EnOcean EASYFIT EMDCB User manual

USER MANUAL
EMDCB –BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY MOTION AND ILLUMINATION SENSOR
© 2019 EnOcean | www.enocean.com EMDCB User Manual | v1.3 | August 2019 | Page 1/67
Patent protected:
WO98/36395, DE 100 25 561, DE 101 50 128,
WO 2004/051591, DE 103 01 678 A1, DE 10309334,
WO 04/109236, WO 05/096482, WO 02/095707,
US 6,747,573, US 7,019,241
Observe precautions! Electrostatic sensitive devices!
EMDCB
2.4 GHz Bluetooth Low Energy Motion And Illumination Sensor
30.11.2018

USER MANUAL
EMDCB –BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY MOTION AND ILLUMINATION SENSOR
© 2019 EnOcean | www.enocean.com EMDCB User Manual | v1.3 | August 2019 | Page 2/67
REVISION HISTORY
The following major modifications and improvements have been made to this document:
Version
Author
Reviewer
Date
Major Changes
1.0
MKA
RS
14.12.2018
First public release
1.1
MKA
MKA
18.02.2018
Additional information on light sensor
1.2
MKA
MKA
07.06.2019
Added 2 Mbit mode and RPA example
1.3
MKA
MKA
06.08.2019
More detailed description of sensor
functionality
Published by EnOcean GmbH, Kolpingring 18a, 82041 Oberhaching, Germany
www.enocean.com, info@enocean.com, phone +49 (89) 6734 6890
© EnOcean GmbH, All Rights Reserved
Important!
This information describes the type of component and shall not be considered as assured
characteristics. No responsibility is assumed for possible omissions or inaccuracies. Circuitry
and specifications are subject to change without notice. For the latest product specifica-
tions, refer to the EnOcean website: http://www.enocean.com.
As far as patents or other rights of third parties are concerned, liability is only assumed for
modules, not for the described applications, processes and circuits.
EnOcean does not assume responsibility for use of modules described and limits its liability
to the replacement of modules determined to be defective due to workmanship. Devices or
systems containing RF components must meet the essential requirements of the local legal
authorities.
The modules must not be used in any relation with equipment that supports, directly or
indirectly, human health or life or with applications that can result in danger for people,
animals or real value.
Recycling information
Components of the modules are considered and should be disposed of as hazardous waste.
Please use suitable recycling operators for modules, components or packaging.

USER MANUAL
EMDCB –BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY MOTION AND ILLUMINATION SENSOR
© 2019 EnOcean | www.enocean.com EMDCB User Manual | v1.3 | August 2019 | Page 3/67
TABLE OF CONTENT
1General Description .......................................................................................6
1.1 Basic functionality ......................................................................................... 6
1.2 Technical data............................................................................................... 7
1.3 Environmental conditions ...............................................................................8
1.4 Packaging information.................................................................................... 8
1.5 Ordering information......................................................................................8
2Functional Description.................................................................................... 9
2.1 EMDCB Product Overview ............................................................................... 9
2.2 Basic functionality ....................................................................................... 10
2.3 Product design ............................................................................................ 10
2.3.1 External product interface..................................................................... 10
2.3.2 Internal product interface ..................................................................... 11
2.4 Functional modes ........................................................................................ 12
2.4.1 Standard operation .............................................................................. 13
2.4.2 Configuration ...................................................................................... 13
2.5 Motion detection.......................................................................................... 14
2.5.1 PIR detection characteristics ................................................................. 14
2.5.2 Installation recommendations................................................................ 15
2.6 Illumination measurement............................................................................ 16
2.6.1 Light level sensor................................................................................. 16
2.6.2 Solar cell ............................................................................................ 16
3Radio transmission ...................................................................................... 17
3.1 Radio channel parameters ............................................................................ 17
3.2 Default radio transmission sequence .............................................................. 18
3.3 User-defined radio transmission sequences..................................................... 18
3.3.1 Three channel sequence ....................................................................... 19
3.3.2 Two channel sequence.......................................................................... 20
3.3.3 Single channel sequence....................................................................... 20
4Telegram format ......................................................................................... 21
4.1 Preamble.................................................................................................... 22
4.2 Access Address ........................................................................................... 22
4.3 Header....................................................................................................... 22
4.4 Source address ........................................................................................... 22
4.4.1 Static source address mode .................................................................. 23
4.4.2 Resolvable private address mode........................................................... 24
4.5 Check Sum................................................................................................. 25
4.6 Payload...................................................................................................... 26
4.6.1 Sensor status encoding ........................................................................ 27
4.6.2 Sensor Data Descriptor......................................................................... 27
4.6.3 Data Size............................................................................................ 28
4.7 Supported parameters ................................................................................. 28
5EMDCB telegram authentication .................................................................... 29

USER MANUAL
EMDCB –BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY MOTION AND ILLUMINATION SENSOR
© 2019 EnOcean | www.enocean.com EMDCB User Manual | v1.3 | August 2019 | Page 4/67
5.1 Authentication implementation...................................................................... 30
6EMDCB commissioning ................................................................................. 31
6.1 Radio-based commissioning.......................................................................... 32
6.2 QR code commissioning ............................................................................... 32
6.2.1 Device label ........................................................................................ 32
6.2.2 Commissioning QR code ....................................................................... 33
6.2.3 Commissioning QR code format ............................................................. 33
6.3 Commissioning via NFC interface................................................................... 33
7NFC interface.............................................................................................. 34
7.1 NFC interface parameters ............................................................................. 34
7.2 NFC access protection .................................................................................. 34
7.3 Using the NFC interface................................................................................ 35
7.3.1 USB NFC Reader.................................................................................. 35
7.3.2 Android Smartphones with NFC ............................................................. 35
7.4 NFC interface functions ................................................................................ 36
7.4.1 NFC interface state machine.................................................................. 36
7.4.2 IDLE state........................................................................................... 37
7.4.3 READY 1 state..................................................................................... 37
7.4.4 READY 2 state ..................................................................................... 37
7.4.5 ACTIVE state....................................................................................... 37
7.4.6 Read command ................................................................................... 38
7.4.7 Write command ................................................................................... 38
7.4.8 Password authentication (PWD_AUTH) command..................................... 39
7.5 Configuration memory organization ............................................................... 40
7.5.1 Changing the PIN code ......................................................................... 40
7.6 NFC memory map ....................................................................................... 41
7.6.1 NDEF Text field.................................................................................... 42
7.6.2 Source Address ................................................................................... 42
7.6.3 TX Channel Configuration ..................................................................... 42
7.6.3.1 TX Channel Mode .............................................................................. 43
7.6.4 Radio Configuration.............................................................................. 44
7.6.4.1 TX Power ......................................................................................... 44
7.6.4.2 Advertising Interval........................................................................... 45
7.6.4.3 Manufacturer ID................................................................................ 45
7.6.5 Optional Data...................................................................................... 46
7.6.6 Security Key ....................................................................................... 46
7.6.7 Security Configuration.......................................................................... 47
7.6.7.1 Security Key Access .......................................................................... 47
7.6.7.2 Address Mode................................................................................... 48
7.6.7.3 LRN Telegram................................................................................... 48
7.6.7.4 Security Mode................................................................................... 49
7.6.8 Attribute Reporting, Optional Data Size and LED Intensity ........................ 49
7.6.8.1 Attribute Reporting............................................................................ 50
7.6.8.2 Optional Data Size ............................................................................ 50
7.6.8.3 LED Intensity.................................................................................... 50
7.6.9 Reporting interval ................................................................................ 51
7.6.10 Low Power Mode.................................................................................. 51

USER MANUAL
EMDCB –BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY MOTION AND ILLUMINATION SENSOR
© 2019 EnOcean | www.enocean.com EMDCB User Manual | v1.3 | August 2019 | Page 5/67
8Regulatory notes ......................................................................................... 52
8.1 European Union........................................................................................... 52
8.1.1 Declaration of conformity...................................................................... 52
8.1.2 Waste treatment.................................................................................. 52
8.2 FCC (United States)..................................................................................... 53
8.2.1 FCC (United States) Certificate .............................................................. 53
8.2.2 FCC (United States) Regulatory Statement.............................................. 54
8.2.3 FCC Usage Conditions .......................................................................... 54
8.2.4 FCC OEM Requirements ........................................................................ 55
8.3 ISED (Industry Canada) ............................................................................... 56
8.3.1 ISED (Industry Canada) Certificate ........................................................ 56
8.3.2 ISED (Industry Canada) Regulatory Statement........................................ 57
9Product history............................................................................................ 58
AParsing EMDCB telegrams............................................................................. 59
A.1 Data telegram example ................................................................................ 59
A.1.1 BLE advertising frame structure ................................................................ 59
A.1.2 Data telegram payload............................................................................. 59
A.1.3 Sensor data ............................................................................................ 59
A.2 Commissioning telegram example ................................................................. 60
A.2.1 BLE advertising data ................................................................................ 60
A.2.2 Commissioning telegram payload .............................................................. 60
BAuthentication example for EMDCB telegrams ................................................. 61
B.1 Input data .................................................................................................. 61
B.2 Constant algorithm parameters ..................................................................... 62
B.3 Intermediate parameters.............................................................................. 63
B.4 RFC3610 execution sequence........................................................................ 64
B.5 Execution example ...................................................................................... 65
CAddress resolution for resolvable private addresses (RPA) ................................ 66
C.1 RPA resolution flow...................................................................................... 66
C.2 Obtaining the IRK........................................................................................ 66
C.3 Address resolution example .......................................................................... 67

USER MANUAL
EMDCB –BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY MOTION AND ILLUMINATION SENSOR
© 2019 EnOcean | www.enocean.com EMDCB User Manual | v1.3 | August 2019 | Page 6/67
1General Description
1.1 Basic functionality
EMDCB is a ceiling-mounted motion and illumination sensor that reports its status using
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) advertising telegrams. It enables the realization of energy har-
vesting wireless occupancy and light level sensors for light, building or industrial control
systems communicating wit the 2.4 GHz Bluetooth Low Energy communication standard.
EMDCB uses a passive infrared (PIR) sensor to detect motion and a dedicated illumination
sensor to measure the amount of ambient light.
EMDCB reports periodically (approximately every 2 minutes when no motion is detected,
approximately every 1 minute when motion is detected) the latest detected motion (motion
detected or no motion detected) together with the measured light level. EMDCB will report
immediately if motion is detected for the first time after a period without detected motion
(e.g. when a person is entering a room).
EMDCB is self-supplied via an integrated solar cell which generates the energy required for
its operation. EMDCB requires 50 lux illumination for 6 hours per day directly at the solar
cell which typically is equivalent 200 lux for 6 hours per day to at room level. EMDCB is
fully self-powered (no batteries required) under these lighting conditions.
For cases where sufficient ambient light is not available, EMDCB provides the option to
mount a CR2032 backup battery.
Radio telegrams transmitted by EMDCB are authenticated AES-128 security based on a de-
vice-unique private key and a sequence counter. This ensures integrity and authenticity of
the transmitted telegrams and prevents telegram replay (retransmission of previously
transmitted telegrams).

USER MANUAL
EMDCB –BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY MOTION AND ILLUMINATION SENSOR
© 2019 EnOcean | www.enocean.com EMDCB User Manual | v1.3 | August 2019 | Page 7/67
1.2 Technical data
Antenna
Integrated antenna
Output power
+ 4 dBm
Configurable via NFC
Communication range (guidance only)
75 m for ideal line of sight
10 m for indoor environment (line of sight)
Communication standard
BLE Advertising
Radio frequency (min / max)
2402 / 2480 MHz
Radio channels (default)
BLE CH 37 / 38 / 39 (2402 / 2426 / 2480 MHz)
Configurable via NFC
Data rate and modulation (default)
1 Mbit/s GFSK
Motion detection radius
Up to 5 m (16 ft.) when mounted 3 m (10 ft.) high
Illumination measurement range / resolution
0 … 65000 Lux / 1 Lux
Illumination measurement accuracy
+-5% at full scale
Update rate with / without detected motion
Approximately every 2 minutes / 1 minute
Configurable via NFC
Initial motion detection is reported immediately
User interface
LRN button
Sensitivity selection switch
Notification LED
Device identification
Unique 48 Bit Device ID (factory programmed)
Adjustable via NFC
Security
AES128 (CBC mode) with sequence counter
Power supply
Integrated solar cell
Required illumination to sustain operation (1)
6 hours per 24 hours at 200 Lux
Charge time from empty to full charge
30 hours at 200 Lux
Charge time from empty to first transmission
10 minutes at 200 Lux
Operating time in darkness
96 hours (after full charge)
Backup power supply (optional)
CR2032
Backup battery life
Infrequent bright light (200 lux for 2 hrs every day)
Consistent low light (65 lux for 5 hrs every day)
Total Darkness
20 years
15 years
7.5 years
Dimensions
113,2 mm L x 65,5 mm W x 30,7 mm H
(4.46” L x 2.58” W x 1.21” H )
Note 1:
The required illumination of 200 Lux for sustaining operation is given for a typical operating environment (e.g. at
desk level in an office). The required minimum illumination directly at the solar cell of EMDCB is 50 Lux.

USER MANUAL
EMDCB –BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY MOTION AND ILLUMINATION SENSOR
© 2019 EnOcean | www.enocean.com EMDCB User Manual | v1.3 | August 2019 | Page 8/67
1.3 Environmental conditions
Maximum Operating Temperature(1)
0 … 60°C / 32 … 140 F (indoor use only)
Recommended Operating Temperature(1)
0 … 30°C / 32 … 85 F (indoor use only)
Humidity
20% to 85% r.h. (non-condensing)
Note 1: PIR detection requires that the moving object to be detected is significantly warmer
than its environment. For the case of human motion, this means that the environment
needs to be significantly colder than the human body temperature of 36.5 °C / 98 F.
1.4 Packaging information
Packaging Unit 12 units
Packaging Method Box / pallet
1.5 Ordering information
Type
Ordering Code
Frequency
EMDCB-W-EO
E6221-K515
2.4 GHz (BLE)

USER MANUAL
EMDCB –BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY MOTION AND ILLUMINATION SENSOR
© 2019 EnOcean | www.enocean.com EMDCB User Manual | v1.3 | August 2019 | Page 9/67
2Functional Description
2.1 EMDCB Product Overview
The energy harvesting ceiling-mounted motion and illumination sensor EMDCB from
EnOcean provides wireless motion and illumination sensing functionality without batteries.
Power is provided by a built-in solar cell. EMDCB transmits sensor data based on the
2.4GHz Bluetooth Low Energy standard.
The outer appearance of EMDCB is shown in Figure 1 below.
Figure 1 –EMDCB external view

USER MANUAL
EMDCB –BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY MOTION AND ILLUMINATION SENSOR
© 2019 EnOcean | www.enocean.com EMDCB User Manual | v1.3 | August 2019 | Page 10/67
2.2 Basic functionality
EMDCB devices contain a passive infrared sensor that detects changes in the received infra-
red radiation which are characteristic for the movement of persons.
EMDCB integrates a solar cell that generates the required energy for its operation from
available ambient light.
The user interface of EMDCB consists of one button for simple configuration tasks and one
LED to provide user feedback.
EMDCB is designed for ceiling mounting. It can be mounted on most ceilings with suitable
screws or mounted on dropped ceilings using wire brackets.
2.3 Product design
Figure 2 below shows the EMDCB product design including key functional elements.
2.3.1 External product interface
EMDCB uses a dedicated infrared lens in conjunction with a passive infrared sensor to de-
tect motion.
EMDCB it contains a dedicated sensor for illumination measurement. In addition, the inte-
grated solar cell can also be used to measure the external light level. It also provides the
required power for operation in normal lighting conditions.
The external user interface consists of one button (LRN) and one LED that together can be
used for simple configuration and test activities.
Figure 2 –EMDCB front and rear view

USER MANUAL
EMDCB –BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY MOTION AND ILLUMINATION SENSOR
© 2019 EnOcean | www.enocean.com EMDCB User Manual | v1.3 | August 2019 | Page 11/67
2.3.2 Internal product interface
EMDCB contains a holder for a CR2032 battery and a PIR sensitivity selection switch as
shown in Figure 3 below.
Figure 3 –EMDCB internal view
The internal product interface is accessible after removing the wall mount plate. If EMDCB
has not yet been mounted onto the ceiling then the wall mount plate can be removed by
using a screw driver (or similar) with the opening slot. If the EMDCB wall mount plate is
already attached to the ceiling, then EMDCB can be removed by gently pulling the housing.

USER MANUAL
EMDCB –BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY MOTION AND ILLUMINATION SENSOR
© 2019 EnOcean | www.enocean.com EMDCB User Manual | v1.3 | August 2019 | Page 12/67
2.4 Functional modes
EMDCB supports three types of functional modes:
◼Standard operation (shown in blue below)
◼Configuration (shown in grey below)
◼Standby (shown in orange below)
The transition between these modes occurs based on user action (press of the LRN button),
motion detection or based on pre-defined timing intervals.
SLEEP
LRN
TELEGRAM
Single
Button Press
Double
Button Press
Triple
Button Press
WALK TEST
LED
ON / OFF
Timer
Initial Motion
DATA
TELEGRAM
Long
Button Press STANDBY
Single
Button Press
Very Long
Button Press FACTORY
RESET
Figure 4 –EMDCB functional modes

USER MANUAL
EMDCB –BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY MOTION AND ILLUMINATION SENSOR
© 2019 EnOcean | www.enocean.com EMDCB User Manual | v1.3 | August 2019 | Page 13/67
2.4.1 Standard operation
During standard operation, EMDCB wakes up periodically and reports the current light level
and motion detection status using data telegrams.
The motion detection functionality is described in chapter 2.5, the light level sensing func-
tionality in chapter 2.6 and the data telegram transmission and format in chapters 3 and 4
respectively.
The EMDCB wake-up timer is configured to wake-up EMDCB approximately every 2 minutes
during periods without detected motion and approximately every 1 minute during periods
with detected motion. If motion is detected for the first time after a period without motion
then EMDCB wakes up immediately.
Both the occupied and the unoccupied wake-up intervals are affected at random in order to
increase the robustness of the radio transmission and to comply with regulatory require-
ments.
It is possible to change the wake-up intervals using the NFC interface as described in chap-
ter 7. In case of reducing the reporting interval, the resulting increase in required energy
(provided by the available light or a backup battery) has to be considered.
2.4.2 Configuration
Most EMDCB device parameters can be configured using the NFC interface as described in
chapter 7. Some of the most common parameters or states can additionally be configured
using the LRN button.
Table 1below lists those.
Table 1 –EMDCB external interface actions
Button Sequence Button Timing EMDCB Action LED Feedback
Single Short press < 1s
Exit from Sleep Mode if light is present
Send Learn Telegram
1 short blink
< 1s press,
< 1s release,
< 1s press
< 1s press,
< 1s release,
< 1s press,
< 1s release,
< 1s press
Error: No feedback
Success: 3 short blinks
Error: No feedback
Success: 5 short blinks
Very Long Press
8s
Factory Reset
Double Short
Press
Start Walk Test
(End after 2 minutes or upon next button press)
1 short blink every time movement is detected
(1 second minimum interval between blinks)
Long Press
3s
Enter Sleep Mode
(Disable LED and Radio)
Triple Short Press
Toggle LED indication
LED enabled: 2 short blinks
LED disabled: No feedback

USER MANUAL
EMDCB –BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY MOTION AND ILLUMINATION SENSOR
© 2019 EnOcean | www.enocean.com EMDCB User Manual | v1.3 | August 2019 | Page 14/67
2.5 Motion detection
EMDCB contains an integrated passive infrared (PIR) detector that can detect moving ob-
jects based on the temperature difference between the moving object and its environment.
2.5.1 PIR detection characteristics
EMDCB is designed to detect movement within a radius of up to 5 m (16 ft.) when mounted
at a ceiling of 3 m (10 ft.) height. The recommended coverage area for best detection per-
formance is within a radius of 3 m (10 ft).
Figure 5 below shows the PIR detection pattern.
Figure 5 –EMDCB PIR detection pattern

USER MANUAL
EMDCB –BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY MOTION AND ILLUMINATION SENSOR
© 2019 EnOcean | www.enocean.com EMDCB User Manual | v1.3 | August 2019 | Page 15/67
2.5.2 Installation recommendations
Motion detection works based on the temperature difference between a moving object and
its environment. Detection accuracy can therefore be affected by the following factors:
•Insufficient temperature difference (leading to no detection)
•Obstructions between PIR detector and moving person (leading to no detection)
•Warm moving objects (leading to false detections)
•Electro-magnetic radiation
For the case of person detection, the temperature of the moving object is the human body
temperature (normally around 36.5 °C / 98 F). If under very hot conditions the tempera-
ture of the environment approaches the temperature of the human body, then detection
performance will be significantly reduced.
For the same reason, hot objects within the detection area should be avoided. Examples
include standing lights, heaters or electrical equipment generating heat.
To reliably detect motion, an unobstructed line of sight from the sensor to the person(s) in
the detection area is required. Walls, room dividers, plants, book shelfs, hanging lights or
other obstacles within the line of sight can limit the detection performance.
The following factors should be considered to avoid the unintended detection of other warm
moving objects:
•Rapid temperature changes in the vicinity of the PIR detector, e.g. caused by fans or
fan heaters being switched on or off
•Lights (especially incandescent or halogen) being switched on or off in the immedi-
ate catchment area
•Warm moving objects such as animals, machines (e.g. cleaning robots or toys), hot
paper output of fax machines and laser printers, falling flower petals
•Motion in areas adjacent to the intended detection area, e.g. in the floor or in the
aisle around the detection area or outside of the window
Strong external electro-magnetic fields might induce noise into the highly sensitive PIR de-
tection circuitry and thereby affect the detection performance. EMDCB should therefore not
be mounted in close vicinity of electro-magnetic radiation sources such as WiFi access
points, gateways, wireless audio or video systems or other wireless devices.
For consistent detection, the mounting site of EMDCB should not be exposed to vibrations
or motion.

USER MANUAL
EMDCB –BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY MOTION AND ILLUMINATION SENSOR
© 2019 EnOcean | www.enocean.com EMDCB User Manual | v1.3 | August 2019 | Page 16/67
2.6 Illumination measurement
EMDCB integrates a dedicated light level sensor used to accurately measure and report the
light level directly underneath (e.g. on the desk surface).
In addition to the light sensor, EMDCB provides the option to use the calibrated solar cell
response to report wide area illumination. This can be used both as input for lighting con-
trol systems (e.g. to report ambient light for daylighting applications) and to verify the
available light level is sufficient for self-powered operation of EMDCB.
2.6.1 Light level sensor
EMDCB contains a dedicated humidity sensor with narrow aperture and a spectral response
optimized to mimic the human eye’s perception of ambient light. This light sensor reports
the light level directly underneath the sensor (spot measurement).
Figure 6 shows the spectrum response of the EMDCB illumination sensor compared to that
of the human eye.
Figure 6 –Spectrum response of EMDCB illumination sensor
2.6.2 Solar cell
EMDCB can report the light level by measuring the energy generated by the solar cell. This
can be used both to ensure that a sufficient ambient light is available to power the device
and to measure incoming light if the solar cell is oriented towards the window. Reporting of
the solar cell light level can be enabled and disabled via the NFC interface as described in
chapter 7.6.8.1.

USER MANUAL
EMDCB –BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY MOTION AND ILLUMINATION SENSOR
© 2019 EnOcean | www.enocean.com EMDCB User Manual | v1.3 | August 2019 | Page 17/67
3Radio transmission
3.1 Radio channel parameters
EMDCB transmits Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) advertising telegrams within the 2.4 GHz
radio frequency band (2402MHz … 2480MHz).
By default, EMDCB will use the three BLE advertising channels (BLE Channel 37, 38 and 39)
defined for transmission. The transmission of a radio telegram on these three advertising
channels is called an Advertising Event.
Use of different radio channels within the frequency band from 2402 MHz to 2480 MHz is
possible using the NFC configuration interface, see chapter 7.
The initialization value for data whitening is set as follows:
◼For BLE channels is set according to specification (value = radio channel)
◼For the custom radio channels the initialization value is equal to the offset from
2400 MHz (e.g. value = 3 for 2403 MHz)
Table 2 below summarizes radio channels supported by EMDCB.
Radio Channel
Frequency
Channel Type
BLE Radio Channels
37
2402 MHz
BLE Advertising Channel
0
2404 MHz
BLE Data Channel
1
2406 MHz
BLE Data Channel
…
10
2424 MHz
BLE Data Channel
38
2426 MHz
BLE Advertising Channel
11
2428 MHz
BLE Data Channel
12
2430 MHz
BLE Data Channel
…
36
2478 MHz
BLE Data Channel
39
2480 MHz
BLE Advertising Channel
Custom Radio Channels
40
2403 MHz
Custom Radio Channel
41
2405 MHz
Custom Radio Channel
…
77
2477 MHz
Custom Radio Channel
78
2479 MHz
Custom Radio Channel
Table 2 –EMDCB supported radio channels

USER MANUAL
EMDCB –BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY MOTION AND ILLUMINATION SENSOR
© 2019 EnOcean | www.enocean.com EMDCB User Manual | v1.3 | August 2019 | Page 18/67
3.2 Default radio transmission sequence
EMDCB transmits telegrams in its standard configuration by using so-called Advertising
Events.
An advertising event is defined as the transmission of the same radio telegram on all se-
lected radio channels (by default this would be on BLE Channel 37, 38 and 39) one after
another with minimum delay in between.
For reliability reasons, EMDCB will send three advertising events for each reporting event.
The resulting transmission sequence is shown in Figure 7 below. The default interval setting
is 20 ms; an alternative setting of 10 ms can be configured via NFC (see chapter 7.6.4.2).
CHANNEL 37 CHANNEL 38 CHANNEL39 INTERVAL
(20ms or 10ms) CHANNEL 37 CHANNEL 38 CHANNEL39 CHANNEL 37 CHANNEL 38 CHANNEL39
INTERVAL
(20ms or 10ms)
Figure 7 –Default radio transmission sequence
3.3 User-defined radio transmission sequences
In certain situations it might be desirable to transmit radio telegrams on channels other
than the three advertising channels.
EMDCB therefore allows selecting the radio channels to be used for the transmission of data
telegrams and commissioning telegrams. The following transmission modes are supported:
◼Both commissioning telegrams and data telegrams are transmitted on the advertis-
ing channels as three advertising events. This is the default configuration and de-
scribed in chapter 3.2 above.
◼Commissioning telegrams are transmitted on the advertising channels as three ad-
vertising events while data telegrams are transmitted in a user-defined sequence as
described below.
◼Both commissioning and data telegrams are transmitted in a user-defined sequence
as described below.
The selection of the transmission mode is done using the TX_CHANNEL_MODE field of the TX
register of the NFC configuration interface as described in chapter 7.6.3.

USER MANUAL
EMDCB –BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY MOTION AND ILLUMINATION SENSOR
© 2019 EnOcean | www.enocean.com EMDCB User Manual | v1.3 | August 2019 | Page 19/67
EMDCB supports the following user-defined sequences:
◼Three channel sequence
This sequence is similar to the default Advertising Event with the difference that the
user can select the radio channels to be used. The three channel sequence is de-
scribed in chapter 3.3.1 below.
◼Two channel sequence
In this sequence the radio telegram is transmitted using six transmissions on two
radio channels. It is described in chapter 3.3.2 below.
◼One channel sequence
In this sequence the radio telegram is transmitted using nine transmissions on one
radio channel. It is described in chapter 3.3.3 below.
3.3.1 Three channel sequence
The three channel radio transmission sequence is similar to the default transmission se-
quence with the difference that the radio channels (BLE Channel 37, 38 and 39 in the de-
fault transmission sequence) can be selected using the registers TX_CHANNEL1, TX_CHANNEL2
and TX_CHANNEL3.
In this mode, the telegram will be transmitted on the radio channel selected by TX_CHANNEL1
first, immediately followed by a transmission on the radio channel selected by TX_CHANNEL2
and a transmission on the radio channel selected by TX_CHANNEL3.
The telegram will be transmitted using this sequence three times in total as shown in Figure
8 below.
This transmission uses a default INTERVAL setting of 20 ms; an alternative setting of 10 ms
can be configured via NFC.
TX_CHANNEL1 TX_CHANNEL2 TX_CHANNEL3 TX_CHANNEL1 TX_CHANNEL2 TX_CHANNEL3 TX_CHANNEL1 TX_CHANNEL2 TX_CHANNEL3
INTERVAL
(20ms or 10ms)
INTERVAL
(20ms or 10ms)
Figure 8 –Three channel radio transmission sequence

USER MANUAL
EMDCB –BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY MOTION AND ILLUMINATION SENSOR
© 2019 EnOcean | www.enocean.com EMDCB User Manual | v1.3 | August 2019 | Page 20/67
3.3.2 Two channel sequence
The two channel radio transmission sequence transmits radio telegrams on two user-
defined radio channels (selected by TX_CHANNEL1 and TX_CHANNEL2) six times in total.
The telegram will in this mode be transmitted on the radio channel selected by TX_CHANNEL1
first, immediately followed by a transmission on the radio channel selected by TX_CHANNEL2.
This transmission sequence uses a default INTERVAL setting of 20 ms; an alternative setting
of 10 ms can be configured via NFC.
TX_CHANNEL1 TX_CHANNEL2 TX_CHANNEL1 TX_CHANNEL2
INTERVAL
(20ms or 10ms) TX_CHANNEL1 TX_CHANNEL2
INTERVAL
(20ms or 10ms)
...
Figure 9 –Two channel radio transmission sequence
3.3.3 Single channel sequence
The single channel radio transmission sequence transmits radio telegrams on one user-
defined radio channel (selected by TX_CHANNEL1) nine times in total.
This transmission sequence uses a default INTERVAL setting of 20 ms; an alternative setting
of 10 ms can be configured via NFC.
TX_CHANNEL1 TX_CHANNEL1
INTERVAL
(20ms or 10ms) TX_CHANNEL1
INTERVAL
(20ms or 10ms)
...
Figure 10 –Single channel radio transmission sequence
This manual suits for next models
1
Table of contents
Other EnOcean Accessories manuals

EnOcean
EnOcean STM 350 User manual
EnOcean
EnOcean EOSC User manual

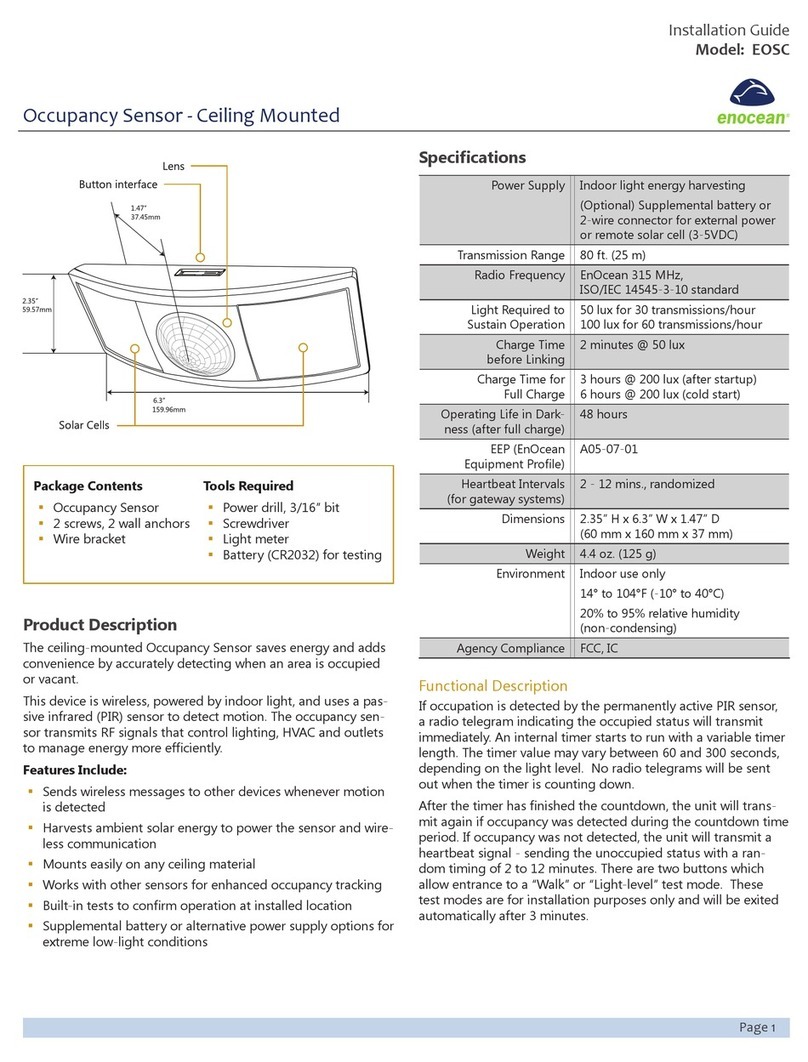
EnOcean
EnOcean TRI02SYS User manual

EnOcean
EnOcean EOSWU Quick start guide

EnOcean
EnOcean Easyfit STM 550B User manual

EnOcean
EnOcean 02LINE TRI02SYS User manual

EnOcean
EnOcean 02LINE TRI02SYS User manual

EnOcean
EnOcean EASYFIT STM 550 User manual

EnOcean
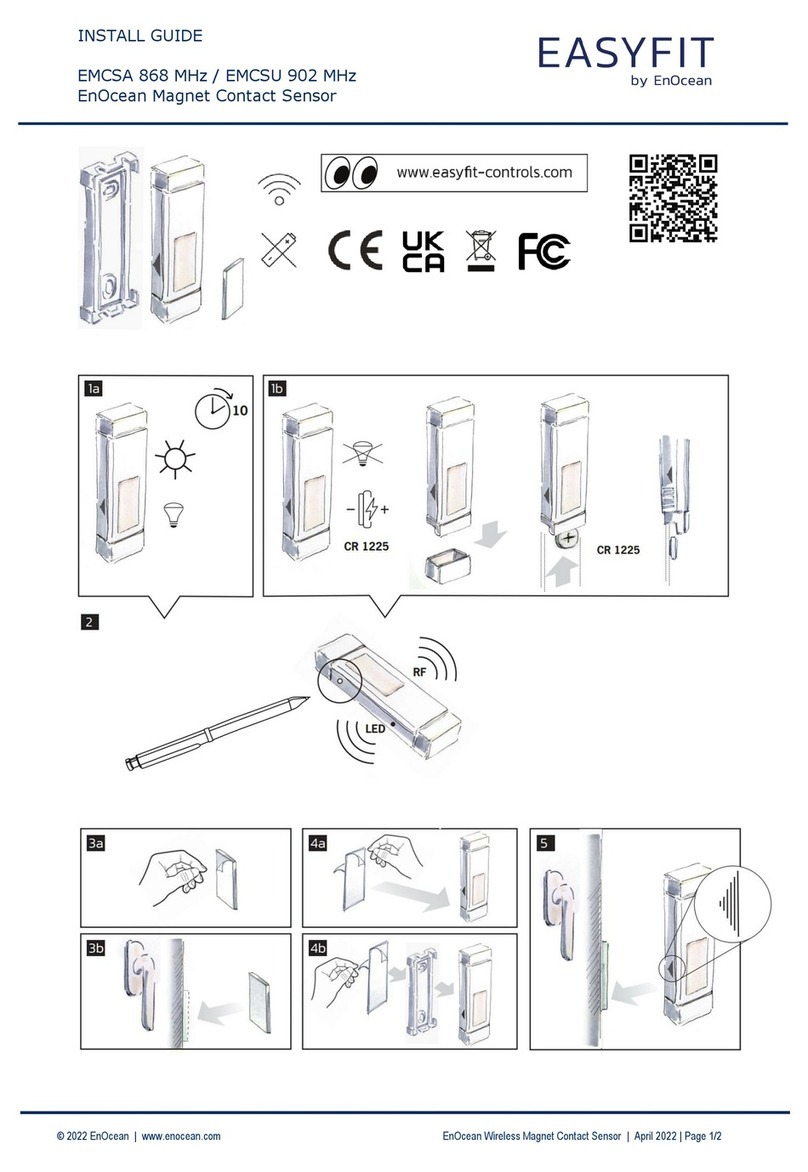
EnOcean EasyFit EMCSA User manual
EnOcean
EnOcean EasyFit EMCSA User manual