8L4442
6.4 Nut and Bolt Loosening Information
•Be aware that more torque is usually required to
loosen a fastener than to tighten it.
•Rusted fasteners (humidity corrosion) may require
up to twice the torque required for tightening.
•Fasteners that are corroded due to contact with
sea water or chemicals will require up to two and a
half times the torque required for tightening.
•Heat corrosion requires up to three times the
torque required for tightening.
Do not apply more than 75 percent of the
wrench’s maximum torque when loosening nuts or
bolts. Avoid making sudden start-stop movements
(“shock loading”). Failure to observe these precautions
may cause a catastrophic failure of the wrench to occur,
and wrench components under high tension could
become dangerous projectiles. Serious personal injury
could result.
6.5 Loosening Procedure
•Apply penetrating oil to the threads. Allow the oil
to soak.
•Set the pump to 10,000 psi (Loosening torque
equals about 100% of tightening torque).
•Change the drive and the reaction arm to the
loosening mode, ensuring the reaction arm abuts
squarely o a solid reaction point.
• Start the pump.
•Operate the pump until the nut has been loosened.
If the bolt / nut does not loosen with the
above procedure, it is an indication that you require the
next larger size DSX to loosen the bolt
7.0 MAINTENANCE
Lubrication frequency depends on factors known only
to the user. The amount of contaminants in the working
area is one factor. Wrenches used in a clean room
environment will obviously require less maintenance
than wrenches used outdoors and dropped in loose dirt
or sand.
1. When lubrication is required, lubricate all moving
parts.
2. Springs are used for the drive pawl assembly.
These springs can be replaced if necessary.
3. If the cylinder requires disassembly, it is
recommended that the cylinder seals be replaced
at the same time. Seal kits are readily available.
4. Hoses should be checked for cracks and leaks
before, and after each job. Hydraulic fittings can
become plugged with dirt and should be flushed
periodically.
5. Fittings should be kept clean and not allowed to
be dragged along the ground or floor as even small
particles of dirt can cause the internal valves to
malfunction.
All structural parts on the tools should be inspected at
least once a year to determine if there are any cracks,
chips, or deformities.
Preventative maintenance can be performed by the
user.
Full maintenance must be performed only by an Enerpac
authorized service center or a qualified and experienced
technician.
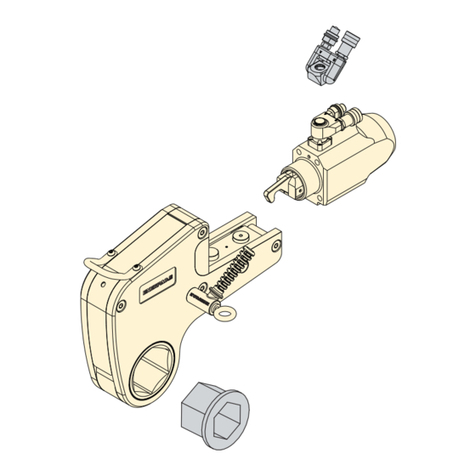
7.1 Preventative Maintenance (Fig.9/ Fig.10)
1. Check tightness of swivel assembly retaining
screws (40) and piston sleeve (7) (see Section 7.2).
2. Pressurize the wrench to 10,000 psi [690 bar]
pressure (in both advance and retract), and check
for any signs of leakage.
3. Relieve pressure and disconnect hydraulic hoses.
4. Clean all exposed components with a mild solvent.
5. Remove the shroud screws (11) and remove the
shroud (27). The tether (37) will continue to link the
shroud to the drive release assembly. To remove
the tether unscrew the round screw, slide o the
washer, and remove the tether line.
6. Remove the square drive (8) and drive retaining
release assembly (12, 13, 14) along with the two
bushes and drive retainer (9, 26)
7. Disengage the two access plugs (21), and slide out
the rod end pin (18). The drive plate (3) can now
separated from the wrench body (1).
8. Remove the ratchet (4), pawl (5) and pawl wave
springs (6).
9. Clean all components with a mild solvent.
10. Inspect all parts for damage. Any damaged
components must be replaced.
11. Dry all components. Apply a thin coat of
molybdenum disulphide grease in the areas shown
in Figure 10.
Be sure that the ratchet, drive plate, pawl,
pawl wave spring, square drive, and access plugs are
correctly installed in the following step. Ensure that the
square drive is inserted through the drive plate and rod
end of the piston assembly before installing the access
plugs. Failure to install these parts correctly will result in
component damage. Refer to figures 9 and 10.
12. Connect the wrench to the pump.
13. With wrench not on nut or bolt, check operation
at a nominal pressure to make sure the piston
advances and retracts freely.
14. Release the pressure and make sure that the piston
fully retracts.