14
WATER AND WATER CONDITIONING, continued
Colloidal and inorganically bound iron is o erric
or ferrous form that will not lter or exc hange out of
water. In some instances, treatment may improve
colloidal iron water, but always CONSULT A QUALI-
FIED WATER CHEMISTRY LAB before attempting
to treat it. Colloidal iron water usually has a yellow
appearance when drawn. After standing for several
hours, the color persists and the iron does not settle,
but remains suspended in the water.
Iron in water causes stains on clothing and plumbing
xtures. It negatively aects the taste o ood, drink-
ing water, and other beverages.
ACIDITY or acid water is caused by carbon dioxide,
hydrogen sulde, and sometimes industrial wastes.
It is corrosive to plumbing, plumbing xtures, water
heaters, and other water using appliances. It can
also damage and cause premature failure of seals,
diaphragms, etc., in water handling equipment.
A chemical analysis is needed to measure the de-
gree of acidity in water. This is called the pH of water.
Water testing below 6.9 pH is acidic. The lower the
pH reading, the greater the acidity. A neutralizer l-
ter or a chemical feed pump are usually recom-
mended to treat acid water.
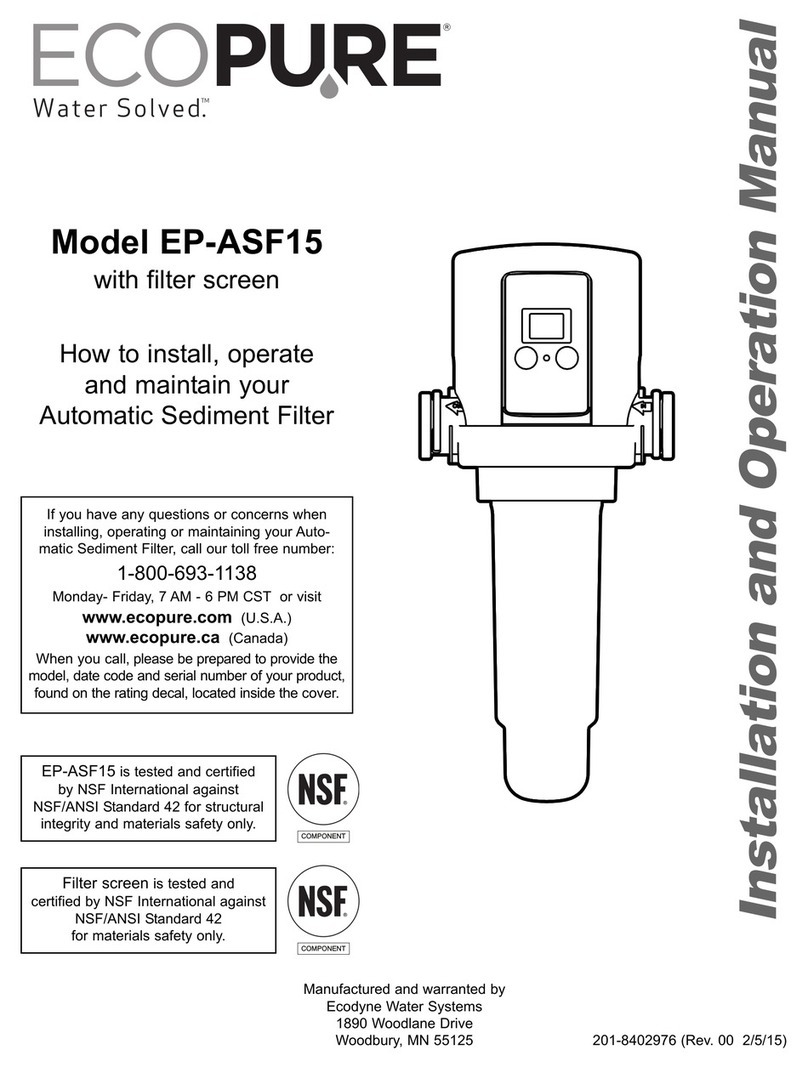
SEDIMENT is ne, foreign material particles sus-
pended in water. This material is most often clay or
silt. Extreme amounts of sediment may give the wa-
ter a cloudy appearance. A sediment lter normally
corrects this condition.
HOW THE WATER SOFTENER WORKS
SOFT WATER SERVICE, AND REGENERATION, see illustrations, page 15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SERVICE
When the softener is providing soft water, it is called
“Service”. During service, hard water ows from the
house main water pipe into the softener. Inside the
softener resin tank is a bed made up of thousands
of tiny, plastic resin beads. As hard water passes
through the bed, each bead attracts and holds the
hardness minerals. This is called ion-exchanging. It
is much like a magnet attracting and holding metals.
Water without the hardness minerals (soft water)
ows from the softener and to the house pipes.
After a period of time, the resin beads become
coated with hardness minerals and they have to be
cleaned. This cleaning is called regeneration, or re-
charge. The Ultra demand timer automatically de-
termines when regenerations occur. Regeneration
is started at 2:00 a.m. (factory setting) by the soften-
er timer, and consists of 5 stages or cycles. These
are: FILL, BRINING, BRINE RINSE, BACKWASH,
and FAST RINSE.
REGENERATION
FILL: Salt, dissolved in water, is called brine. Brine
is needed to clean the hardness minerals from the
resin beads. To make the brine, water ows into the
salt storage area during the ll stage as shown on
page 15.
BRINING: During brining, brine travels from the
salt storage area, into the resin tank. Brine is the
cleaning agent needed to remove the hardness min-
erals from the resin beads. The hardness minerals,
and brine are discharged to the drain.
The nozzle and venturi create a suction to move the
brine, maintaining a very slow rate to get the best
resin cleaning with the least salt.
BRINE RINSE: After a pre--measured amount of
brine is used, the brine valve closes. Water contin-
ues to ow in the same path as during brining, ex-
cept for the discontinued brine ow. Hardness min-
erals and brine ush from the resin tank, to the drain.
BACKWASH: During backwash, water travels up
through the resin tank at a fast ow rate, ushing ac-
cumulated iron, dirt, and sediments from the resin
bed and to the drain.
FAST RINSE: Backwash is followed by a fast ow
of water down through the resin tank. The fast ow
ushes brine from the bottom of the tank, and packs
the resin bed.
After fast rinse, the softener returns to soft water
service.
AUTOMATIC HARD WATER BYPASS DURING REGENERATION
For emergency needs, hard water is available to
the home during the regener ation cycles. However,
you should avoid using HOT water because the wa-
ter heater will rell with the hard water.
4