NOTE: Read the entire instruction manual before starting the
installation.
This symbol →indicates a change since the last issue.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS .....................................................1
INTRODUCTION ..........................................................................1
INSTALLATION CONSIDERATIONS .......................................1
Inspect Equipment ....................................................................1
Select Location..........................................................................2
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION ....................................................2
INSTALLATION ...........................................................................3
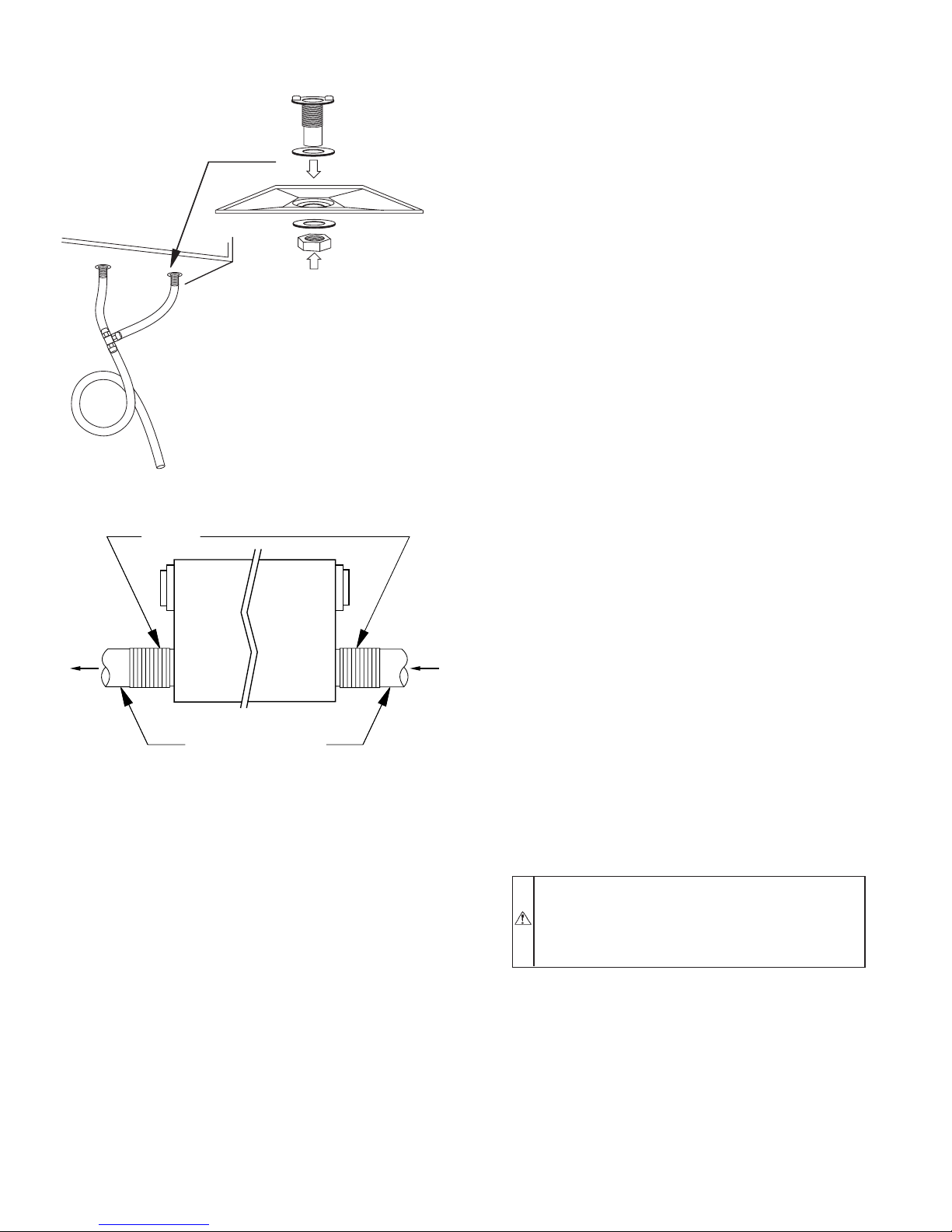
Mount Unit................................................................................3
Independent System Application..............................................3
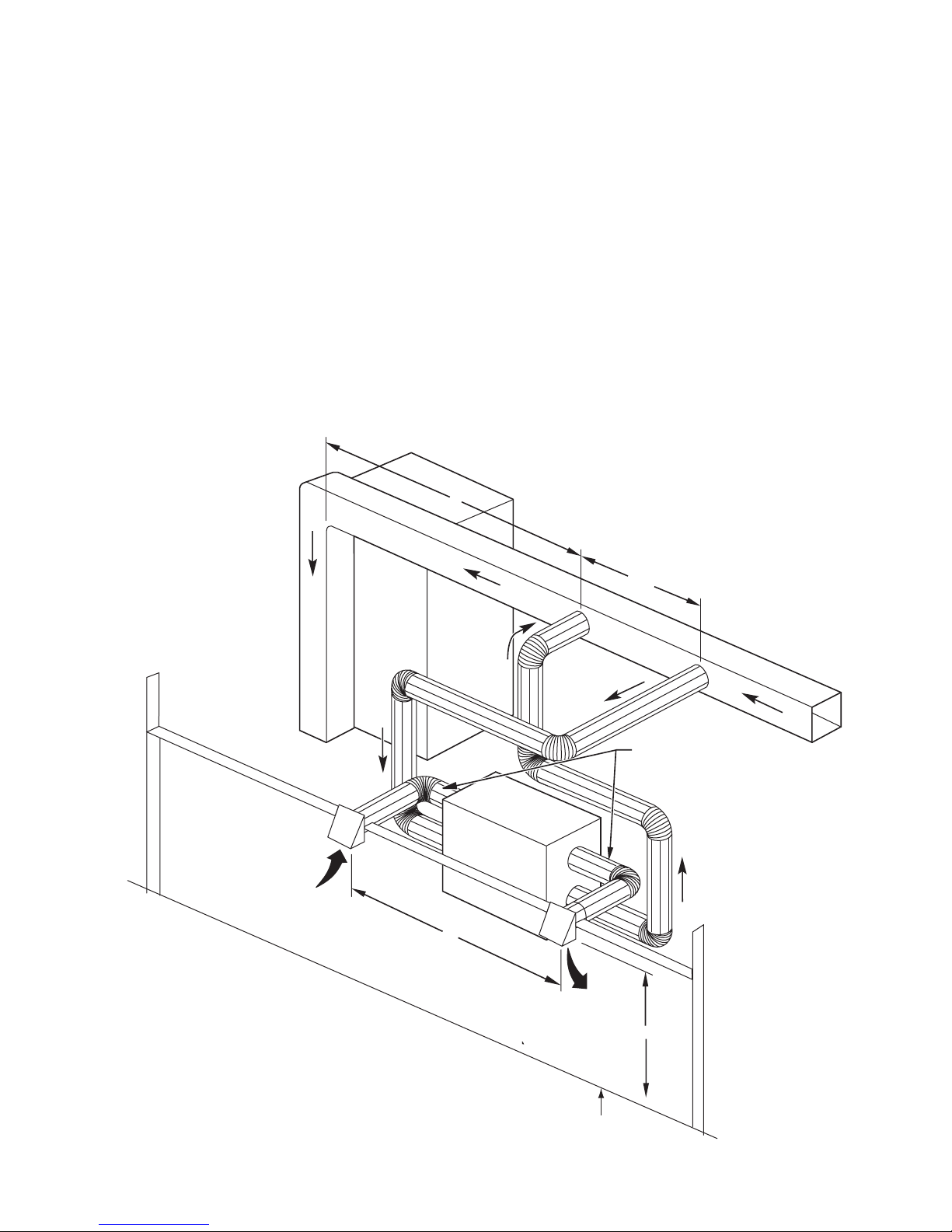
Forced-Air Application.............................................................3
Connect Ducts to ERV .............................................................3
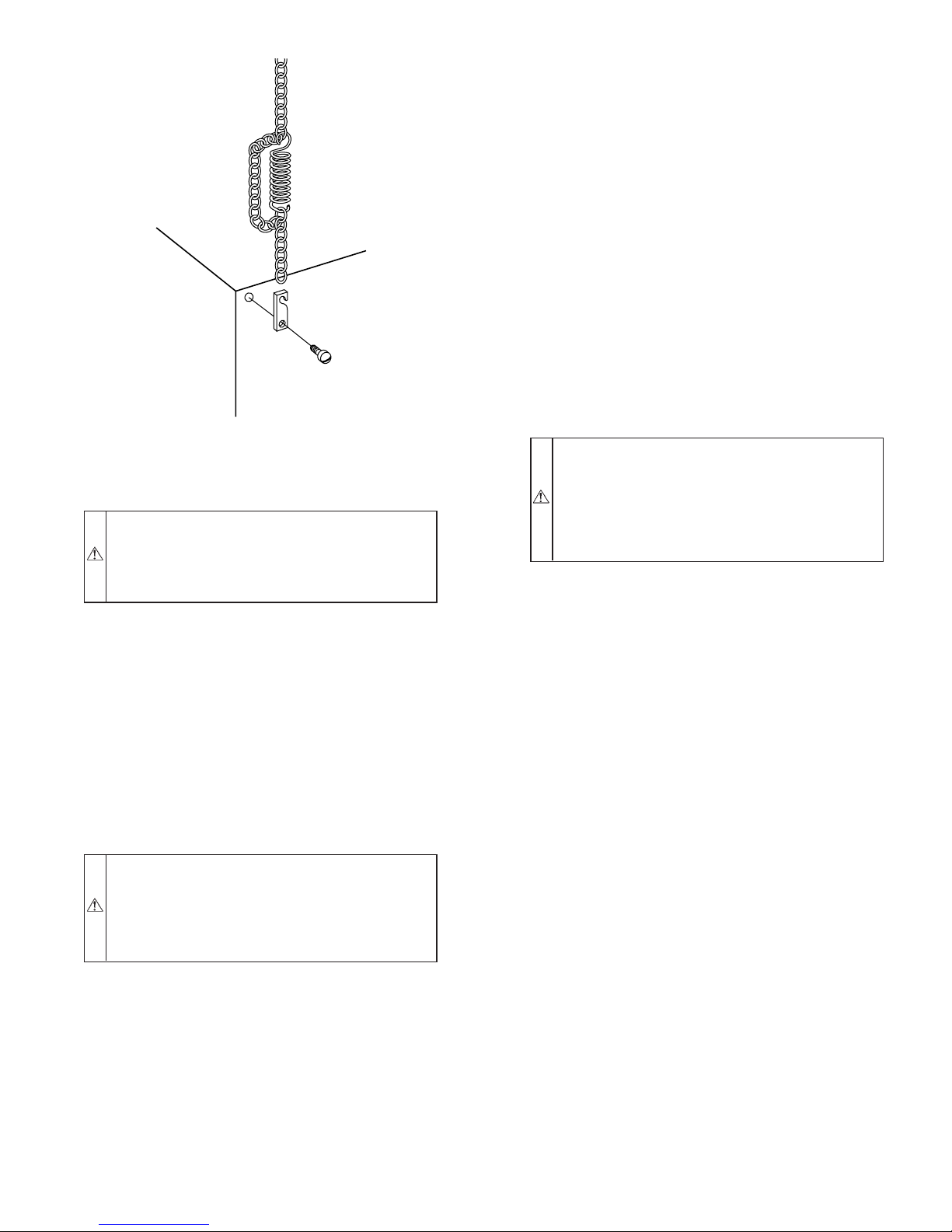
Locate and Install Exterior Hoods ...........................................3
Condensate Drain......................................................................4
Wall Control..............................................................................4
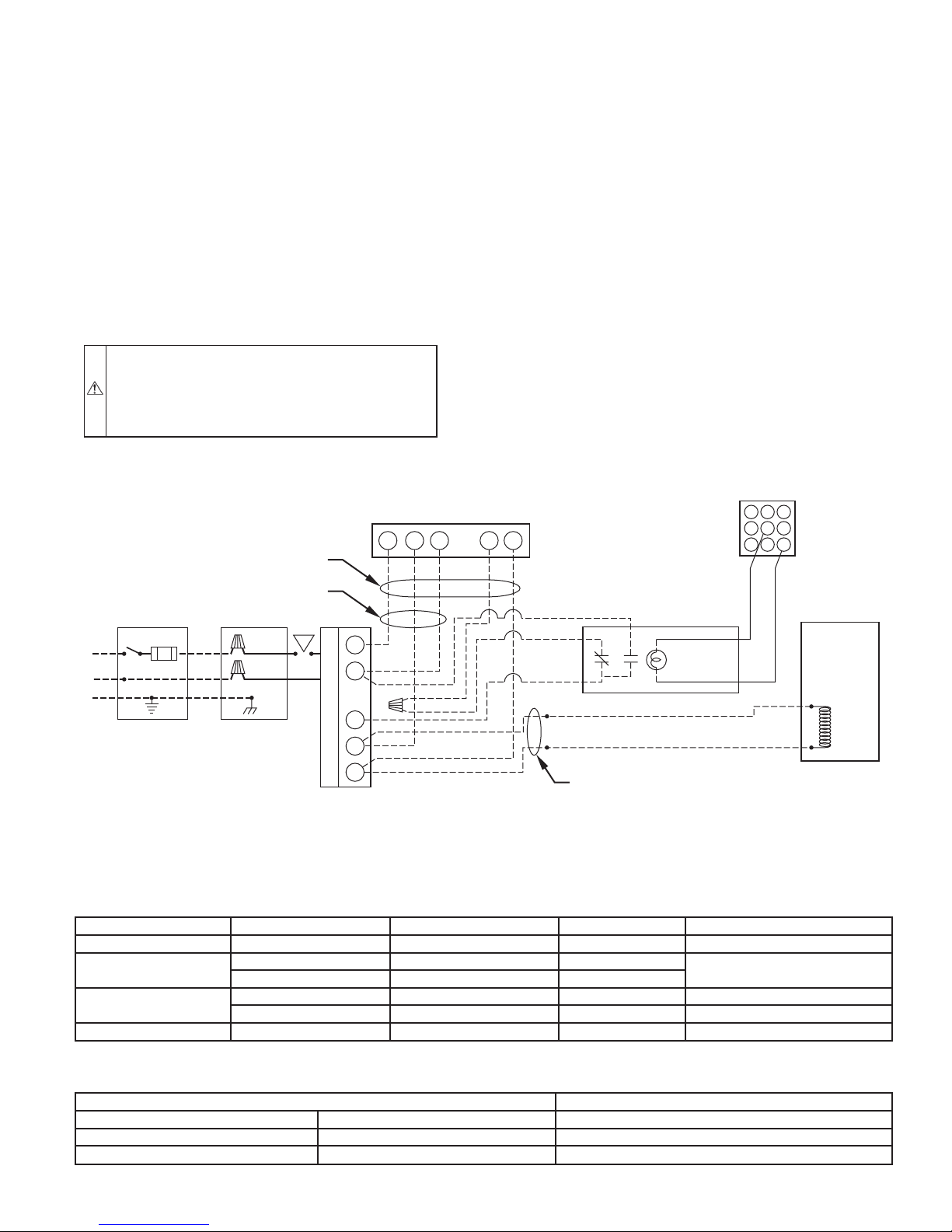
ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS ..................................................4
115–vac Wiring.........................................................................4
12–vdc Wiring ..........................................................................4
ACCESSORIES..............................................................................4
Interlock Relay..........................................................................4
20 Minute Timer.......................................................................5
60 Minute Adjustable Timer ....................................................5
BALANCING ERV .......................................................................5
Balancing Dampers...................................................................6
Flow Collar ...............................................................................6
CONTROL BOARD OPERATION ..............................................8
Board Function..........................................................................8
Defrost.......................................................................................8
OFF and INTERMITTENT/OFF Mode...................................8
High-Speed Air Exchange ........................................................8
Low-Speed Air Exchange.........................................................9
CARE AND MAINTENANCE.....................................................9
Door.........................................................................................10
Filter ........................................................................................10
Blower Motor and Wheel.......................................................10
Cleaning Core .........................................................................10
TROUBLESHOOTING ...............................................................10
Wall Control............................................................................10
Control Board..........................................................................10
Blower Motor..........................................................................10
Blower Speed Selection..........................................................11
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
Installation and servicing of this heating equipment can be
hazardous due to mechanical and electrical components. Only
trained and qualified personnel should install, repair, or service
heating equipment.
Untrained personnel can perform basic maintenance functions
such as cleaning and replacing air filters. All other operations must
be performed by trained service personnel. When working on this
equipment, observe precautions in the literature, on tags, and on
labels attached to or shipped with the unit and other safety
precautions that may apply.
Follow all safety codes. Installation must be in compliance with
local and national building codes. Wear safety glasses and work
gloves. Have a fire extinguisher available during start-up and
adjustment procedures and service calls.
Recognize safety information. This is the safety-alert symbol .
When you see this symbol on the furnace and in instructions or
manuals, be alert to the potential for personal injury.
Understand the signal words DANGER, WARNING, or CAU-
TION. These words are used with the safety-alert symbol. DAN-
GER identifies the most serious hazards which will result in severe
personal injury or death. WARNING signifies a hazard that could
result in personal injury or death. CAUTION is used to identify
unsafe practices which would result in personal injury or product
or property damage. NOTE is used to highlight suggestions which
will result in enhanced installation, reliability or operation.
INTRODUCTION
The ERVBBLHU Energy Recovery Ventilator (ERV) is used to
exchange indoor stale air with outside fresh air. The ERV unit is
equipped with a special energy recovery core which transfers both
sensible and latent heat with the fresh incoming air. The cross-flow
design core allows entering and leaving air streams to transfer heat
energy without mixing (See Fig. 14).
The model ERVBBLHU is available in 2 sizes with airflow ranges
of 64–152 CFM, and 117–214 CFM. The design of this unit is
horizontal. Special attention should be given to duct application,
balancing the ERV, and locating unit for easy access and routine
maintenance.
INSTALLATION CONSIDERATIONS
I. INSPECT EQUIPMENT
Move carton to final installation location. Remove ERVBBLHU
from carton taking care not to damage unit. Remove all packaging
and inspect unit for damage. Remove parts bag from inside unit.
File claim with shipping company if shipment is damaged or
incomplete. Check to make sure ERV unit matches Fig. 2.
Fig. 1–ERVBBLHU Energy Recovery Ventilator
A00092
Installation, Start-Up, and
Operating Instructions
ERVBBLHU
ENERGY RECOVERY VENTILATOR
Cancels: II ERV-64–2 II ERV-64–3
4–05
—1—