2.11.5.5 CONNECTION TO BASIC ETHERNET...................................................................40
2.11.5.6 CONNECTION TO COMPANY ETHERNET INFRASTRUCTURE.........................41
2.11.5.7 CONNECTION TO THE INTERNET........................................................................42
2.11.5.8 FIREWALL CONFIGURATION FOR INTERNET ACCESS....................................43
2.11.5.9 ETHERNET USED FOR THE DSE2610 REMOTE DISPLAY.................................44
2.11.6 MSC (MULTI-SET COMMUNICATIONS) LINK ..............................................................45
2.11.7 CAN PORT (REDUNDANT MSC)...................................................................................46
2.11.8 ECU PORT (J1939).........................................................................................................48
2.11.8.1 CAN SUPPORTED ENGINES.................................................................................48
2.11.8.2 CAN SUPPORTED AVRS .......................................................................................49
2.11.8.3 J1939-75 ..................................................................................................................50
2.11.8.4 CONFIGURABLE CAN............................................................................................51
2.11.9 DSENET®(EXPANSION MODULES).............................................................................52
2.11.9.1 DSENET® USED FOR MODBUS ENGINE CONNECTION ....................................53
2.12 SOUNDER ..........................................................................................................................54
2.12.1 ADDING AN EXTERNAL SOUNDER .............................................................................54
2.13 ACCUMULATED INSTRUMENTATION ............................................................................54
2.14 DIMENSIONS AND MOUNTING........................................................................................55
2.14.1 DIMENSIONS..................................................................................................................55
2.14.2 PANEL CUTOUT.............................................................................................................55
2.14.3 WEIGHT..........................................................................................................................55
2.14.4 FIXING CLIPS.................................................................................................................56
2.14.5 CABLE TIE FIXING POINTS...........................................................................................57
2.14.6 SILICON SEALING GASKET..........................................................................................57
2.15 APPLICABLE STANDARDS .............................................................................................58
2.15.1 ENCLOSURE CLASSIFICATIONS.................................................................................60
2.15.1.1 IP CLASSIFICATIONS.............................................................................................60
2.15.1.2 NEMA CLASSIFICATIONS......................................................................................60
3INSTALLATION.................................................................................................61
3.1 USER CONNECTIONS..........................................................................................................61
3.2 CONNECTION DESCRIPTIONS ...........................................................................................62
3.2.1 DC SUPPLY, E-STOP INPUT, DC OUTPUTS & CHARGE FAIL INPUT.......................62
3.2.2 ANALOGUE SENSOR INPUTS & CAN..........................................................................63
3.2.3 MPU, ECU, MSC & DSENET®........................................................................................64
3.2.4 OUTPUT C & D, & V1 (GENERATOR) VOLTAGE & FREQUENCY SENSING ............65
3.2.5 V2 (BUS) VOLTAGE & FREQUENCY SENSING...........................................................65
3.2.6 CURRENT TRANSFORMERS........................................................................................66
3.2.6.1 CT CONNECTIONS.................................................................................................67
3.2.7 DIGITAL INPUTS ............................................................................................................67
3.2.8 RS485..............................................................................................................................68
3.2.9 RS232..............................................................................................................................69
3.2.10 USB SLAVE (PC CONFIGURATION) CONNECTOR ....................................................70
3.2.11 USB HOST (DATA LOGGING) CONNECTOR...............................................................70
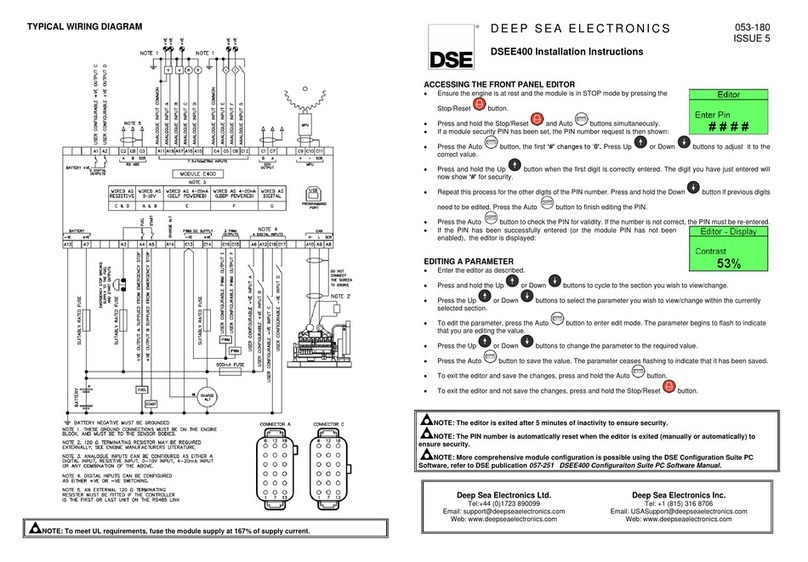
3.3 TYPICAL WIRING DIAGRAM................................................................................................71
3.3.1 3 PHASE 4 WIRE WITH RESTRICTED EARTH FAULT................................................72
3.3.2 EARTH SYSTEMS..........................................................................................................73
3.3.2.1 NEGATIVE EARTH..................................................................................................73
3.3.2.2 POSITIVE EARTH ...................................................................................................73
3.3.2.3 FLOATING EARTH..................................................................................................73
3.3.3 TYPICAL ARRANGEMENT OF DSENET®.....................................................................74
3.3.4 TYPICAL ARRANGEMENT OF MSC LINK ....................................................................75
3.4 ALTERNATE TOPOLOGY WIRING DIAGRAMS .................................................................76
3.4.1 SINGLE PHASE (L1 & N) 2 WIRE WITH RESTRICTED EARTH FAULT......................76
3.4.2 SINGLE PHASE (L1 & N) 2 WIRE WITHOUT EARTH FAULT ......................................77
3.4.3 SINGLE PHASE (L1 & L2) 3 WIRE WITH RESTRICTED EARTH FAULT.....................78
3.4.4 SINGLE PHASE (L1 & L2) 3 WIRE WITHOUT EARTH FAULT.....................................79
3.4.5 SINGLE PHASE (L1 & L3) 3 WIRE WITH RESTRICTED EARTH FAULT.....................80
3.4.6 SINGLE PHASE (L1 & L3) 3 WIRE WITHOUT EARTH FAULT.....................................81
3.4.7 2 PHASE (L1 & L2) 3 WIRE WITH RESTRICTED EARTH FAULT................................82