SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Although all valve-regulated batteries have the elec-
trolyte immobilized within the cell, the electrical hazard
associated with batteries still exists. Work performed
on these batteries should be done with the tools
and the protective equipment listed below. Valve-
regulated battery installations should be supervised by
personnel familiar with batteries and battery safety
precautions.
Protective Equipment
To assure safe battery handling, installation and main-
tenance, the following protective equipment should be
used.
1. Safety glasses or face shield
2. Acid-resistant gloves
3. Protective aprons
4. Proper lifting devices
5. Tools with insulated handles
Procedures
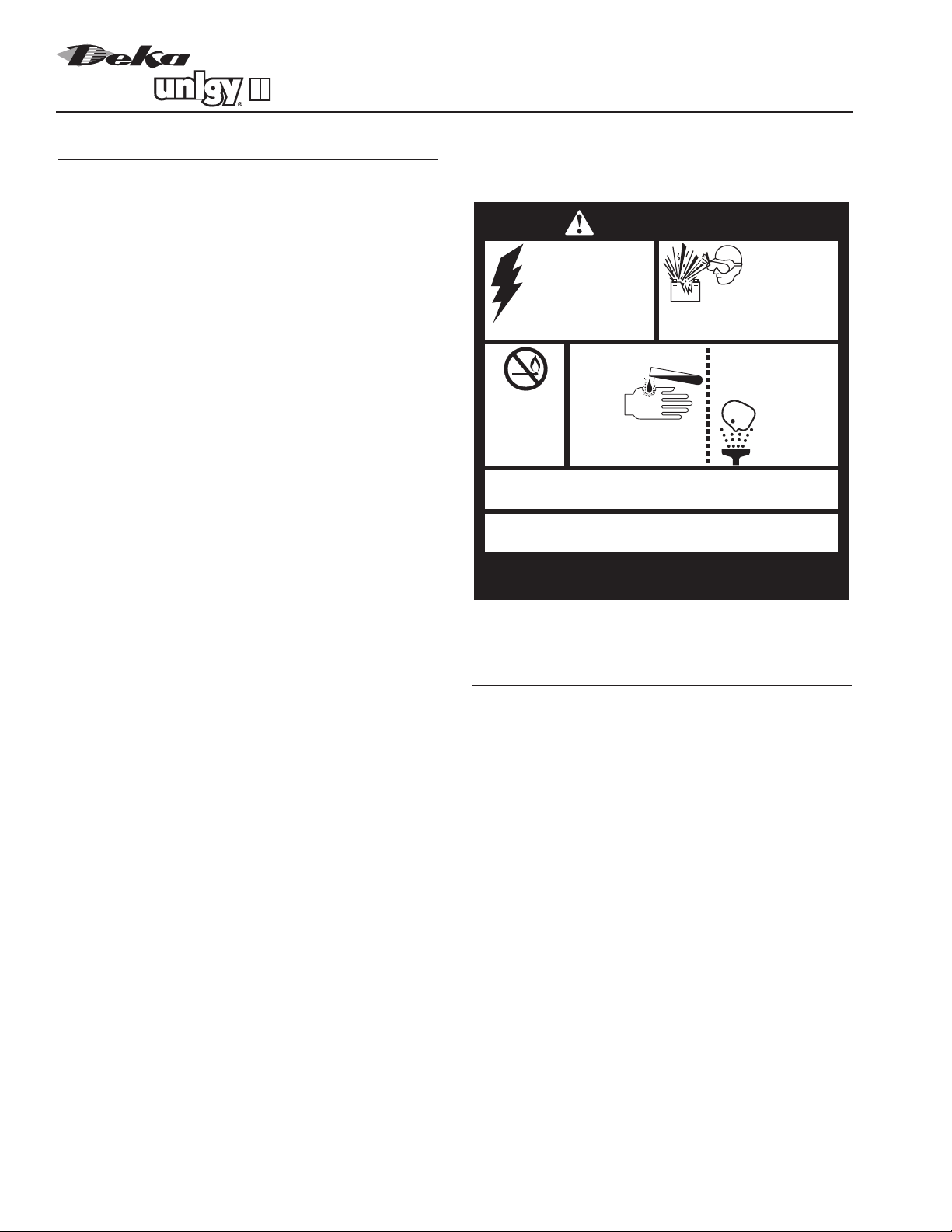
(Always wear safety glasses or face shield when
working on or near batteries. Refer to Fig. 1-1 on
pg. 2.)
The following safety procedures should be followed
during installation:
1.These batteries are sealed and contain no free
electrolyte. Under normal operating conditions, they
do not present any acid danger. However, if the
battery jar or cover is damaged, acid could be
present. Sulfuric acid is harmful to the skin and
eyes. Flush affected area with water immedi-
ately and consult a physician if splashed in the
eyes.
2. Prohibit smoking and open flames, and avoid
arcing in the immediate vicinity of the battery.
3. Do not wear metallic objects, such as jewelry,
while working on batteries.
4. Keep the top of the battery dry and clear of tools
and other foreign objects.
5. Provide adequate ventilation and follow recom-
mended charging voltages.
6. Refer to Material Safety Data Sheet for proper extin-
guishing mehod (See Appendix B, Sect. 4, pg 15.).
7. Never remove or tamper with the pressure relief
valves.Warranty void if vent valve is removed.
8. Inspect all flooring and lifting equipment for func-
tional adequacy. Specifically review floor-loading
capacity.
9. Adequately secure battery modules to the floor.
10. Connect support structures to ground system in
accordance with applicable codes.
RECEIVING & STORAGE
Receiving Inspection
Upon receipt of the battery and at the time of unload-
ing, each package should be visually inspected for
damage. If damage is evident, a more detailed inspec-
tion of the entire shipment should be conducted and
noted on the bill of lading. Record receipt date and
inspection data, and notify the carrier of any damage.
Unpacking
1. Always wear eye protection.
2. Check for visible defects.
3. Check the contents of the package against the
packing list. Report any missing parts or shipping
damage to your East Penn agent or East Penn Mfg.
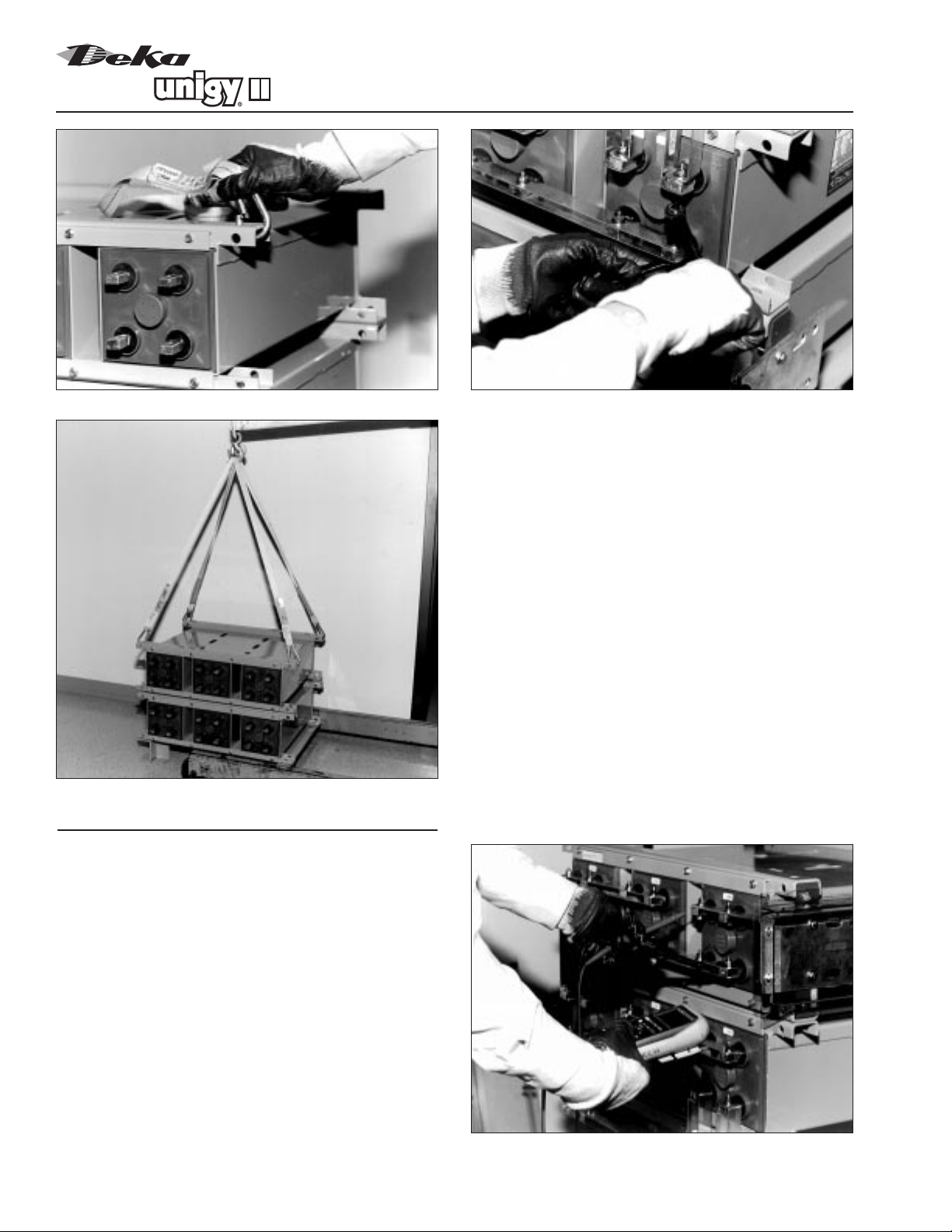
Co. immediately. (See Fig. 2-1 and 2-2 on pg. 3.)
4. Never lift the batteries by the terminal posts. Always
lift batteries by the module mounting holes with the
lifting straps provided. (See Fig. 3-2, pg. 8.)
5.When lifting batteries, the proper equipment is
needed such as a forklift or a portable crane.
Always check the lifting capacities of the equipment
being used and never lift more than one module at
a time by the module mounting holes.
EYES.
CONNECTORS.