AEZ GCM02 Manual

,
GCM02 Rel 6.0
AUTOMATIC MICROPROCESSOR CONTROL PANEL FOR STAND-
BY GENERATOR
MANUAL OF:
•INSTALLATION
§USE
•MAINTENANCE

FILE VER DATA ULT. VERSIONE LINGUA
PAGINA
GCM02-MT-ING4 NEW.doc c/02 04/03/2003 ITA Page 2of 57
INDEX
AUTOMATIC MICROPROCESSOR CONTROL PANEL FOR
STAND-BY GENERATOR.........................................................................................................................1
INDEX......................................................................................................................2
1. USER MANUAL.........................................................................5
NTRODUCTION...........................................................................................................5
We congratulate you for having purchased the GC-M02 control panel for handling your generator unit. As you
read through this manual you will realise the outstanding performance and variety of applications offered by
this supremely technological unit............................................................................................5
This electronic microprocessor module not only completely controls the generator and its switching but is also
pre-arranged for the direct serial communication with a PC or, using a GSM unit your generator can be
completely remote controlled from miles away............................................................................5
The GC-M02 unit is equipped with a complete set of digital testers that are required to monitor all mains,
generator and motor parameters............................................................................................5
To make the control of the unit absolutely comprehensible the manual is split up into two parts, namely:..........5
1.1 PURPOSE..............................................................................................................................................................................5
1.2 OPERATIONAL PRINCIPLE...........................................................................................................................................6
1.3 VIEW OF THE GC-M02 UNIT................................................................................................................................................7
1.4 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION OF THE CONTROL PANEL COMPONENT.......................................................................7
1.4 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION OF THE CONTROL PANEL COMPONENT.......................................................................8
1.5. COMMANDS AND OPERATIONAL MODES.....................................................................................................................11
1.6 PROGRAMMING..................................................................................................................................................................12
1.7. VARIOUS CONTROLS.......................................................................................................................................................12
LED TEST.......................................................................................................................................................................12
ALARM SILENCING.......................................................................................................................................................12
1.8. SPECIAL FUNCTIONS.......................................................................................................................................................12
1.9 SIMPLE MAINTENANCE WORK..................................................................................................................................13
2. TECHNICAL MANUAL..................................................................................................14
2.1 CONSTRUCTIONAL DESCRIPTION OF THE CONTROL PANEL .............................................................................14
2.2. OPERATION........................................................................................................................................................................15
2.3 DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF HOW THE CONTROL UNIT WORKS...............................................................................15
2.4 MANUALLY CONTROLLED FUNCTIONS..........................................................................................................................17
2.4.1 POWER SUPPLY FROM MAINS (manual command)........................................................................................17
2.4.2 MANUAL STARTING............................................................................................................................................17
2.4.3 POWER SUPPLY FROM GENERATOR.............................................................................................................17
2.4.4 MANUAL STOPPAGE...........................................................................................................................................17
2.5 VARIOUS FUNCTIONS AND UTILITIES......................................................................................................................18
2.5.1 CC12 AND 24V POWER SUPPLY CIRCUITS....................................................................................................18
2.5.2 COMMAND RELAYS ............................................................................................................................................18
2.5.3 MOTOR STARTED READING..............................................................................................................................18
2.5.4. MOTOR PRE-HEATING......................................................................................................................................18
2.5.5 AUTOMATIC BATTERY CHARGER ....................................................................................................................19
2.6 MOTOR AND ALARM PARAMETER READING................................................................................................................20
2.6.1 POSITIVE MOTOR PROTECTION INPUTS........................................................................................................20
2.6.2 ANALOGUE MOTOR PARAMETER READING INPUTS (PRESSURE, TEMPERATURE AND FUEL LEVEL)20
2.6.3. OIL PRESSURE...................................................................................................................................................21
2.6.4. MOTOR TEMPERATURE....................................................................................................................................21
2.6.5. FUEL LEVEL(15)..................................................................................................................................................22
PROGRAMMING............................................................................................................................................................22
2.6.6 FUEL PUMP COMMAND......................................................................................................................................22

FILE VER DATA ULT. VERSIONE LINGUA
PAGINA
GCM02-MT-ING4 NEW.doc c/02 04/03/2003 ITA Page 3of 57
2.7. MEASURING THE GENERATOR’S AND MAINS PARAMETERS...................................................................................23
Mains control ..................................................................................................................................................................23
Three phase....................................................................................................................................................................23
Mains control ..................................................................................................................................................................23
Network control...............................................................................................................................................................23
Connections....................................................................................................................................................................27
2.8 INPUT / OUTPUT..................................................................................................................................................................29
2.9. FUNCTIONS OF BUILT-IN WEEKLY CLOCK.....................................................................30
2.9.1. WEEKLY CLOCK.................................................................................................................................................30
2.9.2. CLOCK FOR AUTOMATIC TESTING.................................................................................................................30
2.9.3. AUTOMATIC STOPPING OR STARTING...........................................................................................................30
2.10 REMOTE COMMAND AND CONTROLS..........................................................................................................................31
2.10.1 EJP FUNCTION ..................................................................................................................................................31
2.10.2 SCR FUNCTION OR FORCED STARTING WITH OUTPUT (default) ..............................................................31
2.10.3 LOCK FUNCTION (default).................................................................................................................................31
2.10.4 TEST FUNCTION (default) .................................................................................................................................31
2.10.6. FUNCTION FOR TWO UNITS WORKING ALTERNATELY.............................................................................32
2.10.7. MAINS POWER SUPPLY EMERGENCY BACKUP..........................................................................................32
2.10.8. POWER SUPPLY PLANT WITH TWO GENERATORS, ONE ON STANDBY.................................................32
2.11. SPECIAL FUNCTIONS.....................................................................................................................................................33
2.11.1. PROGRAMMING...............................................................................................................................................33
2.11.2. MOTOR PRE-HEATING (out 28) ( Default ).....................................................................................................33
2.11.3 SPARKPLUGS PRE-HEATING (out 28).............................................................................................................33
2.11.4 STARTING MOTOR (out 28)..............................................................................................................................33
2.11.5. GAS SOLENOID VALVES (for gas motors) (out 28).........................................................................................33
2.11.6. RESET (out 28)..................................................................................................................................................34
2.11.7. DOUBLE STARTING (out 28) UNI 9490 NFPA NFS61.940..................................................................34
Note: for the adjustment to the rules of safety fireproof, the “FORCED RUNNING” can be required, to see 2.10.5 ...34
2.11.8. ANTI-THEFT PROTECTION..............................................................................................................................34
2.11.9. ALARM HISTORY RECORDS...........................................................................................................................35
2.12 PROGRAMMING..............................................................................................................................................................36
2.12.1 SETTINGS...........................................................................................................................................................36
2.12.2 PARAMETERS................................................................................................................................................37
2.12.3 TIME SETTINGS.............................................................................................................................................37
2.12.4 THRESHOLDS....................................................................................................................................................38
2.12.5 VARIOUS SETTINGS .........................................................................................................................................39
2.12.6. REMOTE CONTROL SETTINGS......................................................................................................................40
2.13. SELF-PROGRAMMING....................................................................................................................................................41
2.14 CONNECTIONS AND RELATIVE DESCRIPTIONS.........................................................................................................42
2.14.1 VIEW OF THE GCM02MP CONNECTION UNIT...........................................................................................42
2.14.2 CONNECTIONS ON THE MP02 POWER UNIT............................................................................................43
2.15 TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS....................................................................................................................................44
IP 55 ...............................................................................................................................................................................44
2.16 DIMENSIONS....................................................................................................................................................................45
2.16.1 DRILLING TEMPLATE OF THE GC-M02 UNIT.............................................................................................45
2.16.2 DIMENSIONS OF THE MP 02 POWER UNIT...............................................................................................45
2.16.2..............................................................................................................................................................................46
ADJUSTMENT TO THE LANGUAGES.........................................................................................................................46
2.17. OPTIONAL EXPANSIONS................................................................................................................................................47
2.17.1. REMOTE SIGNALS –INTERNET –INTRANET -ETHERNET........................................................................47
2.17.2. REMOTE CONTROL .........................................................................................................................................47
COMMUNICATION PROTOCOL...................................................................................................................................49
2.18 INSTALLATION .............................................................................................................................................................51
2.18.1 POSITIONING.....................................................................................................................................................51
2.18.2. EARTH CONNECTIONS (PE) ...........................................................................................................................51
2.18.3 POWER CONNECTIONS...................................................................................................................................52
2.18.4. CONNECTIONS TO THE BATTERY.................................................................................................................52
2.18.5 STARTING AND STOPPING..............................................................................................................................52
2.18.6 STOPPAGE WITH SOLENOID VALVE..............................................................................................................53
2.18.7 MOTOR CONTROLLING PROBES....................................................................................................................53
2.18.8 ELECTRICAL STRENGTH TEST.......................................................................................................................53
2.19 SERVICE PROCEDURES..................................................................................................................................................54
2.19.1. SERVICING PROCEDURE ..............................................................................................................................54
2.19.2 SERVICING PROCEDURE WITH THROUGH MAINS (GENERATOR DISABLED).........................................54

FILE VER DATA ULT. VERSIONE LINGUA
PAGINA
GCM02-MT-ING4 NEW.doc c/02 04/03/2003 ITA Page 4of 57
2.19.3. BATTERY REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE .....................................................................................................54
2.19.4. GC-M02 BOARD REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE ..........................................................................................55
2.19.5 MP02 POWER BOARD REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE.................................................................................55
3. MAINTENANCE .........................................................................................................56
3.1 ELECTRICAL MAINTENANCE............................................................................................................................................56
3.2. EFFICIENCY TEST..............................................................................................................................................................56
3.3. MOTOR SAFETY DEVICES................................................................................................................................................56
3.4 GENERATOR SAFETY DEVICES.......................................................................................................................................56
3.5 OVERLOAD SAFETY DEVICE 51.......................................................................................................................................56
3.6 BATTERY EFFICIENCY.......................................................................................................................................................56
3.7 SWITCHING SCALING TEST..............................................................................................................................................57
3.8 TROUBLE SHOOTING.........................................................................................................................................................57
N.B.: THE INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THIS DOCUMENT MAY BE CHANGED DUE TO TECHNICAL IMPROVEMENTS
WITHOUT NOTICE

FILE VER DATA ULT. VERSIONE LINGUA
PAGINA
GCM02-MT-ING4 NEW.doc c/02 04/03/2003 ITA Page 5of 57
1. USER MANUAL
INTRODUCTION
We congratulate you for having purchased the GC-M02 control panel for handling your generator unit. As you
read through this manual you will realise the outstanding performance and variety of applications offered by
this supremely technological unit.
This electronic microprocessor module not only completely controls the generator and its switching but is also
pre-arranged for the direct serial communicationwith a PC or, using a GSM unit your generator can be
completely remote controlled from miles away.
The GC-M02 unit is equipped with a complete set of digital testers that are required to monitor all mains,
generator and motor parameters.
To make the control of the unit absolutely comprehensible the manual is split up into two parts, namely:
The first USER MANUAL part has been prepared to provide a clear and simple guide to help you use the
generator rapidly, completely and safely.
1.1 PURPOSE
The manual has been prepared specifically for the user of the generator unit.
Information required for the following is provided:
1. to learn the operational principle of the unit;
2. to interpret the indications given on the electronic control panel;
3. to control it for the various operational requirements;
4. to perform the basic checks required to ensure the efficiency of the generator itself.
Technical or adjustment matters are not dealt with as these involve the installation engineer when setting up
the system.

FILE VER DATA ULT. VERSIONE LINGUA
PAGINA
GCM02-MT-ING4 NEW.doc c/02 04/03/2003 ITA Page 6of 57
1.2 OPERATIONAL PRINCIPLE
HOW A STAND-BY GENERATOR UNIT WORKS
Fig. 1 illustrates the system components that consist of a public mains R,ageneratorunit G-M, a QGE command and control panel
with a built-in mains contact maker CR, a generator unit contact maker CGand the M02 module that controls the system.
Supposing that the mains R is within the normal limits, the CR mains contact maker is closed therefore the
utility is powered from the mains. The M02 module controls the R mains and if there should be a drop in
voltage, a phase should be missing or the phases should be dissymmetrical, the control panel:
1. opens the CR mains contact maker;
2. starts the G-M generator unit, which when the established operating conditions are reached, the M02
module closes the CG contact maker that then powers the utility from the generator unit G;
NOTE: When running, the M motor and G generator are safeguarded against possible anomalies, which if
encountered, cause the generator to stop immediately and the cause for the alarm is saved and displayed (i.e.
low oil pressure, overload and so on);
3. When the R mains is restored within the normal limits, the M02 after an adjustable delay, opens the
contact maker of the CG generator and one second later closes the CR contact maker, thus powering the
utility from the mains again;
4. The generator continues to run for at least another minute to cool down after which it stops automatically;
NOTE: Even when the generator is stopped, some safety devices relating to the fuel and water level are
enabled and if an anomaly is detected an alarm status is triggered. The switching of the mains/generator is
also constantly controlled and if there should be an overload on the mains contact maker an alarm buzzer is
triggered.
To ensure the perfect efficiency of the generator a battery charger automatically holds the battery perfectly
efficient. An automatic fuel filling system constantly keeps the correct level in the daily tank. A pre-heating
system maintains the motor at the ideal temperature so that it is ready to start whenever necessary.
G
CR
CG
GC-M02
M
Fig. 1
UTILITY
QGE
R

FILE VER DATA ULT. VERSIONE LINGUA
PAGINA
GCM02-MT-ING4 NEW.doc c/02 04/03/2003 ITA Page 7of 57
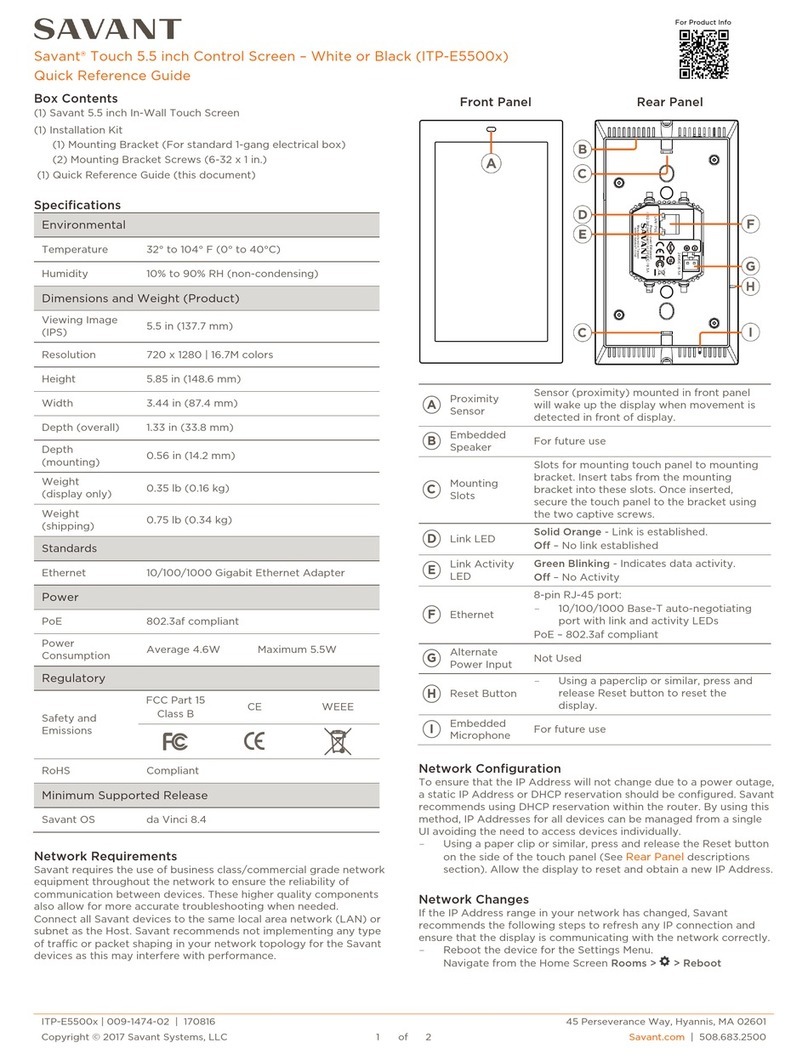
1.3 VIEW OF THE GC-M02 UNIT
Functional description of the block diagrams.
1. Alphanumeric display of visualization of all the
measures and the literal description of the type of alarm
(es. Reserve Fuel).
3. Butt
on + /
-
of selection measures
and button of reset for restoration
functions or unlock alarm.
2. Commutator of programming:
1 Automatic test. (T)
2 Automatic running. (A)
3 Block (Locked) excluded logic.
4 Feeding forced from mains (CR)
5 Manual starting.
6 Feeding forced from generating (CG).
4. Mains and s
witching
mains/gen-set situation
5. Manual command fuel
pump
6. Intervention of the
differential protection
7. Fed battery charger
and battery
8. Signalings gen
-
set running and
alarm motor
9. Buttons for the manual command
of work or stop
10. The flash indicates that the
microprocessor is elaborating a
function.

FILE VER DATA ULT. VERSIONE LINGUA
PAGINA
GCM02-MT-ING4 NEW.doc c/02 04/03/2003 ITA Page 8of 57
1
2
3
4
5
6
1.4 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION OF THE CONTROL PANEL COMPONENT
Description of the components.
Programming switch.
Type of operational mode selection
1. Automatic test (T)
2. Standard automatic run mode (A)
3. Locked status –electronics disabled, used for
maintenance.
4. Utility power supply forced from mains (CR).
5. Enable start push button to start in manual mode.
6. Utility power supply forced from generator (CG).
Display reading selection push buttons.
These are used to select the reading page required and to program the weekly timer.
DIFFERENTIAL TEST, with the switchin BLOCK,tooperate for 2”the buttons+/-“TEST
LED”and whiletheled areturned on,topress RESETto havethedifferential protection.
Reset/Enter push button used to reset the functions and to eliminate an alarm status
(RESET)and also to confirm parameters entered in the programming phase (ENTER)
To push one time to exclude the acoustic alarm (SILENT) and to fix the signalling of
alarm, two times to reset.
DESCRIPTION OF THE VARIOUS READING PAGES
When the mains are connected these readings are automatically displayed
that indicate the mains voltage and frequency. The current on the phase 1
is displayed if the CT are connected and reseted on the load.
The three line voltages between one phase and another are displayed for
the detailed control of the mains…
It indicates the three star voltages between phase and neutral
The three currents of phase enable to verify the situation about the load on
the single phase of the mains. This page is displayed if the CT are
connected and reseted on the load.
The powers indicate the state and the load type on the mains:
KVA=kilovoltampere=apparentpower; KW=kilowatt=real power;
KVAr=kilovar=reactive power. This page is displayed if the CT are
connected and reseted on the load.
Cosfì= power factor = phase displacement angle between voltage and
current, with the normal load it indicates L 0,xx, if with capacitive load it
indicates C 0,xx. This page is displayed if the CT are connected and
reseted on the load
When the gen-setis running the gen-set voltage, the frequency and the
current on the phase 1 are displayed.
RETE
V12 389
HZ 50.0 I1 22
RETE
V12 V23 V13
389 388 394
RETE
V1N V2N V3N
224 221 224
GEN.
V12 389
HZ 50.1 I1 32
RETE
I1
32
I2 33 I3 31
0
RETE
0KVAr
7KVA 7KW
RETE
COS.
L 1.00
FREQ 50.0HZ

FILE VER LAST ISSUE LANG. PAGE
GCM02-MT-ING4 NEW.doc c/02 04/03/2003 ENG Page 9of 57
For a control more detailed of the gen-set, the three linked voltages are visualized
between phase and phase.
It indicates the three starry voltages between phase and neutral of the gen-set.
The three current of phase allow to verify the state of the load on the single phase of the
gen-set.
The powers indicate the state and the type of load on the gen-set:
KVA= kilovoltampere = apparent power; KW = kilowatt = real power;
KVAr = kilovar = reactive power.
Cosfì= power factor = phase displacement angle between voltage and current, with the
normal load it indicates L 0,xx, if with capacitive load it indicates C 0,xx. (ATTENTION! In
thislast caseit meansthatthe automatic rephasingisinserted
oftheplant, thatduringthe operationofthe gen-set Has absolutely to be
disconnected:DANGEROUS CONDITION)
The kilowatthour indicates the supplied power from the gen-set.
Thevoltageofthebatteryandthecurrent ofloadarebroughtincaseof present mains,
firmgroupandofinferiortideto2A.Latensiondoesn'thavetoovercomethe13,5Vsincaseof
12Vdcbatteriesandthe27Vforthe24Vdcbatteries;whenthegroupisrunningthevoltage are
superiorsinceconditionedbythegeneratorbatterycharger.
RPM: motor revolutions. LC: percentage of the fuel in the tank.
PO: oil pressure. TM: motor temperature.
Attention! LC, PO, TM are displayed only if the the respective probes are connected
Hour counter totalizator: the value remains memorized even if the battery is not
connected.
State of the inputs: it is displayed by the technicians in phase of test of the plant.
State of the outputs: it is displayed by the technicians in phase of test of the plant.
Counter succeeded and failed starts
Weekly clock: every time is reseted that the battery is interrupted, and it serves for the operation
oftheautomatictest,oftheautomaticblockandofthereservegen-sets.
GEN.
V12 V23 V13
389 388 392
GEN.
V1N V2N V3N
222 221 221
GEN.
I1
32
I2 0 I3 0
GEN.
0KVAr
7KVA 7KW
GEN. COS.
L 1.00
FREQ 50.0HZ
IN
123456789ABCD
00111111111101
OUT
123456789ABC
01010000
MON 18:02:05
BATTERY CHARGER
27.2V 1.4A
1500RPM LC 92%
PO 4.4bar TM83°C
CONTAORE
4 h 7m 40S
GEN.
KWh 13953
SUCCEEDED ST. 135
FAILED ST. 1

FILE VER LAST ISSUE LANG. PAGE
GCM02-MT-ING4 NEW.doc c/02 04/03/2003 ENG Page 10 of 57
Differential protection:theintervention issuitablefromthesignalingTRIP, andit
interveneswhenthecurrentofdispersiontoearthitovercomestheprogrammed
values(signedamongparenthesis). Thispageisdisplayedonlyifthedifferentialis
active.DIFFERENTIAL TEST, with the switch in BLOCK, to operate for 2” the
buttons +/-“TESTLED”andwhile the leds are turnedon,topress RESET, it will
havethedifferential protection.
Itindicateshow muchhoursmisstothe requestofmaintenance 1. Among
parenthesistheintervalofmaintenance.Thispageisonlyvisualizediftheapplication
of maintenanceisactivated.
Itindicateshow muchhoursmisstothe requestofmaintenance 2. Among
parenthesistheintervalofmaintenance.Thispage isonlyvisualized if the application
of maintenanceisactivated.
Advertising page brings name and telephone number of the producer or the
technician. This page is only visualized if it is compiled in the settings
Theblock indicatesthattheplantfeedstheuse.
Thepylonrepresents thepublicmainsandtheturned onledindicates
thatthethreephasesareintheestablishedparameters,whilewhenit
isturnedoffitindicatesthecontraryone.TheledsCGandCR
indicatewhatcontactorisclosedtofeedtheuse.TheledTRIP
indicatesthe intervention of the differential protection, ifflashing
protectionitmeans that there isasuperior dispersion to 50%than the
foreseenvalue.The ledonthegeneratorindicatesthat thegroupis
running.
Theledonthemotorindicatesstateofalarmofthegen-set.
Battery charter and battery.
Theledindicates feededbatterychargerandfeedingof M02module
fromthebattery
The ledWAIT/PROG indicatesanelaboration inprogressfromthemicrocontroller:to the
endoftheflashing the result of the elaborationitwillbe had. Es.: when the ledisturnedon, on
thepylonofthe mains itmeansthatthemainshasreenteredin the normalvalues;theswitching
gen-set-mainsCG/CRishadonlyafteracertaindelay,during which the led WAIT/PROG
flashes.
TheGCM02isprovidedwithautomaticcommandofthe pomp of restocking gas-oil: when the
ledisturned andthebuttonservesto themanualcommand.
Thebuttonofstarting motor (START)istrainedonlywhentheswitchis in pos. MANUAL
START.Thecommandisdirectedandtomotorinrunningit isnecessarytoleavethebutton.The
ledindicatesthatthecommandofstartingisinprogress.
Thebuttonofarrest (Stop), alwaystrained,ithastobepresseduptothesuitarrest of the
motor.Theled indicates thatthecommandofarrestis inprogress.
DIFFER 0,00 (0,
03 ) A
DELAY ( 0,06) S
MAINTENANCE 1
TRA 237h ( 500)
NomeCliente
Numero telefono
MAINTENANCE 2
TRA 794h ( 1000)

FILE VER DATA ULT. VERSIONE LINGUA
PAGINA
GCM02-MT-ING4 NEW.doc c/02 04/03/2003 ITA Page 11 of 57
1.5. COMMANDSAND OPERATIONALMODES
The operational modes that can be selected with the programming switch are six, namely:
1.5.1 Automatic test: This starts to test the generator without disconnecting the mains power supply from the utility. When the
switch is turned back to automatic mode the generator stops following a delay of roughly one minute (it is used for periodic
tests or to check the running efficiency following maintenance).
1.5.2 Automatic mode; if there should be a failure in the mains the circuit board responds by opening the mains contact maker. If
the generator fails to start another 4 starting attempts are made. 10 seconds after it has started the generator powers the
utility. While running the generator and motor are constantly controlled and a possible anomaly is immediately displayed
(examples: fuel reserve, water level, overload, min. voltage etc.) and the relative stopping cycle is triggered. Once the mains is
re-connected, following the set time, the utility is switched back to the mains and the generator is stopped following a delay of
roughly one minute to allow it to cool down (this is the normal operational situation ).
1.5.3 Lock: this sets the generator in a locked status. It completely disables every possibility of starting while the mains power the
utility. This mode is used to work on the system in complete safety, being certain that the generator will not start even if the
mains should be disconnected ( it is used during maintenance).
1.5.4 Manual mains: this enables the forces the power supply from the mains even if the command and control electronics are
faulty (it is used when the generator is left inoperative).
1.5.5 Manual starting: this enables the generator to be started manually using the start push button. The control is direct without
the involvement of electronic components. It ensures the operation of the generator even when the electronics are faulty (it is
used for the manual emergency controls or for maintenance purposes).
WARNING
When the programming switch is in this position all the utility circuits of the generator are powered such as the solenoid
valves, electronic rpm regulators etc. If the switch is forgotten in this position with the generator stopped the starting battery
would run flat very quickly.
1.5.6 Manual generator: this enables the forced power supply from the generator (it is available for manual procedures or in
the case of problems with the automatic functions).
STOP
This is enabled whatever the situation.
It is to be held down until the motor stops completely
EMERGENCY STOP
If pressed, the red mushroom push button in the middle of the door stops the generator immediately, instantaneously opening the
contact maker of the generator (CG) thus locking it.
To release the emergency status set the programming switch in Lock position and then turn the emergency push button and pull up.
FUEL PUMP CONTROL (if foreseen)
The M02 module electronically controls the fuel level. It automatically controls the fuel pump so that the daily tank
requirements are constantly ensured. A push button enables the direct control of the pump with only a maximum
safety level safety function.
WAIT/PROG
A newly conceived and remarkably useful LED has been fitted on the GCM02 module to assist the operator, namely the WAIT/PROG
LED. This LED flashes each time the timer is triggered informing the operator what is happening even over a lengthy timer period.
All LEDs are provided with a general description that make the control panel easily comprehensible.
SUMMARY
The unit is normally programmed in AUTOMATIC mode.
When any jobs are to be performed on the generator it is to be set in the LOCKED status.
If the generator is not to start even if the mains is disconnected it is to be set in the MANUAL MAINS status. The reason for this is that if,
while the generator is not working, there should be a failure in the electronics, the power supply from the mains would be ensured in any
case.
HOW TO PROCEED IF THE GENERATOR SHOULD FAIL TO WORK.
A possible alarm status will be shown on the display. Whatever the anomaly, the cause is to be found first and foremost then press the
RESET push button. The causes and the solutions differ depending on the type of anomaly involved:
1. Electrical anomalies due to min./max. voltage and frequency. If the anomaly should persist after the RESET push button has been
pressed then request technical assistance;

FILE VER LAST ISSUE LANG. PAGE
GCM02-MT-ING4 NEW.doc c/02 04/03/2003 ENG Page 12 of 57
2. Anomaly due to low oil pressure, high motor temperature, low water or oil level, fuel reserve. Check the relative levels (water, oil,
fuel) and top-up if necessary then reset;
3. Anomaly of the battery dynamo. In this case request technical assistance;
4. Alarm due to local or remote emergency stop status. Set the programming switch on LOCKED mode and turn and pull the
emergency push button enabled then reset;
5. Alarm due to failed starting. Try starting with manual control and inform the supplier;
6. The generator overload protection switch has tripped. It is to be reset manually by a qualified engineer (see simple maintenance
jobs section).
1.6 PROGRAMMING
If the electronic module should be disconnected from the power supply, the established weekly timer programming is deleted,
consequently all the functions foreseen for the internal timer would fail to work at the time and on the day programmed therefore the
weekly timer is to be re-programmed.
Access the page below to re-program it.
Press ENTER, the day flashes. Using the +/-keys modify the day and press
ENTER to confirm. The time flashes. Using the +/-keys modify the time and
confirm with ENTER. The same goes for the minutes and seconds.
You cannot change page until programming is complete.
1.7. VARIOUS CONTROLS
LED TEST
Hold the + /-push buttons down together for 2 seconds. All the LEDs barring the start, stop and battery charger LED will light up.
ALARM SILENCING
With the state of alarm the red led of alarm on the motor flashes and the sonorous is active alarm. Pressing once the SILENT button the
acoustic alarm is interrupted, the red led on the motor remains turned on to fixed light
FUNCTIONS RESET
Pressing the RESET button two times the conditions of alarm are annulled, all the functions are restored and the red led on the motor is
turned off.
PROTECTION DIFFERENTIAL TEST (if active)
To activate the TEST LED and with the turned on led to press RESET, the TRIP has to intervene with the detached load.
1.8.SPECIALFUNCTIONS
The GCM02 is set up for special operating functions, such as: automatic testing or cut-out, routine
maintenance, remote control, etc.
When these are active, a page comes up on the display when they are activated, indicating which
function is active.
There are functions that affect how the unit operates and that require direct intervention to allow the unit to be used:
GE CUT-OUT
The cut-out function is mainly used when the unit is run in a built-up area, and emergency standby is not required outside of working
hours. During the cut-out hours, if the mains power supply fails the unit does not react, and should it be necessary to start up the unit
during this time, this can only be done manually.
SERVICE REQUEST
This does not change the operating status, but raises an acoustic alarm to mark the set time, and a message reading SERVICE appears
on the display ALARM MAINTENACE 1 or ALARM MAINTENANCE 2, pressing RESET the function is restored.
REMOTE CONTROL
The unit can run under remote control by using remote communication (PC or modem or GSM), and this can be activated automatically.
GENOPERATION
CUT-OUT

FILE VER LAST ISSUE LANG. PAGE
GCM02-MT-ING4 NEW.doc c/02 04/03/2003 ENG Page 13 of 57
1.9 SIMPLEMAINTENANCEWORK
USER SAFETY PROCEDURE
WARNING
It is strictly prohibited for anyone to touch powered parts.
1.9.1. ELECTRICAL MAINTENANCE
All jobs must be performed by skilled personnel.
The control unit is equipped externally with all the possible command, control and reset functions.
Proceed as follows to access the equipment within the control panel:
1. Set the programming switch on LOCKED mode.
2. Check if the unit has stopped completely.
3. Disconnect the mains line that powers the control panel and switch the main ON/OFF switch of the mains off.
4. Check if the mains has been effectively disconnected, which can be seen by the mains OK LED switched off and by the
display switched to the mains that must indicate zero.
5. Open the control panel and check for any anomalies in the:
•fuses;
•automatic switches;
•thermal relays.
Once maintenance has been completed repeat the procedure in reverse order to reset the unit.
Overload fault
This may cause the unit’s trip switch to open (lever in central “TRIPPED” position). This must be reset by
pushing the lever down to the OFF position and then returning it to the ON position. Where switches have been
installed inside the electrical board, follow the ELECTRICAL MAINTENANCE procedure before opening the
board.
1.9.2. MECHANICAL MAINTENANCE
If the generator should fail to start due to an anomaly in the fuel circuit and also in an emergency status, the following tips may prove
useful.
How to restore the fuel circuit:
1. Set the programming switch on Manual Start mode without starting the generator. In this way the 15/54? that powers the fuel
interception solenoid valve is activated.
2. Once you have filled up with fuel, operate the hand pump situated on the motor until the circuit is restored, which can be seen
by the pump becoming harder to move.
3. Start in manual mode (It is advisable to restrict the starting attempts to 10 seconds each with a pause of 15 seconds in-
between to allow the battery to recover efficiently). Once the unit has started and is running regularly reset the automatic
functions.
1.9.3. PERIODIC CHECKS
To keep the unit efficient some periodic checks must be made together with those scheduled by the manufacturer of the motor and by
the installation engineer:
1. check the electrolytic level of the battery every 15 days following installation and request the assistance of an engineer if an
excessive consumption is noticed. Following the initial period check every 30 -60 days;
2. In generators complete with motor pre-heating system check if the motor iswarm each time a check is made otherwise request
technical assistance. (WARNING: a cold motor at low temperatures could have difficulty in starting or outputting once started);
3. If the generator is rarely triggered due to the lack of mains power supply execute an automatic test for at least 2 minutes.
4. if new electrical machines are installed in the system powered by the generator, request technical assistance to check the suitability
of the CG/CG mains/generator switching to the new load.
SUMMARY:
On a periodic basis check the electrolytic level of the clear batteries. Touch the motor to feel if it is warm (if equipped with pre-
heating system) and execute an automatic test.

FILE VER LAST ISSUE LANG. PAGE
GCM02-MT-ING4 NEW.doc c/02 04/03/2003 ENG Page 14 of 57
2. TECHNICAL MANUAL
2.1 CONSTRUCTIONALDESCRIPTIONOFTHECONTROLPANEL
The control panel is entirely manufactured in compliance with the following European standards:
ANS low voltage electrical control panels EN 60439-1
EMC electromagnetic compatibility directive 89/336/EEC
Each control panel or device is completely tested and supplied with test certificate, declaration of conformity and EC marking in
compliance with 626 safety standards.
The control panel is manufactured in a steel sheet cabinet, 15-20/10 that is skilfully treated and painted with standard grey silicon epoxy
powder, Ral 7032, and has a standard protection rating of IP 42.
EXTERNAL COMPOSITION
The control panel consists of the following:
1. GCM02 electronic circuit board that houses the control logic, control and reading of the operational parameters of the generator;
2. Emergency stop mushroom push button (optional) ;
3. Nameplate with operational standards;
4. Nameplate with safety instructions.
INTERNAL COMPOSITION
1. numbered cables placed within PVC sheathing;
2. 10 x 38 fuses with disconnectable fuse boxes;
3. battery charger transformer of adequate capacity;
4. automatic generator protection switch (if provided);
5. switch with tetrapolar contact makers of adequate capacity for the power of the unit, interlocked mechanically and electrically and
scaled in AC1 in compliance with standard ISO DIS 8528-4 ;
6. three amperometric transformers for measuring the generator and mains current;
7. terminal for the mains and generator inputs, the utility output and any auxiliary connections;
8. safety fuse gauges and connection terminals nameplate.
Switching is controlled directly by CG and CR relays built in the MP-M02 module, which directly command switching via unpowered
contacts.
IMPORTANT
The CG and CR command contacts are normally closed to allow the command circuits, in the case of
certain anomalies, to force the mains contact maker to close. For example by disconnecting the battery
and also the power supply to the battery charger transformer the mains contact maker is forced to close.

FILE VER LAST ISSUE LANG. PAGE
GCM02-MT-ING4 NEW.doc c/02 04/03/2003 ENG Page 15 of 57
2.2. OPERATION
READINGS
All readings are shown on the display on two lines of 16 alphanumerical characters.
All the reading pages are controlled using the +/-push buttons, which run in both directions.
The reading pages available are the following:
•mains status, volts, hertz and amperes of phase 1
•R, S, T line mains voltage.
•RN, SN TN mains star voltage.
•Current on the three phases mains;
•KVA, KW, KWAr mains powers;
•Power factor, cosfì HZ mains;
•Generator status, volts, hertz and amperes of phase 1
•X, Y, Z line generator voltage.
•XN, YN, ZN generator star voltage;
•Current on the three phases gen-set;
•KVA, KW, KWAr gen-set powers;
•Kilowatthour gen-set;
•Power factor, cosfì, HZ;
•Differential trip switch, programmed current, dispersion current and programmed time;
•Battery, voltage and charging current;
•Status of the inputs;
•Status of the output;
•Start counter;
•Weekly timer for programming the automatic test.
•Operation active, automatic test, forced start, pilot GE, cut-out, etc.;
•Supplier’s name and telephone number;
•Maintenance, with programmed hours and working hours remaining before service.
If an alarm is triggered it will be shown on the display. For example a low oil pressure, fuel reserve, high battery voltage alarm, etc.
2.3 DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF HOW THE CONTROL UNIT WORKS
All operational modes are controlled by the GC-M02 control panel equipped with a programming switch to select the following functions:
1. TEST
2. AUTOMATIC MODE
3. LOCK MODE
4. POWER SUPPLY FROM MAINS.
5. MANUAL START.
6. POWER SUPPLY FROM GENERATOR.
1 TEST
1.A. it performs allthe automatic functions with the exception of the switching function.
1.B. it tests the efficiency of the whole system without disconnecting the mains power supply
to the utility.
1.C. all safety devices are enabled while the test is running.
1.D. if the mains should be disconnected while the test is running the generator starts immediately .
1.E. the test ends automatically when the mains power supply is restored or following a programmed external command.
2 AUTOMATIC MODE
2.A. A special three-phase voltage relay is capable of working at a voltage of 8Kv to safeguard the mains against:
•sagging of over -20% of the rated voltage (this can be modified);
•excessive rise in the rated voltage of over +15% (this can be modified);
•missing phase;
•incorrect angle between the phases (phase displacement).
2.B. If one of the above-mentioned anomalies should occur the CR mains contact maker is immediately opened to safeguard its
integrity also in the case of excessive voltage sagging.
2.C. When the mains is disconnected a starting delay timer is triggered (programmable time). It makes the system insensitive to
brief mains disconnections. A buzzer will sound in this case.

FILE VER LAST ISSUE LANG. PAGE
GCM02-MT-ING4 NEW.doc c/02 04/03/2003 ENG Page 16 of 57
2.D. Following the STARTING DELAY phase 4 starting cycles of 5 seconds each start, split up by pauses of 5 seconds (these may
be programmed).
2.E. At the end of the start cycles if the gen-set has not started, there isthe FAILED START signalling, if the gen-set starts but it
doesn’t reach the speed values, after 120” there will be the min voltage or frequency alarm.
2.F. With the motor running at a steady state the voltage output by the generator is read. When this is within the established
parameters the generator delay timer is triggered (this may be adjusted from 1 sec. to 30 min. approx.). At the end of this
timing the generator (CG) contact maker is closed on.
2.G. By means of a normal VDO probe for reading the motor temperature the minimum temperature beyond which the load output
is enabled can be programmed. This is to prevent operating at a low temperature in the case of the failure or failed pre-heating
of the motor.
2.H. While the generator is running two pre-alarm safety devices are enabled, oil pressure and motor temperature. When these trip
a buzzer sounds. The following safety devices and indications, when tripped, are displayed and trigger the programmable
functions described:
No. DESCRIPTION ON DISPLAY LED COLOUR
BUZZER IMMED. STOP
DELAYED
STOP
MOTOR
1Failed starting A
2Failed stoppage A
3Low oil level A
4Low oil pressure AYES
5Minimum oil pressure (pre-alarm) A
6High oil temperature ASR
7Low water level A
8Very high water temperature AYES
9High water temperature (pre-alarm)
10 Battery charger generator AYES
11 Lack fuel A
12 Low fuel level (pre-alarm) A
13 Starting R
14 Stoppage R
15 Fuel pump running (ON) V
16 Minimum temperature A
BATTERY
17 Battery connected V
18 Excessive battery voltage A
19 Low battery voltage A
20 Battery charging V
21
GENERATOR
22 Excessive voltage (59) AYES
23 Low voltage (27) ASR
24 Overload (51) ASR
25 Short-circuit (50) ASR
26 Maximum frequency (81) AYES
27 Minimum frequency (81) ASR
28 Phase sequence A
29 Inverted power ASR
30 Generator connected G
30 Generator contact maker closed (ON) G
32 Differential trip switch (earthing fault) ASR
33
MAINS
34 Mains connected V
35 Excessive voltage (59) V OFF
36 Low voltage (27) displacement V OFF
37 Overload (51) ASR
38 Phase sequence A
39 Mains contact maker closed G
VARIOUS
40 Emergency push button pressed AYES

FILE VER LAST ISSUE LANG. PAGE
GCM02-MT-ING4 NEW.doc c/02 04/03/2003 ENG Page 17 of 57
41 CR mains contact maker anomaly GA
42 CG generator contact maker anomaly GA
2.I When an alarm is triggered and the generator is stopped, the following occurs:
•The alarm triggered appears on the display.
•The generator contact maker is immediately opened.
•Activation of the immediate stop SI or delayed SR after the phase of cooling motor (if enabled stop)
•Activation of the acoustic alarm and lighting of the flashing red led on the drawing of the engine.
•The alarm cause is saved.
•The LOCKED status is triggered until the alarm is reset, the first impulse to SILENT /RESET/ACK button it silents the acoustic
alarm, it recognizes the alarm with function ACK (function ISA M) and the alarm led from flashing it becomes fixed, to restore the
functions excluding the block for alarm, to press a second time the RESET button and alarm red led will be turned off.
2.J. When the voltage returns within the rated parameters the switch back to mains delay timer is triggered that enabled the mains to
settle before switching back the load.
2.K. Once the load is switched, the motor cooling phase of roughly 1 minute begins. At the end of this phase the immediate or delayed
stoppage phase is enabled.
2.L. Pre-arrangement for a new cycle
2.M. With the mains connected the overload safety device (51) of the mains contact maker is enabled (EXCLUSIVE) , which when
tripped, triggers the buzzer without interfering with the mains output, warning the operator that the rated current of the CR contact
maker has been exceeded.
2.N. To the command of the contactors CR and CG it is done the control of the real closing, contrarily there is the alarm (it is activated
inserting the ADJUSTABLE DELAY).
2.O. If there is a stop not trained (DELAY STOP TO ZERO) the Ge supplies with any alarm, the gen-set can be stopped only manually
2.P. The change of the switching from CG to CR or from CR to CG, it is alternated by a break of 1”, to avoid a malfunction of the
mechanical interlock
3 LOCKED STATUS
3.A. It immediately stops the generator if this is running.
3.B. It disconnects the power supply from all starting circuits.
3.C. it ensures safety throughout maintenance.
It deactivates the fuel pump and the preheating in order to there is not any components in voltage during the maintenance.
2.4 MANUALLY CONTROLLED FUNCTIONS
The manual operational mode is considered as an emergency back-up mode for the automatic functions. It also ensures the operating
efficiency with the micro-controller in an abnormal condition. The programming switch ensures the direct commands that are not
backed-up by electronic logics. This means that when the START push button is pressed for example, the starting motor will be
operated for as long as the push button is held down.
The following functions are possible:
1. Forced power supply from the mains CR;
2. Manual starting, the generator CG contact maker is opened;
3. The mains CR contact maker is opened and the power supply is forced from the generator;
4. Manual stoppage;
2.4.1 POWER SUPPLY FROM MAINS (manual command)
This enables the mains power supply permanently and disables all the electronic functions with the exception of the battery charger and
the EMERGENCY stop function.
2.4.2 MANUAL STARTING
Enable the start button, and the 15/54 relay that provides power to all the unit’s services (solenoid valves, actuator, etc.) will be activated
simultaneously.
2.4.3 POWER SUPPLY FROM GENERATOR
Once the unit is running in normal mode, switching the commutator to GENERATOR POWER SUPPLY causes the contactor for the
Generator unit to close, and the unit then draws power from the generator.
While the unit is supplying power all the trip switches are active. However, since these are entirely controlled electronically, any fault in
this system could render it inactive.
2.4.4 MANUAL STOPPAGE
The stop push button is enabled at all times. Press it until the motor stops completely.
By moving the jumper 1 on the MO2 module the stop push button is enabled only when the programming switch is in MANUAL START
mode.

FILE VER LAST ISSUE LANG. PAGE
GCM02-MT-ING4 NEW.doc c/02 04/03/2003 ENG Page 18 of 57
2.5 VARIOUS FUNCTIONS AND UTILITIES
2.5.1 CC12 AND 24V POWER SUPPLY CIRCUITS
The M02 module is arranged to operate at 12 and 24V. By bridging connections 3 and 4 all the functions are adapted, including the
control threshold of the battery charger for the 12V voltage and the same without bridge for the 24V power supply voltage.
The first level safety device against excessive power supply voltages are fitted in the MP02 module: it is capable of operating constantly
up to 40V, it can also withstand transitory voltages above 250V. A second level safety device is also fitted against inverted polarity of the
power supply, which prevents the circuits in which it is encountered from being powered. Any anomalies cause the F1 fuse to trip (25A)
that cuts-out all the electronic circuits.
WARNING if, after having powered the control panel the battery LED should fail to light up, check the POLARITY OF
THE BATTERY before operating any commands. Possible connection errors could cause electronic anomalies in the MP02
module if commands are operated with the poles inverted.
2.5.2 COMMAND RELAYS
Two 30A relays command the starting and stopping and one 16A relay the utilities 15/54. Two 10A relays with free contacts command
the contact makers of the mains and generator (CG-CR) switching. An additional relay with contact that can be configured in NA/NC is
pre-arranged to command the opening of the generator switch. It is designed to trip the differential or for overloads.
2.5.3 MOTOR STARTED READING
This requires no external signal. The control is achieved on the frequency of the generator. During the motor starting phase, once 540
rpms are reached which correspond to 18Hz programmable, the 1st motor started signal is received. If due to an anomaly the generator
is not powered ( at least 7V) the starting phase is stopped once and for all by the second safety control established when the oil is
pressurised, which triggers a delay of 3 seconds that stops the starting phase.
N.B. For the safety engine, if theoil pressure switch is not connected, the gen.set can notto start
2.5.4. MOTOR PRE-HEATING
Afeeding is foreseen for the engine preheating system; the M02 has a transistorised command which controls a contactor in direct
current to deactivate automatically the preheating when the gen-set is running or above the max programmed temperature (OFF), and to
activate it automatically when the engine temperature is inferior than least value (ON) (this function is enabled only when the
temperature transducers is connected to terminal 16).
3 4 3 4
12 Volt 24 Volt
On the selected voltage, the M02 is automatically shaped for the alarm
voltages for min battery voltage, contemporarily also the battery charger is
shaped.
1 + Batt 5 Start 6 Stop 7 15/54
30 A 30 A 16 A
8
1
Hz
51
52
Generator
voltage
Start
Krank
0 10 20 Hz
Reached the programmed frequency:
-9Hz for 3000 rpms
-18Hz for 1500 rpms
The start command is cut off
ON
Off
= > 7V
28
-B
The contactor commando the preheating system.
PROGRAMMING
Preheating command (to activate out 28 = preheating in different
settings). Two levels are established in thresholds setting: ON,
activation; OFF, stop.

FILE VER LAST ISSUE LANG. PAGE
GCM02-MT-ING4 NEW.doc c/02 04/03/2003 ENG Page 19 of 57
2.5.5 AUTOMATIC BATTERY CHARGER
The automatic battery charger is the double semi-wave type with phase choker, totally controlled by the micro-controller. It keeps the
starting battery charged with a max. load of 8A and the charge is self-adjusted to compensate for consumption and for when the battery
automatically runs flat. The voltage of the battery and the charging current can be displayed on the GCM02 unit.
The electronics are built in the MP02 unit whereas the battery charger transformer is fitted externally.
It is equipped with:
•Automatic cut-out of the charge during the starting phase;
•Electronic restriction of the current to prevent excessive loads;
•Electronic restriction of the voltage to limit the maximum load levels (2,3 V/E) 13,5/27V.
•Protection against short-circuits.
•Protection against inverted polarity.
•Protection against excessive input voltage.
•Auto programming of the voltmeter thresholds on the battery voltage
•Protection with low battery voltage for excessive discharge
•Programmable values also for batteries Nichel Cadmio.
Technical features
Programmed work voltages 12 V 24 V
Work frequency 50 and 60 Hz 50 and 60 Hz
Max programmable current From 1 to 8 A From 1 to 8 A
Max voltage threshold 14,5 V 29V
Alarm voltage threshold 10,8 V 21,6 V
Battery charter transformer Min Max
Voltage II° for battery 12V 17 Vac 20 Vac
Power in VA/A for battery 12V 50VA / 3 A 150VA / 8 A
Voltage II° for battery 24V 29 Vac 32 Vac
Power in VA/A r batt. 24V 100VA / 3 A 250VA / 8 A
PROGRAMMING
Tosetthe valueofmax current ofchargeon thepowerof the installed transformer
V/elem
2,42Ve
1,9Ve
1,8Ve
Corr. A
I max
0
Max charge voltage limit
Discharged battery
Alarm min voltage for discharged battery
Charge max of programmed current
Current auto regulated to compensate the
electric consumptions and the auto drain of the
battery
T
CHARGE DIAGRAM FOR PLUMB BATTERIES
Ve = Volt for component 12V Battery = 6 components 24V Battery = 12 components
I°
Feed.
100/440 50/60Hz
II° 17/29V
Fuse
Fuse
21
22
MP02
1 +B
2
-
B
Battery
12 or 24V
µ P
CONTROL
Shunt
SCR
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM

FILE VER LAST ISSUE LANG. PAGE
GCM02-MT-ING4 NEW.doc c/02 04/03/2003 ENG Page 20 of 57
2.6 MOTOR AND ALARM PARAMETER READING
2.6.1 POSITIVE MOTOR PROTECTION INPUTS
Some modern motors are equipped with positive outputs to indicate the Low Oil Pressure and High Motor Temperature anomalies. The
M02 is pre-arranged to communicate with these motors by modifying the JUMPERS on the MP02 unit.
2.6.2 ANALOGUE MOTOR PARAMETER READING INPUTS (PRESSURE, TEMPERATURE AND FUEL
LEVEL)
The three inputs 15-16-17 used to read the pressure, temperature and fuel level can be configured using the SW2 switch (on the MP02
unit) for motors type MTU that output 0-10V for the above-mentioned readings.
When SW2 is configured to “ON”, normal motor probes (transducers) of a VDO or VEGLIA type can be used (which can be configured
from the Misc. Settings Menu). Since they are not linear, the working fields available are restricted by the limits of the transducers.
Where the probe is not installed, no indication will appear on the display automatically.
When individually configured as “OFF” the three inputs operate at between 0 and 10V, and are connected directly to the MTU motors
and others of the same concept for taking motor measurements. The reading scale can be changed from the Measurements Menu.
NEG. INPUTS
POS. INPUTS
JUMPER
SW2 ANALOGUE INPUTS
N° DESCRIPTION OFF ON
1FUEL LEVEL NEGATIVE
2MOTOR.TEMP 0-10V NEGATIVE
3OIL PRESSURE 0-10V NEGATIVE
4
JUMPER INPUT
1 + Batt OP WT
9 11
2 -Batt OP WT
9 11
Modifying the jumpers placet on the electronic unit of
the power module, the M02 can to work with posive
inputs.
IT IS NOT REQUIRED ANY PROGRAMMING
SOFTWARE.
15 16 17
FUEL LEVEL WATER TEMP.
OIL PRESS.
ANALOGIC SETTABLE INPUTS VEGLIA OR VDO
16 17
0
-
10V
ANAL.
0
-
10V
ANAL.
ANALOGIC SET INPUTS 0-10V
Other manuals for GCM02
2
Table of contents
Other AEZ Control Panel manuals