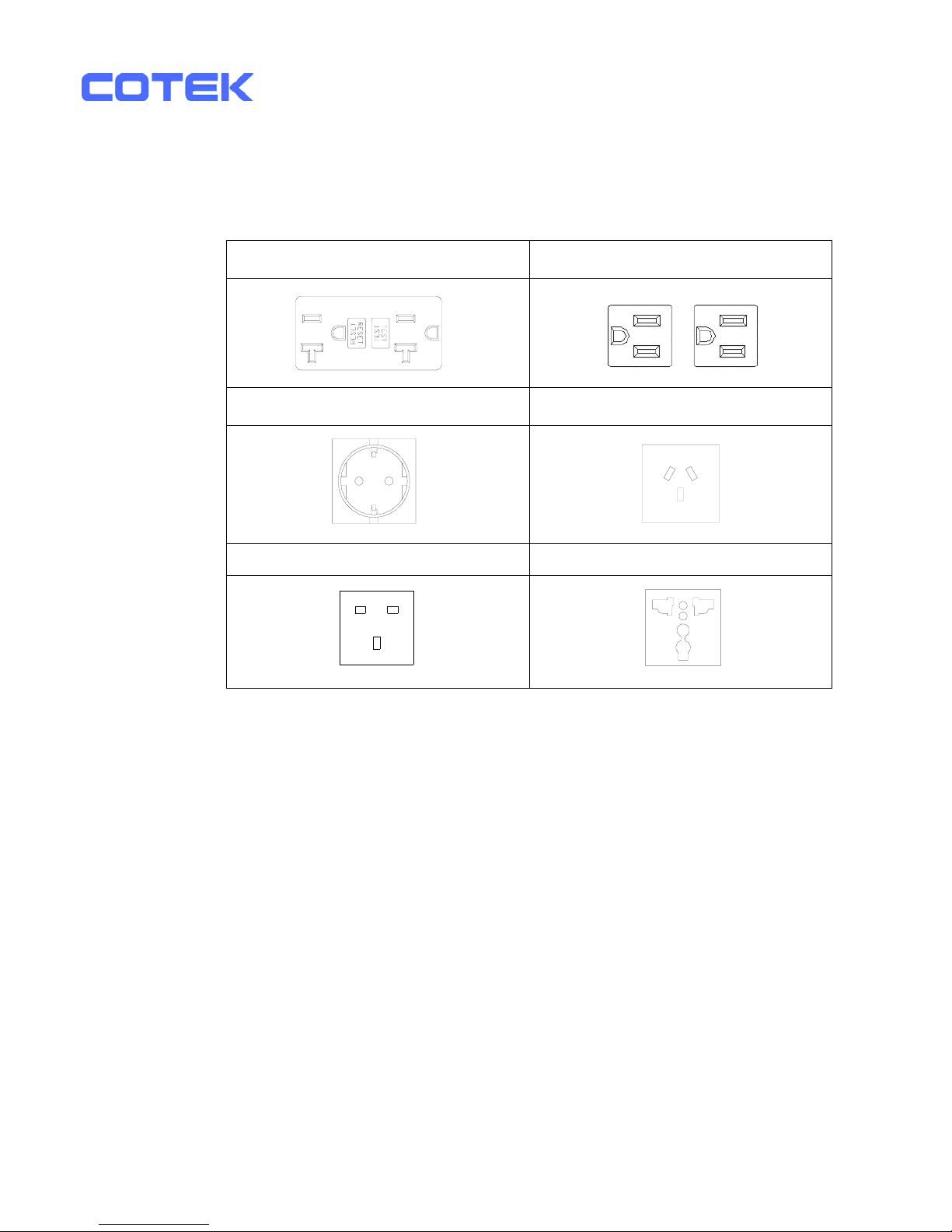
Cotek S1500-112 User manual
Other Cotek Inverter manuals

Cotek
Cotek SR1000 User manual

Cotek
Cotek SP Series Reference manual

Cotek
Cotek S600 Series User manual

Cotek
Cotek S600 Series User manual

Cotek
Cotek SK700-112 User manual

Cotek
Cotek S1500-112 User manual

Cotek
Cotek SP Series User manual

Cotek
Cotek ST Series User manual

Cotek
Cotek SK120 Series User manual

Cotek
Cotek SR1000 User manual

Cotek
Cotek S Series User manual

Cotek
Cotek SP-700-148 User manual

Cotek
Cotek SD2500-112 User manual

Cotek
Cotek SK120 Series User manual

Cotek
Cotek SK700-112 User manual

Cotek
Cotek SE350 series User manual

Cotek
Cotek SR series User manual

Cotek
Cotek S1500-112 User manual

Cotek
Cotek SE200-124 User manual

Cotek
Cotek SK700-112 User manual
Popular Inverter manuals by other brands

BARRON
BARRON EXITRONIX Tucson Micro Series installation instructions

Baumer
Baumer HUBNER TDP 0,2 Series Mounting and operating instructions

electroil
electroil ITTPD11W-RS-BC Operation and Maintenance Handbook

Silicon Solar
Silicon Solar TPS555-1230 instruction manual

Mission Critical
Mission Critical Xantrex Freedom SW-RVC owner's guide

HP
HP 3312A Operating and service manual