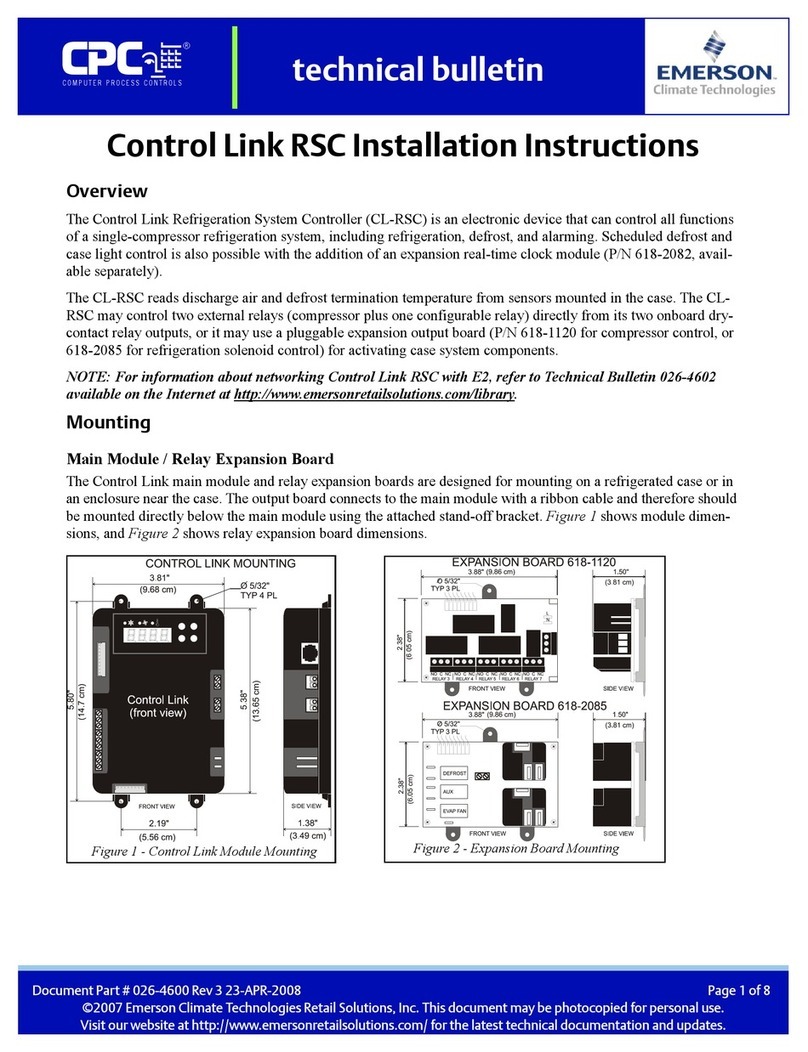
Instruction Manual
D100304X012
656 Actuator
June 2017
3
Maximum Pressure Limitations
The casing and diaphragm of 656 actuators are pressure operated. This air pressure provides energy to compress the
spring, to stroke the actuator, and to seat the valve. The following explanations describe the maximum pressure limits
for an actuator. Refer to the nameplate or table 1 for maximum values for your actuator.
D Maximum Casing Pressure for Actuator Sizing: This is the maximum pressure that can be applied at less than full
travel of the actuator. If this stroking pressure is exceeded before the upper diaphragm plate contacts the travel
stop, damage to the stem or other parts might result.
D Maximum Excess Diaphragm Pressure: Additional pressure may be added when the actuator is at full travel. If the
Maximum Excess Diaphragm Pressure is exceeded, damage to the diaphragm or diaphragm casing might result.
Because the actuator has traveled its specified travel, and the diaphragm head is physically stopped from movement,
the energy from any additional air pressure is transmitted to the diaphragm and diaphragm casings. The amount of air
pressure that can be added once the actuator has traveled to the stops is limited by the resultant adverse effects that
may occur. Exceeding this limiting factor could result in leakage or casing fatigue due to the deformation of the upper
diaphragm casing.
D Maximum Diaphragm Casing Pressure: If the Maximum Diaphragm Casing Pressure is exceeded, damage to the
diaphragm, diaphragm casing, or actuator might result.
Installation
When an actuator and valve are shipped together, the actuator is normally mounted on the valve. Follow the valve
instructions when installing the valve and actuator in a pipeline. If the actuator is shipped separately, or if it is
necessary to mount the actuator on the valve, four holes have been tapped into the yoke boss to anchor it to a
mounting bracket.
WARNING
Always wear protective gloves, clothing, and eyewear when performing any maintenance operations to avoid personal
injury.
To avoid personal injury or property damage caused by bursting of pressure retaining parts, be certain the diaphragm
casing pressure does not exceed the limits listed in the Specifications table. Use pressure relieving or pressure limiting
devices to prevent the diaphragm casing pressure from exceeding these limits.
If installing into an existing application, also refer to the WARNING at the beginning of the Maintenance section in this
instruction manual.
To make the stem connection, follow the appropriate assembly step 10 in the Maintenance section. Standard actuator
sizes 30 and 40 have mounting holes tapped 3/8 inch UNC, and the size 60 mounting holes are tapped 1/2 inch UNC.
A 1/4 NPT loading pressure connection is located in the top of the upper diaphragm case. Using either pipe or tubing,
connect either the loading pressure connection or valve positioner input connection (if a valve positioner is furnished,
the loading pressure connection to the actuator will be made at the factory) to the output pressure connection on the
controller. Keep the length of the pipe or tubing as short as possible to avoid transmission lag in the control signal.
Adjustment
When the actuator is completely installed and connected to the controller, it should be checked for correct travel,
freedom from friction and correct PDTC or PDTO action.