Anybus®Communicator™CAN PROFINET®IRT (2.32) User Manual SCM-1202-035 1.0
Table of Contents Page
1 Preface ............................................................................................................................... 3
1.1 About This Document.....................................................................................................3
1.2 Related Documents .......................................................................................................3
1.3 Document history...........................................................................................................3
1.4 Trademark Information ...................................................................................................3
1.5 Conventions ..................................................................................................................4
2 Description ....................................................................................................................... 5
2.1 Introduction ...................................................................................................................5
2.2 Basic Operation .............................................................................................................6
2.3 Data Exchange Model ....................................................................................................7
2.4 PROFINET IRT Protocol.................................................................................................8
2.5 CAN Network Protocol ...................................................................................................9
3 Installation ...................................................................................................................... 13
3.1 Installation Overview ....................................................................................................13
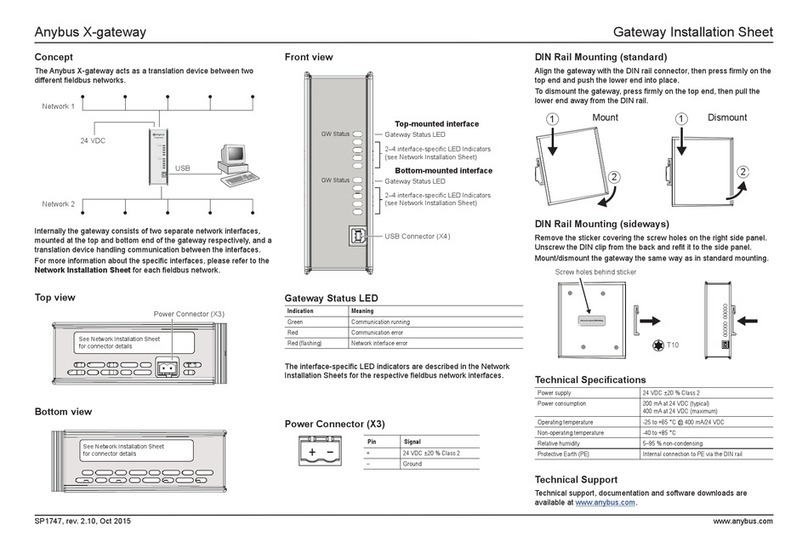
3.2 Connectors and Indicators............................................................................................14
3.3 DIN Rail Mounting........................................................................................................14
3.4 CAN Interface..............................................................................................................15
3.5 PROFINET Interface ....................................................................................................15
3.6 Power Connector .........................................................................................................15
3.7 USB Connector............................................................................................................15
3.8 LED Indicators.............................................................................................................16
4 Configuration ................................................................................................................. 17
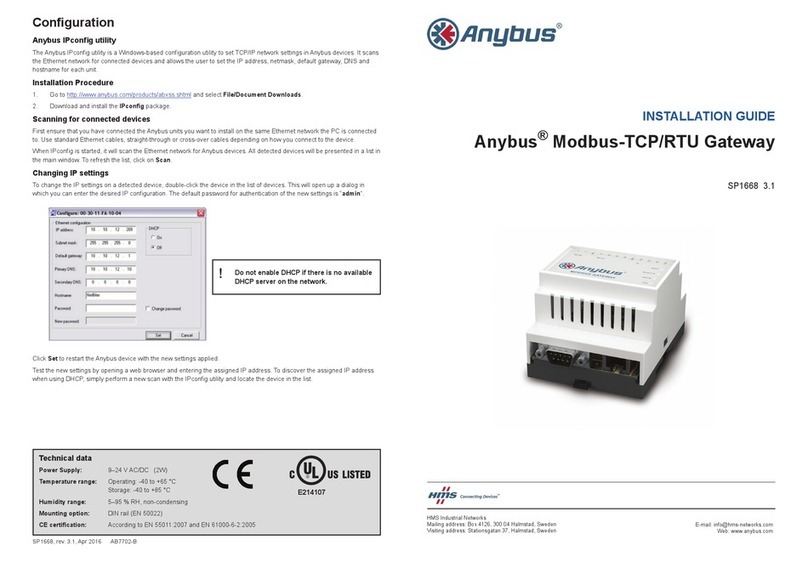
4.1 Configuration Overview ................................................................................................17
4.2 Network Configuration..................................................................................................18
4.3 Web Pages..................................................................................................................22
5 Anybus Configuration Manager ................................................................................ 23
5.1 Main Window...............................................................................................................23
5.2 Basic Settings..............................................................................................................24
A Technical Data................................................................................................................ 27
B Regulatory Compliance............................................................................................... 28
C Licenses .......................................................................................................................... 29