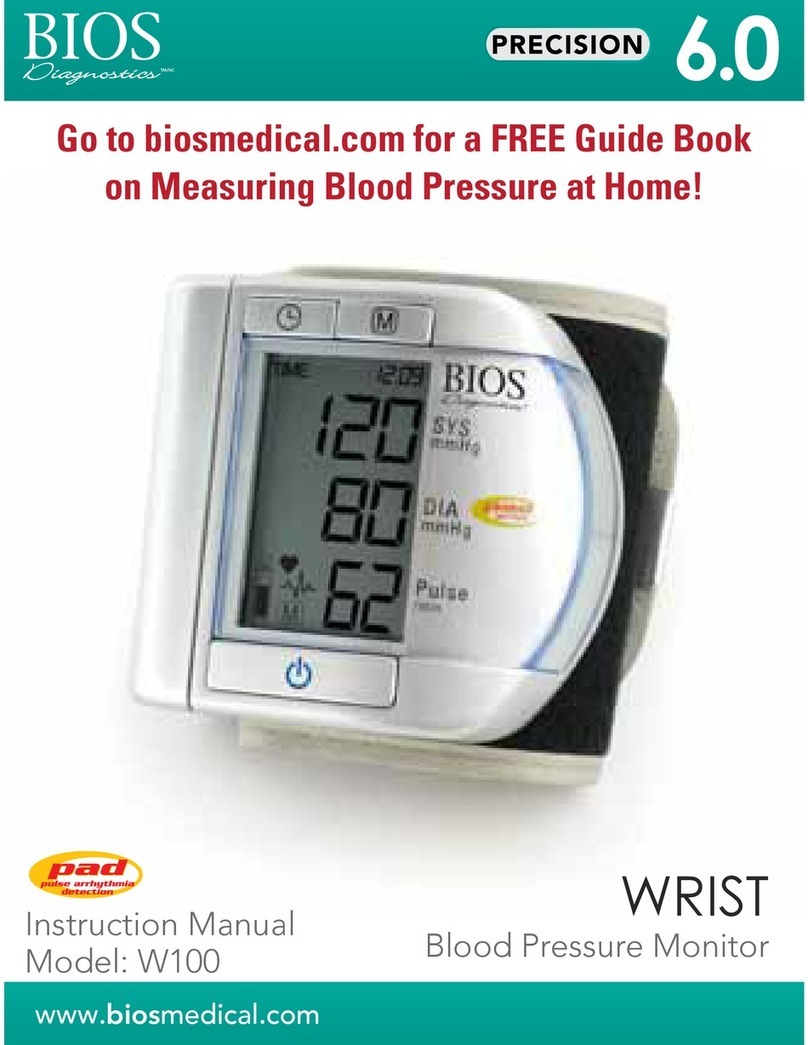
BIOS W100 User manual

WRIST
Blood Pressure Monitor
Instruction Manual
Model: W100
www.biosdiagnostics.com
Go to biosdiagnostics.com for a FREE Log Book!
PRECISION SERIES

Trusted by Canadians for 3 Generations
At BIOS Diagnostics, we are proud of our legacy in blood pressure monitoring across
Canada. From the early 1930’s to 1987 we manufactured Tycos professional blood
pressure equipment for doctors and hospitals in Canada.
In the 1970’s we pioneered the first blood pressure devices for monitoring at home,and
in the 1980’s we introduced digital technology in Canada. We haven’t been counting,
but we know that millions of our home-use monitors have been used by Canadians in
the last 25 years
All Bios Diagnostics devices are developed in collaboration with physicians and clinical
tests prove their measurement accuracy. For more information on clinical tests and other
Bios medical products, visit our website at www.biosdiagnostics.com
If you have questions about this device or blood pressure monitoring at home, email us
Or: Call the BIOS Diagnostics Hotline 1-866-536-2289
Office and manufacturing plant,Church St,Toronto 1934

Table of Contents
1. Introduction
1.1 Features
1.2 Important Information
1.2A Safety Information
2. About Blood Pressure
2.1 Normal Blood Pressure Values
2.2 Common Blood Pressure Questions and Answers
3. Getting Started
3.1 About the W100
3.2 About the LCD Screen
3.3 Inserting the Batteries
4. Using the Device
4.1 Setting the Date and Time
4.2 Obtaining Accurate Measurements
4.2A Before Measuring
4.2B Fitting the Wrist
4.3 Data Memory
4.4 Setting the Alarm Function
5. PAD - Pulse Arrhythmia Detector Feature
6. Trouble Shooting
7. Care and Maintenance
8. Reference to Standards
9. Technical Specifications
10. 10 Year Warranty
Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor Instruction Manual

Thank you for purchasing the BIOS Diagnostics™Wrist Blood Pressure
Monitor. Designed for convenient and easy operation, this device provides a
simple, yet accurate method to measure your blood pressure.
Your blood pressure is an important parameter that can be used to monitor
your health.This device enables you to monitor your blood pressure
regularly, and maintain a record of your blood pressure measurements.
You can then use this record to assist your physician in diagnosing and
maintaining a healthy blood pressure level.
1.1 Features
• Displays:
- Systolic and diastolic pressure
- Pulse rate
• 2 medication alarms
• 200 memories
Readings taken by the blood pressure monitor are equivalent to those
obtained by a trained observer using the cuff and stethoscope method.
Clinical performance were successfully done against ANSI/AAMI SP10
and international protocol, and The B.H.S. which has rated this product
“recommended for clinical and home use”, this is the highest grading
available for blood pressure monitors. Please refer to BHS website http://
www.bhsoc.org

PAD - PulseArrythmia Detection technology displays pulse
irregularities detected during a blood pressure reading. If the PAD
symbol appears on a regular basis (e.g.several times a week with
measurement taken daily,) we advise you to consult your doctor.
Before using the Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor, please read this instruction
manual carefully and keep it in safe place.
1.2 Important Information
Refer to the following sections to learn about important safety instructions
and how to take care of the BIOS Diagnostics™Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor.
1.2A Safety Information
• Self-measurement means control, not diagnosis or treatment. Your
values must always be discussed with your doctor or a physician who is
familiar with your family history.
• If you are undergoing medical treatment and receiving medication,
consult your doctor to determine the most appropriate time to measure
your blood pressure. Never alter the dosages of any medication without
direction from your doctor.
• Your blood pressure depends on several factors, such as age, gender,
weight, and physical condition. It also depends on the environment
and your state of mind at the time of measurement. In general, your
blood pressure is lower when you are asleep and higher when you are
active.Your blood pressure may be higher when recorded at a hospital
or a clinic and may be lower when measured in the relaxing comfort of
your home. Due to these variations, we recommend that you record your

blood pressure regularly at home as well as at your doctor’s clinic.
• Try to record your blood pressure regularly at the same time
of the day and under the same conditions. This will help your
physician detect any extreme variations in your blood pressure
and thus treat you accordingly.
• Morning Hypertension ( > 135 / 85 mm Hg): Recently, several
studies have identified elevated cardiovascular risks (heart
failure, stroke, angina) associated with “morning hypertension”.
There is a typical rise in blood pressure during the physiological
changes from sleep to arising for the day.
• The ideal time to measure your blood pressure is in the morning
just after you wake up, before breakfast and any physical activity,
and in the absence of the urge to urinate. If this is not possible,
try to take the measurements later in the morning, before you
start any physical activity. Relax for a few minutes before you
record your blood pressure.
• Your blood pressure increases or decreases under the following
circumstances:
Blood pressure is higher than normal:
— when you are excited, nervous, or tense
— while taking a bath
— during and after exercise or strenuous physical activity
— when it is cold
— within one hour after meals
— after drinking tea, coffee, or other caffeinated drinks
— after smoking tobacco
— when your bladder is full

Blood pressure is lower than normal:
— after consuming alcohol
— after taking a bath
• The pulse display is not suitable for checking the frequency of
heart pacemakers.
• If you have been diagnosed with a severe arrhythmia or
irregular heartbeat, vascular constriction, liver disorders,
or diabetes, have a cardiac pacemaker, or are pregnant,
measurements made with this instrument should only be
evaluated after consultation with your doctor.
• Take care while handling the batteries in the device. Incorrect
usage may cause battery fluid leakage.
To prevent such accidents, refer to the following instructions:
— Insert batteries with the correct polarity.
— Turn off power after use. Remove and store the batteries
if you are not planning to use the device for an
extended period of time.
— Do not mix different types, brands, or size of batteries.
This may cause damage to the product.
— Do not mix old and new batteries.
— Remove batteries and dispose of them according to the
proper regulations in your area.
— Do not disassemble batteries or expose them to heat or fire.
— Do not short-circuit the batteries.
— Do not use rechargeable batteries.

2. About Blood Pressure
Your blood pressure level is determined in the circulatory center of
your brain.Your nervous system allows your body to adapt or alter
blood pressure in response to different situations.Your body alters
your pulse or heart rate and the width of blood vessels through
changes in muscles in the walls of blood vessels.
Your blood pressure reading is highest when your heart pumps or
ejects blood.This stage is called your systolic blood pressure.
Your blood pressure is lowest when the heart rests (in-between
beats).This is called your diastolic blood pressure.
It is critical to maintain blood pressure values within a “normal”
range in order to prevent cardiovascular diseases. Increased blood
pressure values (various forms of hypertension) have associated long
and medium term health risks.These risks concern the arterial blood
vessels of your body, which are endangered due to constriction caused
by deposits in the vessel walls (arteriosclerosis).A deficient supply of
blood to important organs (heart,brain, muscles) can be the result.
Furthermore, with long-term increased blood pressure values, the
heart will become structurally damaged.
There are many different causes of the appearance of high blood
pressure. We differentiate between common primary (essential)
hypertension, and secondary hypertension.The latter group can be
ascribed to specific organic malfunctions. Please consult your doctor
for information about the possible origins of your own increased blood
pressure values.

2.1 Normal Blood Pressure Values
Blood pressure is too high when, at rest, the diastolic pressure is above
90 mmHg or the systolic blood pressure is over 140 mmHg.
If you obtain readings in this range, consult your doctor immediately.
High blood pressure values over time can damage blood vessels, vital
organs such as the kidney, and your heart.
Should the systolic blood pressure values lie between 140 mmHg
and 160 mmHg or the diastolic blood pressure values lie between 90
mmHg and 95 mmHg, consult your doctor. Regular self-checks will be
necessary.
With blood pressure values that are too low (i.e., systolic values under
105 mmHg or diastolic values under
60 mmHg), consult with your doctor.
Even with normal blood pressure values, a regular self-check with your
blood pressure monitor is recommended.This way you can detect
possible changes in your values early and react appropriately.
Refer to the following table for classifying blood pressure values (units:
mmHg) according to the World Health Organization (WHO):

Category Systolic Blood
Pressure
Diastolic Blood
Pressure
Optimal < 120 < 80
Normal < 130 < 85
High Normal 130 - 139 85 - 89
Hypertension
• Stage 1: Mild 140 - 159 100 - 109
• Stage 2: Moderate 160 - 179 > 110
• Stage 3: Severe > 180 90 - 99
Important for Canadians: The Canadian Hypertension
Education Program (CHEP) recommends that patients with
average measurements of 135mmHg (systolic) or 85mgHg
(diastolic) at home be considered hypertensive. Should your
average readings be in this range, consult your physician.
For further information, see our website
www.biosdiagnostics.com.
If your values are mostly “normal” under resting conditions but
exceptionally high under conditions of physical or psychological stress, it
is possible that you are suffering from so-called ”labile hypertension”. In
any case, please discuss the values with your doctor.
Correctly measured diastolic blood pressure values above 120 mmHg
require immediate medical treatment.

2.2 Common Blood Pressure Questions and
Answers
a) Why is my blood pressure reading always
different?
Your blood pressure changes constantly. It is quite normal for blood
pressure to fluctuate significantly (50 mmHg to 60 mmHg) throughout
the day. Blood pressure is normally lowest at night, but increases
during waking hours when the stress and activities of everyday life are
highest.
mmHg
AM Time PM
Your blood pressure also increases and decreases under the following
circumstances
Blood pressure is higher than normal:
• when you are excited, nervous, or tense
• while taking a bath
• during and after exercise or strenuous physical activity
• when it is cold
• within one hour after meals

• after drinking tea, coffee, or other caffeinated drinks
• after smoking tobacco
• when your bladder is full
Blood pressure is lower than normal:
• after consuming alcohol
• after taking a bath
b) Why is the doctor’s reading different from the
reading taken at home?
Your blood pressure can vary due to the environment (temperature,
nervous condition).When measuring blood pressure at the doctor’s office,
it is possible for blood pressure to increase due to anxiety and tension.
c) Why should I monitor blood pressure at home?
One or two readings will not provide a true indication of your normal
blood pressure. It is important to take regular, daily measurements
and to keep records over a period of time.This information can be used
to assist your physician in diagnosing and preventing potential health
problems.

3. Getting Started
3.1 About the W100
1
4
2
3
6 5
1. ON / OFF ButtON
2. Display
3. BattERy COMpaRtMENt
4. CuFF
5. M-ButtON (MEMORy)
6. tiME ButtON
3.2 About the LCD Screen
The LCD screen displays the systolic and diastolic blood pressure
measurements along with your heart rate. It also displays previously
recorded measurements and the date and time, when the appropriate
button is pressed 7. systOliC valuE
8. DiastOliC valuE
9. pulsE
10. DatE / tiME
11. alaRM tiME
12. stORED valuE
13. hEaRt aRRhythMia
iNDiCatOR
14. pulsE RatE
15. BattERy Display
7
8
9
14
11
15
12 13
10

3.3 Inserting The Batteries
Follow these steps to insert the two “AAA” batteries in
the device.
1. Open the battery compartment cover in the
direction shown.
2. Insert the two “AAA” batteries with the correct
polarity as indicated.
3. Replace the battery compartment cover.
NOTE: Replace the batteries whenever the weak battery mark
shows, the display is dim, or the display does not illuminate
when the power is on. Replace all the batteries at the same
time - it is dangerous to mix old and new batteries.
Contact your local waste disposal authority for instructions on how
to dispose of used batteries. Used batteries can be harmful to the
environment, and should not be thrown out with household trash.
4. Using The Device
This section describes how to get the maximum benefit from your
Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor. Follow the instructions carefully to get
an accurate measurement of your blood pressure and pulse rate.
4.1 Setting the Date and Time
It is important to set the clock before using your blood pressure
monitor, so that the correct time stamp can be assigned to each record
that is stored in the memory.

1.After the new batteries are inserted, the year number flashes in the
display.You can set the year by pressing the M-button .To confirm
and then set the month, press the time button .
2.You can now set the month using the M-button . Press the time
button to confirm and then set the day.
3. Please follow the instructions above to set the day, hour and minutes.
4. Once you have set the minutes and pressed the time button , the
date and time are set and the time is displayed.
5. If you want to change the date and time, press and hold the time
button down for approximately 3 seconds until the year number
starts to flash. Now you can enter the new values as described
above.
4.2 Obtaining Accurate Measurements
Your blood pressure can vary based on numerous factors,
physiological conditions, and your surroundings. Follow these
guidelines to obtain accurate and error-free measurements of your
blood pressure and pulse rate.
4.2A Before Measuring
• Avoid eating, smoking as well as all forms of exertion directly before
the measurement.All these factors influence the measurement
result. Relax by sitting in an armchair in a quiet atmosphere for
about 5 minutes before the measurement

• Always take measurements on the same wrist (normally left) and in
the same posture. Do not switch between right and left arms while
recording your blood pressure as there may be a difference of up to
10 mmHg pressure between the two wrist.
• Attempt to carry out the measurements regularly at the same time
of day, since blood pressure changes during the course of the day.
The ideal time to measure your blood pressure is in the morning
after you wake up, before breakfast and physical activity, and in the
absence of the urge to urinate.
• Rest for 5 minutes sitting quietly and release all the tension in
your body especially the arm muscles before beginning with the
measurement.Remain calm and quiet when the measurement is
in process.Do not speak or move your arm (as well as other body)
muscles during the process.
• With repeated measurements, blood accumulates in the arm, which
can lead to false results.Consecutive blood pressure measurements
should be repeated after at least a 15 second pause or after the arm has
been held up in order to allow the accumulated blood to flow away.
• Do not lean backward or bend your wrist inward while taking a
measurement.
4.2B Fitting the Wrist
a) Remove all accessories (watch,bracelet, etc.) from your left wrist. If
your physician has diagnosed you with poor circulation in your left
arm, use your right wrist.

b) Roll or push up your sleeve to expose the skin.
c) Apply the cuff to your left wrist with your palm facing up and the LCD
display facing you.
d) Fit the cuff comfortably but not too tight.The cuff will cover a wrist
diameter of 13.5 to 21.5 cm (5.25 to 8.5 inches).
e) IMPORTANT: Support your arm in a relaxed position and ensure
that the instrument is at the same height as your heart.
f) Remain seated in a comfortable room temperature for at least 5
minutes, then start the measurement.
g) Press the ON/OFF button to start the measurement.
h) The cuff will now pump up automatically. Relax, do not move and
do not tense your arm muscles until the measurement is displayed.
Breathe normally and do not talk.
i) When the correct pressure is reached, the pumping stops and the
pressure falls gradually. If the required pressure was not reached,
the instrument will automatically pump some more air to the cuff.

j) During the measurement,the heart symbol flashes in the display
and a beep sounds every time a heartbeat is detected.
k) The result, comprising the systolic (7) and the diastolic (8) blood
pressure and the pulse (9) is displayed and longer beep is heard. See
section 3.2 about the LCD screen for explanation of the icons.
l) Remove and switch off the monitor and enter the result in the blood
pressure log book (go to www.biosdiagnostics.com to download a
free log book).
Note: The monitor does switch off automatically after approximately
one minute).
You can stop the measurement at any time by pressing the ON/OFF button
(e.g. if you feel uneasy or an unpleasant pressure sensation).
4.3 Data Memory
At the end of a measurement, this instrument automatically stores
each result,including date and time.
Viewing the stored values
• Press the M-button briefly, when the instrument is switched off.
The display first shows << M >> and then a value, e.g.
<< M17 >>. This means that there are 17 values in the memory.
The instrument then switches to the last stored result.
• Press the M-button again displays the previous value. Pressing
the M-button repeatedly enables you to toggle between one
stored value and another.

Memory Full
• When the memory has stored 200 results, the display shows
<< Full M >> after a measurement. From this point onwards, a
new measured value is stored by overwriting the oldest value.
Clear all Values
• If you are sure that you want to permanently remove all stored
values, hold down the M-button (the instrument must have
been switched off beforehand) until << CL >> appears and then
release the button.To permanently clear the memory, press the
M-button while << CL >> is flashing. Individual values cannot
be cleared.
4.4 Setting the Alarm Function
This instrument allows you to set 2 alarm times at which an alarm signal
will then be triggered.This can be a useful aid,for instance as a reminder
to take medication.
a) To set an alarm time, without releasing, push the time button “ ”,
followed by the M button , do not release until the bell symbol
“ ” appears in the bottom left of the display. Then release both
buttons. The flashing <<1>> in the display indicates that the first
alarm time can now be set.
b) Press the time button to set the hours - the hour display flashes
and pressing the M-button allows you to set the alarm hour.To
confirm, press the time button .

c) The minute display will now flash.The minutes can be set using the
M-button .To confirm, press the time button .
d) The bell symbol will now flash . Use the M-button to select
whether the alarm time is to be active or inactive .To confirm,
press the time button .
• To set a second alarm time, proceed as above but if the << 1 >>
flashes, press the M-button to select << 2 >> and confirm with
the time button .
• An active alarm time is indicated by the bell symbol in the display .
• The alarm will sound at the set time every time.
• To switch-off the alarm when it is sounding, press the ON / OFF
button .
• To permanently switch off the alarm, proceed as above and select the
crossed-out bell symbol .This will then disappear from the display.
• The alarm times must be re-entered each time the batteries are
replaced.
5. PAD - Pulse Arrhythmia Detector
This symbol indicates that certain pulse irregularities
were detected during the measurement. In this case, the result
may deviate from your normal basal blood pressure – repeat the
measurement.In most cases, this is no cause for concern. However, if
the PAD symbol appears on a regular basis (e.g. several times a week
Other manuals for W100
1
Table of contents
Other BIOS Blood Pressure Monitor manuals