kind is PNP transistor such as the S8550 we
provided. The transistor we used is as shown in below:
There are two driving circuit for the buzzer:
Figure1 Figure2
Figure 1: Set the Arduino GPIO as a high level, the transistor S8050 will
conduct, and then the buzzer will sound; set the Arduino GPIO as low level, the
transistor S8050 will cut off, then the buzzer will stop.

- 9 -
Figure 2: Set the Arduino GPIO as low level, the transistor S8550 will conduct,
and the buzzer will sound; set the Arduino GPIO as a high level, the transistor
S8550 will cut off, then the buzzer will stop.
Procedures
1. Build the circuit
2. Program
3. Compile the program and upload to Arduino MEGA 2560 board
Now, you should be able to hear the sound of the buzzer.
This manual suits for next models
1
Table of contents
Other ADEEPT Educational Equipment manuals
Popular Educational Equipment manuals by other brands

Nasco Healthcare
Nasco Healthcare Lifeform GERi LF04040U manual

Demco
Demco Copernicus Regal RC107 Assembly guide

LeapFrog
LeapFrog Tag Parent guide & instructions

Rompa
Rompa Magic Cloud manual

CAE Healthcare
CAE Healthcare METIman user guide

fischertechnik
fischertechnik micro:bit 548884 Assembly instruction

promethean
promethean Chromebox 2 user guide

JP
JP TURN Connect T101 user guide

fischertechnik
fischertechnik STEM Optics SECONDARY SCHOOL Assembly instruction
SMART
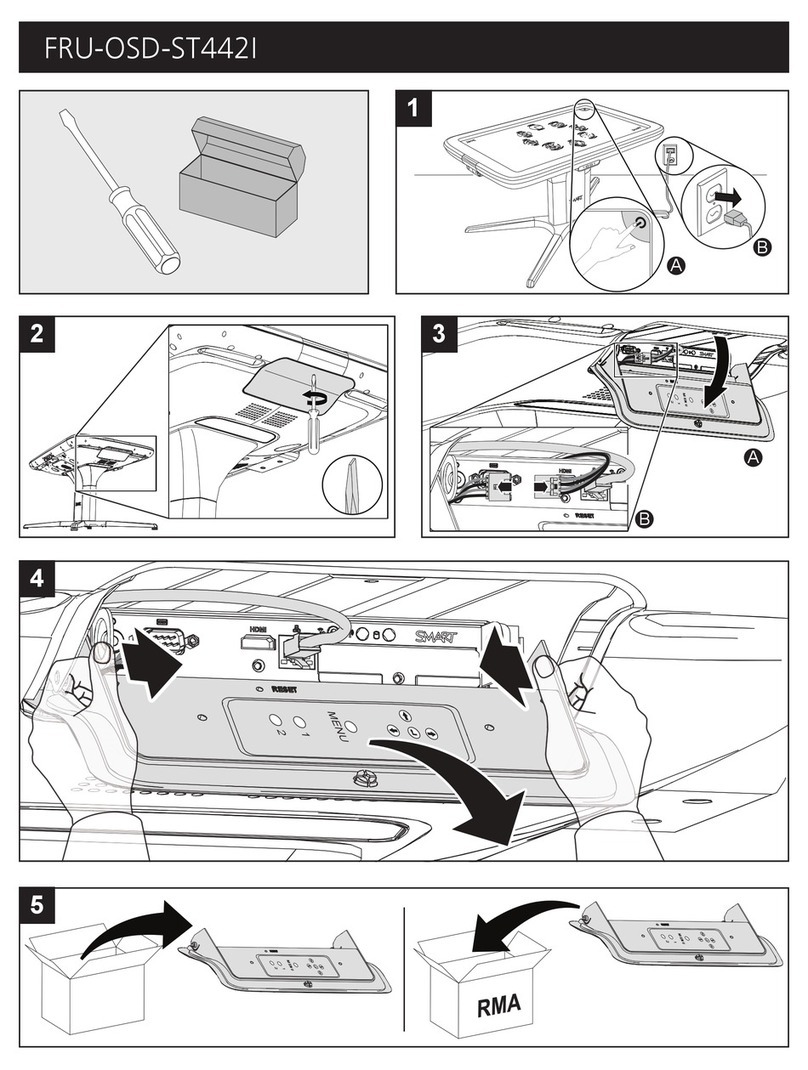
SMART FRU-OSD-ST442I quick start guide

Nasco Healthcare
Nasco Healthcare Simulaids LifeForm LF00698U instruction manual

laerdal
laerdal Choking Charlie Directions for use