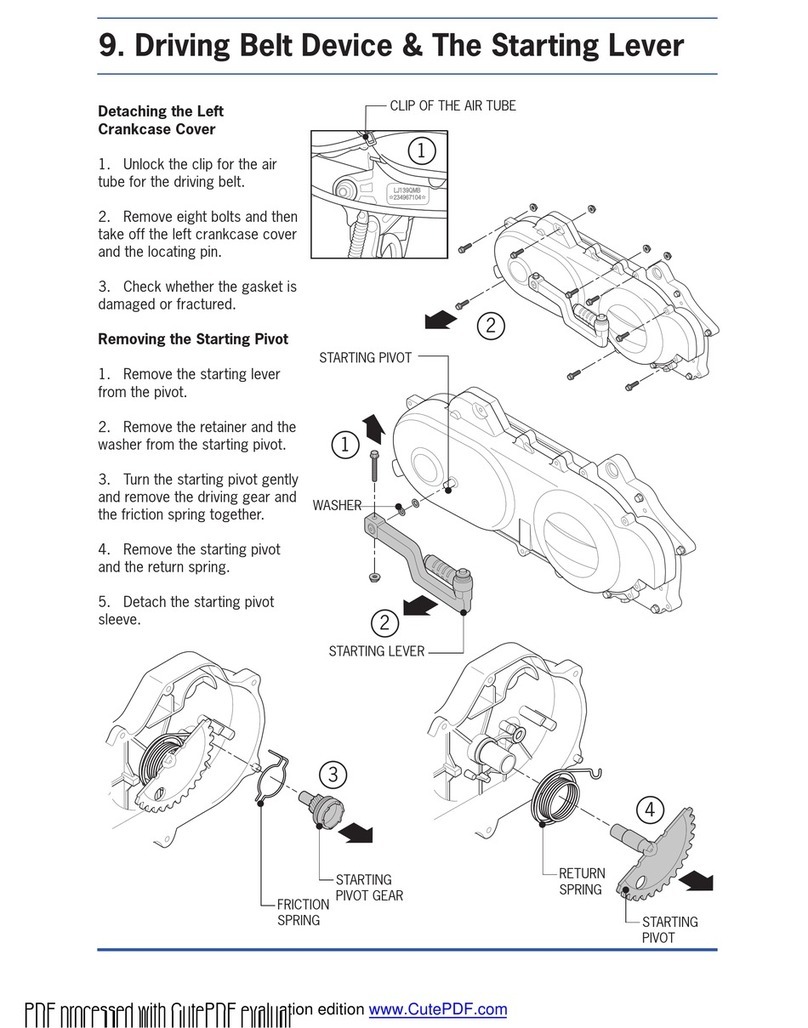
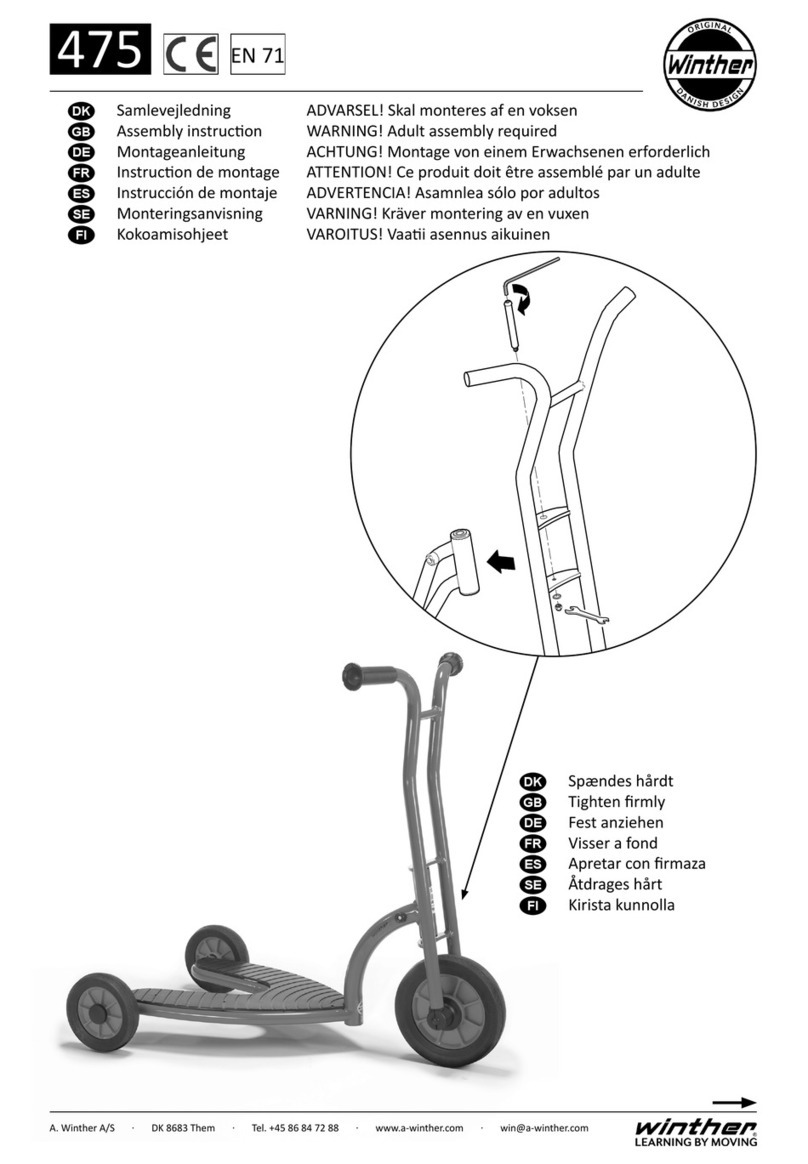
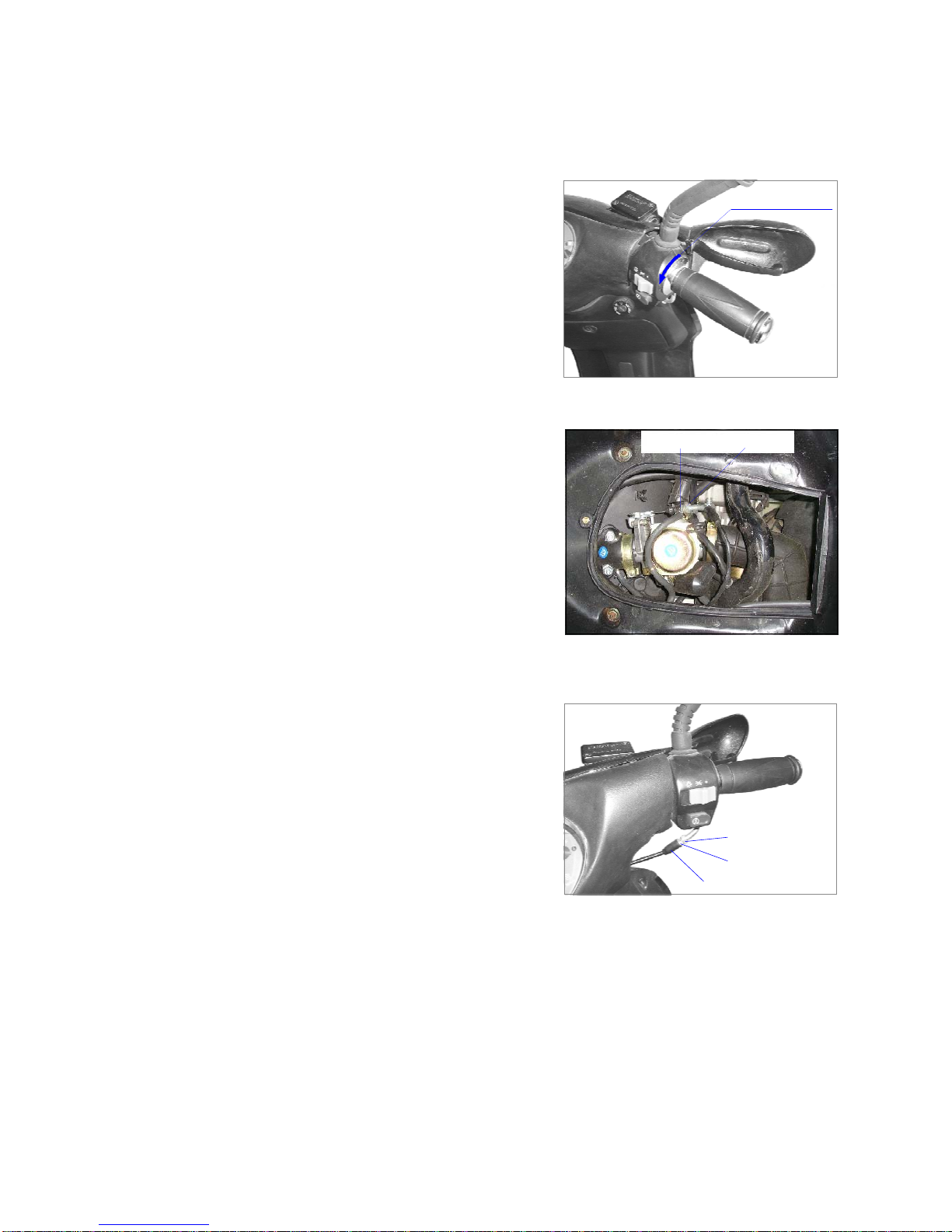
CHAPTER ONE MAINTENANCE OF THE MOTORCYCLE
Ⅰ. ITEMS OF MAINTENANCE
When the motorcycle is used, loosening of parts and mechanical wear inevitably occur to
varied extents. Neglect of timely maintenance not only reduces its mechanical function,
economic performance, stability and durability, but also threatens the safety of the motorcycle
and the rider. Correct and timely maintenance of the motorcycle is a must. Items of maintenance
refer to the parts and positions for maintenance. Different items of maintenance are effected at
different intervals and in different manners.
1. Running-in Maintenance
This is the maintenance at the end of the first 1000km and is an all-round inspection of the
motorcycle. A newly-bought motorcycle or a motorcycle fresh from an overhaul might be
severely overheated as a result of severe friction between the moving parts which might be
imperfect in finishing or fitting. Neglect in use might lead to damage of the friction surfaces and
might threaten the performance, and the service life, of the motorcycle. Please observe the
following points:
zRestrict the speed in speed range specified in the instruction manual.
zRestrict the load to 2/3 of the maximum load and ride in fairly good road conditions.
zRestrict the length of riding time to avoid long-time running of the engine.
zReplace engine oil at short intervals so that metal chips caused in the running-in period
can be discharged. It is recommended to replace engine oil for 3 times during the
running-in period.
2. Routine Maintenance
Routine maintenance is the basis of all kinds of maintenances. It refers to the daily
maintenance, including cleaning, inspection and common troubleshooting.
3. Periodic Maintenance
This maintenance is to restore normal performance of the motorcycle. The maintenance is
classified into first-grade periodic technical maintenance and second-grade periodic technical
maintenance (also known as items of maintenance) according to different mileages. Generally
speaking, a first-grade maintenance is effected after the initial 4000km and a second-grade
maintenance is effected every 8000km. As the service time extends, maintenance intervals
should be shortened accordingly.
Ⅱ. PERIODIC MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE AND MAINTENANCE LOCATIONS
After a period of use (one day, one month or half a year, for example) or a certain mileage
(1000km, 4000km, 8000km, for example), an all-round maintenance operation should be
effected, including comprehensive inspection, adjustment, tightening, lubrication, cleaning or
replacement. The specific regulation made according to time intervals or mileages is known as
maintenance interval. The motorcycle maintenance schedule is as follows.
1