entegris A192-81M-0215 Guide

CRITICAL MATERIALS HANDLING
D1
B2
D3b
Datum A
B3
BB
D3a
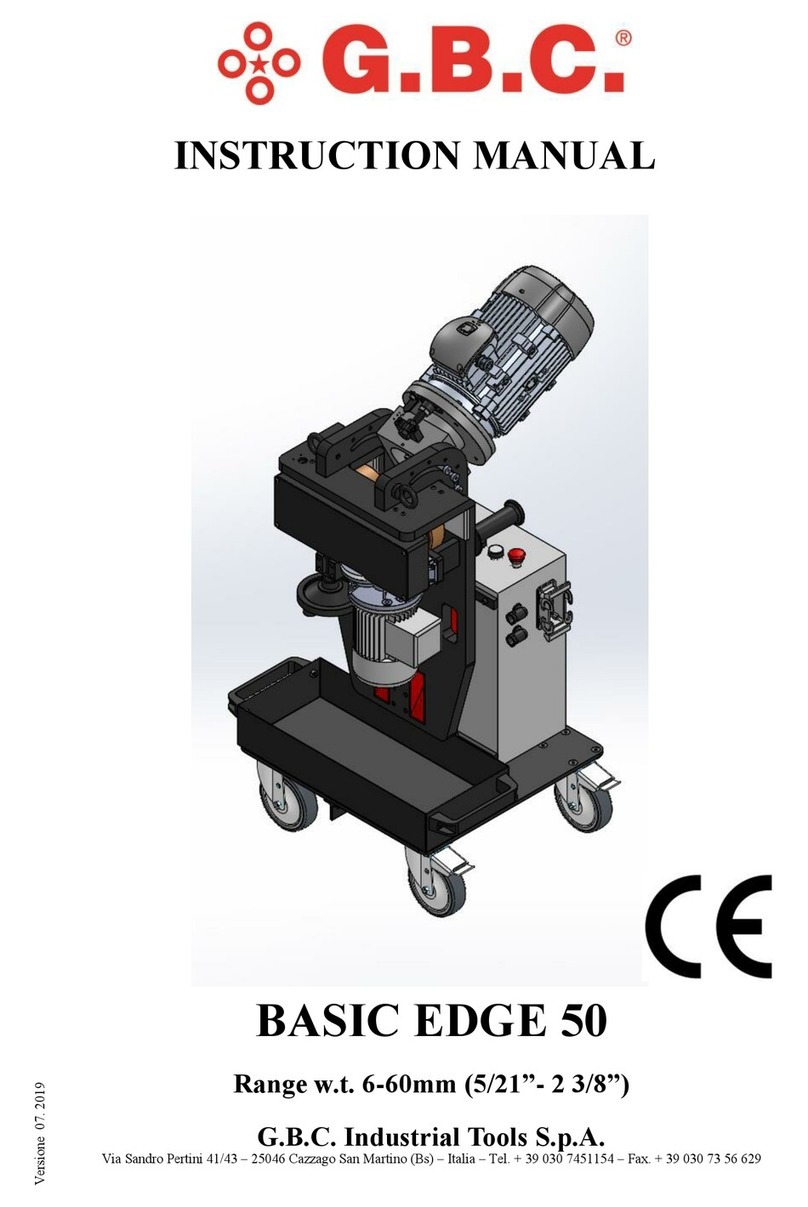
Installation and use manual
200 MM WAFER CARRIER
INTERFACE MANUAL

200 MM WAFER CARRIER INTERFACE
ENTEGRIS, INC. INSTALLATION AND USE MANUAL 1
Table of Contents
Overview ............................................ 1
General Terminology and Definitions ......... 2
Definitions .............................................3
Wafer Plane ........................................ 4
Specification Purpose ...............................4
Benefits ................................................4
General Definitions ..................................4
Specification Description ..........................5
Specification Values .................................5
Use with Automated Equipment ..................5
Four Point Contact ................................ 6
Contact Location .....................................6
Benefits of Four Point Contact ....................6
Equipment Interface ................................6
Wafer Carriers Included and Exceptions ........6
General Interface Information .................. 7
Recommended Contact Points ....................6
Print Based Interface Design .....................6
Benefits of Four Point Contact ....................6
Interface Points: Wafers Horizontal ........... 7
General Recommendations ........................7
Sample Interface Plate .............................7
Contact Area A ........................................8
Contact Area B ........................................8
Contact Area C ........................................8
Interface Points: Wafers Vertical .............. 9
General Recommendations ........................9
Sample Interface Plate .............................9
Contact Area A ........................................9
Contact Areas B and C ............................. 10
Interface Points: Robotic Handling ........... 10
General Recommendations ...................... 10
Robotic Handling Features ...................... 10
Endwall Flanges .................................... 10
“H” Bar End Flanges ............................... 11
Endwall Handle ..................................... 11
Top Flanges ......................................... 11
Material Information ............................12
Material Properties and
Equipment Interface ........................... 12
Static Protection ................................... 12
Moisture Absorption ............................... 12
Applications ......................................... 12
Wafer Transport Carriers ........................ 12
Process Wafer Carriers ........................... 13
Detailed Material Properties ..................13
For More Information ...........................14
Terms and Conditions ...........................14
Product Warranties ..............................14
Overview
At Entegris, we are committed to working with you, the equipment
supplier, to provide simple solutions for our joint customers in the
semiconductor industry. Our experience has shown that semiconduc-
tor manufacturers want to order their equipment and their wafer car-
riers without worrying about wafer carrier/equipment interface
issues. By sharing information with you we can provide our joint
customers a compatible equipment and wafer
carrier combination.

200 MM WAFER CARRIER INTERFACE
2 INSTALLATION AND USE MANUAL ENTEGRIS, INC.
C3 C2
C11
Section E-E
General Terminology and Definitions
This section contains dimensions called out on standard
carrier drawings. These dimensions, as well as general wafer
carrier terms, are defined below.
Number Description
OVERALL DIMENSIONS
A1 Length
A2 Width (with/without flanges) includes stripper rails
A3 Height (excluding pin)
CAPACITY
B1 Pockets per carrier
B2 Pocket spacing
B3 Center distance from the first to last pocket
DETAIL DIMENSIONS
C1 Pocket width
C2 Pocket depth
C3 Pocket flat
C4 Pocket size (inside pocket across to
inside pocket)
MACHINE FIT SPECIFICATIONS
D1 Distance from Datum A to the center line of the
first pocket
D3a Distance from Datum A to the front of the
“H” bar at the center of the carrier
D3b Distance from Datum A to the front of the “H”
bar 13 mm (0.5”) from the side of the carrier
D4a Distance from Datum B to the center line of the
“H” bar
D4b Distance from Datum B to the center line of the
wafer
D5a Bar web width
D5b Bar width
D5c Distance from Datum A to the front of the
“H” bar web
D6a Inside width of the bottom track
D6b Overall width of the “H” bar at the top of the
wafer carrier
D8a Overall width of the robotic pick-up flanges
D6b
D4a
D6a
D8a
A2
C4
Wafer
D4b
EE
Section A-A
D1
B2
D3b
-A-
BB
D3a
B3
-A-A
A
-B-
A1
A3
D5b
Section B-B
D5c
D5a

200 MM WAFER CARRIER INTERFACE
ENTEGRIS, INC. INSTALLATION AND USE MANUAL 3
Definitions
Bar end See “H” bar.
Crossbar The mass of material connecting the two sides of the carrier at the bar end
of the carrier.
End wall The wall of the carrier opposite the “H” bar end of the carrier.
Flange Mass of material on the exterior of a carrier, perpendicular to the side walls.
”H“ bar The end of the wafer carrier that has only one crossbar and is capable of
elevator equipment interface.
Hole The area for the pin of another carrier to enter for transferring wafers.
Left side The left side of the carrier when viewed from the “H” bar end while
positioned on its track.
Overall size Overall size is measured by length by width by height as shown in the diagram.
Pin height is not included in the height measurement for wafer carriers.
Pin The mass of material which enters the hole or slot of another carrier for
transferring wafers.
Pocket The area in which the wafer is located in the carrier.
Pocket flat The width of the pocket along the vertical walls at its most narrow distance.
Pocket spacing The distance between pocket centerlines.
Pocket width The width of the pocket at its widest distance.
Right side The right side of the carrier when viewed from the “H” bar end while
positioned on its track.
Track clearance The unobstructed area between the two carrier sides on the bar end.
Wafer transfer The act of relocating wafers from one carrier into another.

200 MM WAFER CARRIER INTERFACE
4 INSTALLATION AND USE MANUAL ENTEGRIS, INC.
Wafer Plane
This section provides an explanation of the
wafer plane concept and discusses the benefits
of an improved wafer plane. Carriers that hold
each wafer in a predictable location perform
better on automated wafer transfer equipment.
A carrier that does not hold wafers in a predictable
location can cause numerous robotics and wafer
transfer problems. To reduce these problems,
Entegris continually strives to improve wafer
plane dimensions.
Specification Purpose
The wafer plane specification provides the specific,
predictable location of each wafer in a carrier.
Benefits
The benefits of an improved wafer plane include:
• Reduced equipment adjustments
• Improved accuracy in wafer transfers
• Minimized missed wafer transfers
• Reduced equipment shut downs
• Minimized damage or breakage of wafers
• Reduced particle generation caused by wafers
rubbing on carriers
General Definitions
The following definitions define and clarify the
wafer plane concept:
Wafer plane The position of the wafer in a carrier.
Wafer plane
zone
The acceptable position for a wafer,
defined by the offset dimension and
tolerance.
Pocket center
plane
The imaginary plane that exactly
bisects each pocket.
Wafer seated
surface
The bottom of the wafer, typically the
unfinished side of a wafer in process.
All dimensional data is derived from
this surface.
Offset
dimension
The distance from the pocket center
plane to the bottom, or seated surface
of the wafer.
Datum A The flat surface defined by the “H” bar
end of a wafer carrier. Datum A can be
established by placing the carrier “H”
bar end down on a flat surface.
Datum B The flat surface defined by the bottom,
or track of the carrier. Datum B can be
established by placing the carrier track
end down on a flat surface.

200 MM WAFER CARRIER INTERFACE
ENTEGRIS, INC. INSTALLATION AND USE MANUAL 5
Specification Description
Wafer plane is defined by an offset dimension and
a tolerance. The offset dimension is called out from
the pocket center plane, a distance calculated
from Datum A (“H” bar).
Offset Dimension
The offset dimension is the distance from the
pocket center plane to the center of the wafer
plane zone, toward Datum A. This dimension,
always negative, defines the center of the wafer
plane zone.
Tolerance
The tolerance defines the thickness of the wafer
plane zone.
Calculating Pocket Center Plane Distance
The pocket center plane distance varies for
each specific pocket in a wafer carrier. It can
be calculated with the following formula:
X = D1 + (N - 1) ×B2
Where:
X = Pocket center plane distance for pocket N
from Datum A
D1 = Distance from Datum A to the center plane
of pocket one
N = Pocket number (pocket one is closest to
Datum A)
B2 = Wafer carrier pitch (pocket spacing)
Calculating Wafer Plane Zone
The pocket center plane distance varies for
each specific pocket in a wafer carrier. It can
be calculated with the following formulas:
Y = X - Offset + Tolerance
Z = X - Offset - Tolerance
Where:
Y = Top limit of the wafer plane zone for pocket N
Z = Bottom limit of the wafer plane zone
for pocket N
X = Pocket center plane distance for pocket N
NOTE: The offset value is given as a negative
value. Please use the absolute, or non-negative,
value in the above calculations.
Specification Values
Wafer plane specifications vary between various
wafer carrier series and materials. Typical offset
dimensions range between -0.9 mm and -1.1 mm
(-0.04" and -0.05"). Typical tolerances are
±0.6 mm (0.03"). Please reference the specific
drawings for each wafer carrier for exact
dimensions and tolerances.
Use with Automated Equipment
Automated wafer transfer equipment is pro-
grammed to locate the wafer within the wafer
plane zone. Difficulties can arise when the wafer’s
seated surface is outside this zone. The size of
the zone is also important. As the tolerances are
tightened, the zone becomes smaller and wafer
transfer equipment operates with fewer difficulties.
Pocket center plane
Wafer seated surfacePocket
center
place
distance
(X)
Datum A
Offset
Ø50.8 mm (2.0”)
Standard Version CS5
Y
Z
+
–Tolerance

200 MM WAFER CARRIER INTERFACE
6 INSTALLATION AND USE MANUAL ENTEGRIS, INC.
Four Point Contact
Entegris utilizes a patented four point contact
on the “H” bar end and on the track of most
200 mm wafer carriers. Supporting the carrier
on four specific points eliminates the variation
inherent in trying to maintain a precise dimension
over a long feature such as conventional “H” bar
rails and track.
Contact Location
The location of the four points is shown by the
arrows in the diagram.
Benefits of Four Point Contact
“H” bar
When the carrier is used with the wafers in a
horizontal position, the four point contact ensures
correct wafer orientation and wafer height in
relation to the centerline of the first pocket.
Track
When the carrier is used with the wafers in the
vertical position and located by the center notch on
the carrier track, the four point contact eliminates
rocking to ensure consistent placement of wafers
for vertical transfer.
Equipment Interface
For optimum use on equipment, the portion of
equipment in direct contact with the wafer carrier
(stage and/or “H” bar nest) should be designed to
provide planar support for all four points.
Wafer Carriers Included and Exceptions
Most 200 mm carriers have a four point contact
feature on both the “H” bar end and the track with
the following exceptions:
The Entegris wafer carriers listed below do not
have a four point contact feature on either the “H”
bar end or the track. They should be supported
along the length of the two “H” bar rails with wafers
in the horizontal position or along the length of the
track with wafers in the vertical position.
• A192-81M-0215
• A192-82M-0215
The Entegris wafer carriers listed below have a
four point contact feature on the “H” bar end only.
They do not have a four point contact on the track.
They should be supported along the length of the
track with wafers in the vertical position.
• A192-80M-0215
• A198-80M-47C02
• A198-80MB-47C02
The Entegris wafer carriers listed below have a four
point contact feature on the track only. They do not
have a four point contact on the “H” bar end. They
should be supported along the length of the two “H”
bar rails with wafers in the horizontal position.
• PA192-80M-XXXX
• PA192-80MN-XXXX
• PA195-80M-XXXX
”H“ Bar (for Wafer’s Horizontal Interface)
Datum A
Track (for Wafer’s Vertical Interface)

200 MM WAFER CARRIER INTERFACE
ENTEGRIS, INC. INSTALLATION AND USE MANUAL 7
General Interface
Information
Recommended Contact Points
Entegris strongly urges the use of only recom-
mended contact points in developing wafer
carrier interfaces. These are typically tightly
controlled dimensions that will provide optimal,
consistent interface.
Entegris cannot guarantee reliable equipment
interface if contact points other than the
recommended contact points are used.
Print Based Interface Design
Interfaces should be designed based on prints
detailing wafer carrier specifications using
controlled dimensions. Controlled dimensions
are identified on prints with a circle around
the dimension. Use of a sample wafer carrier
is not recommended as it does not incorporate
nominal, minimum and maximum dimensions.
Tolerances
It is critical to use the entire tolerance ranges
provided on the prints when developing interfaces
for wafer carriers.
Reducing Particle Generation
Properly designed interface plates can greatly
reduce particle generation. The use of radius edges
and smooth surfaces on areas that interface the
wafer carrier will reduce the number of particles
generated by abrasion of the wafer carrier.
Interface Points:
Wafers Horizontal
General Recommendations
Entegris strongly recommends that only the contact
points detailed in this section be used to locate
wafer carriers for horizontal wafer handling. These
are typically tightly controlled dimensions that will
provide optimal, consistent interface.
Entegris cannot guarantee reliable equipment
interface if contact points other than the
recommended contact points are used.
Sample Interface Plate
When designing an interface plate, use generous
radiuses for optimum wafer carrier lead in. In
addition, minimize registration points for ease
of carrier placement.
The interface plate should be designed to locate
the wafer carrier with the wafers horizontal using
only an appropriate combination of Entegris
recommended contact areas.
Height of contact area interface pads should be
no greater than 3.8 mm (0.15").
Recommended Contact Areas
• A + B
• A + C
Contact Areas Not Recommended
• A + B + C
• B + C
Area B
Area A
Area C

200 MM WAFER CARRIER INTERFACE
8 INSTALLATION AND USE MANUAL ENTEGRIS, INC.
Contact Area A
When designing an area A interface, use the
following dimensions.
D6a: Inside Width at “H” bar
The interface location should be within 25.4 mm
(1.00") of the crossbar.
D5b: “H” bar WidthTrack
Contact Area B
When designing an area B interface, use the
following information.
D6b: Inside Width at Top (#1)
The interface location should be within 12.7 mm
(0.50") of the top opening of the wafer carrier.
Four Point “H” Bar Contact
Ensure the wafer carrier is supported only on the
four points of the “H” bar contact to ensure proper
height to pocket (D1). Please see page 7 for more
information.
Contact Area C
When designing an Area C interface, use the
following dimensions.
D6a: Inside Track Width
D4a: Cross Bar Centerline
The interface location should be within 9.5 mm
(0.38") of the wafer carrier track.
Four Point “H” Bar Contact
Ensure the wafer carrier is supported only on
the four points of the “H” bar contact to ensure
proper height to pocket (D1). Please see page 7
for more information.
25.4 mm
(1.00”)
25.4 mm
(1.00”)
D6a
D5b
D6b
12.7 mm
(0.50”)
maximum
D6a
9.52 mm
(0.375”)
D4a

200 MM WAFER CARRIER INTERFACE
ENTEGRIS, INC. INSTALLATION AND USE MANUAL 9
Interface Points:
Wafers Vertical
General Recommendations
Entegris strongly recommends that only the
contact points detailed in this section be used to
locate wafer carriers for vertical wafer handling.
Entegris cannot guarantee reliable equipment
interface if contact points other than the
recommended contact points are used.
Sample Interface Plate
This sample interface plate locates the wafer
carrier with the wafers vertical by using Entegris
recommended interface points. Use of the center
notches provides the most accurate wafer carrier
registration for vertical handling.
Recommended Contact Areas
• A + B + C
Contact Area A
Center Notch
Use of the center notches provides the
most accurate wafer carrier registration
for vertical handling.
D9a, D9b, D9c, D9e
Center Notch Location (#1)
The center of the center notches on 200 mm wafer
carriers, measured from Datum A, are:
• 25 Capacity: 101.6 mm (4.00")
• 26 Capacity: 104.8 mm (4.13")
The center of the center notch may not be at the
center of the track length (#1).
For 25 capacity wafer carriers, the center notches
on the wafer carrier track (Datum B) are located
within 0.3 mm (0.01") of the pocket centerline for
pocket 13.
For 26 capacity wafer carriers, the center notches
on the wafer carrier track (Datum B) are located
within 0.3 mm (0.01") of the centerline of the tooth
between pockets 13 and 14.
Maximum
track length
+ 1.0 mm
(0.04”)
Minimum
6.4 mm
(0.25”)
Minimum
6.4 mm
(0.25”)
Minimum inside track
width (D6a)
25 Capacity
102.1 mm
(4.02”)
26 Capacity
105.3 mm
(4.15”)
9.5 mm
(0.38”)
9.5 mm
(0.38”)
”H“ bar end
Contact Area A
Contact Area B
Contact Area C
D9a
D9b
D9c
D9e
Detail B
Datum B
“H-bar” End
#1
#2
Datum B
Datum A

200 MM WAFER CARRIER INTERFACE
10 INSTALLATION AND USE MANUAL ENTEGRIS, INC.
Contact Areas B and C
Track Length (#2 on previous diagram)
D6a: Inside Track Width
The depth of the recess for the wafer carrier track
should be a maximum of 6.4 mm (0.25").
Four Point Track Contact
Ensure the wafer carrier is supported only on the
four points of the track to ensure proper orienta-
tion. Please see page 6 for more information.
Interface Points:
Robotic Handling
General Recommendations
When developing interfaces to robotic handling
features, it is important to reference the specifi-
cations for the specific wafer carrier as features
vary in design and location. If additional informa-
tion is required, contact Entegris Applications
Engineering.
Robotic Handling Features
Entegris provides many different features
to facilitate robotic handling. The following
general categories of robotic handling features
are detailed below.
• Endwall flanges
• “H” bar end flanges
• Endwall handle
• Top flanges
Endwall Flanges
Robotic flanges on a wafer carrier endwall are
available in many styles including outboard and
inboard flanges. Outboard flanges are near the
outer edges of the wafer carrier. Inboard flanges
are in towards the center of the end wall.
The controlled dimension (#1) for end wall flanges
is the overall length from Datum A to the inside
(backside) of the flange.
6.35 mm
(0.256”)
maximum
D6a
Interface
plate
Endwall Flanges
Inboard flanges
Outboard flanges
Endwall Flange Controlled Dimension
#1

200 MM WAFER CARRIER INTERFACE
ENTEGRIS, INC. INSTALLATION AND USE MANUAL 11
“H” bar End Flanges
Robotic flanges on a wafer carrier “H” bar end
are near the outer edges of the wafer carrier.
This placement is required to avoid interference
with the inside “H” bar surface.
Endwall Handle
Endwall handles are placed towards the center
of the endwall and above the center of gravity of
the carrier.
Top Flanges
Top flanges run along the top length of the wafer
carrier, parallel to the track.
Use of the top flanges for robotic movement and
placement of the wafer carrier is acceptable only
when precise placement is not required.
“H”-bar End Flanges
Endwall Handle
Top Flanges

200 MM WAFER CARRIER INTERFACE
12 INSTALLATION AND USE MANUAL ENTEGRIS, INC.
Material Information
Material Properties and Equipment
Interface
Material properties can have a direct effect on
equipment interface. The primary properties that
affect equipment interface are dimensional stabil-
ity, static protection and moisture absorption.
Dimensional Stability
Dimensional stability is the ability of a material
to retain consistent dimensions over time. Highly
rigid materials remain dimensionally consistent,
ensuring reliable interface.
Static Protection
Static protection is the ability of a material to avoid
buildup of static charges that may later discharge,
causing damage to devices and causing equipment
to shut down. Materials that offer static protection
prevent static charges from building up, hence
avoiding the problems of electrostatic discharge.
Moisture Absorption
Moisture absorption is the amount of moisture that
a material will absorb. The level of absorption will
directly affect vacuum pump down times.
Applications
Wafer carrier materials can be divided into two
primary categories based on the wafer carrier’s
primary application.
• Wafer transport carriers
• Process wafer carriers
Wafer Transport Carriers
Wafer transport carriers are used to store and
transport wafers throughout the production
process. They offer limited chemical resistance
and should not be used with harsh chemicals.
Standard Material Definitions
STAT-PRO®9000 Material
STAT-PRO 9000 black static dissipative material
is a blend of Carbon Nanotube (CNT) enhanced
polyetheretherketone (PEEKTM polymer) carbon
compound.
STAT-PRO 3000 Material
STAT-PRO 3000 black static dissipative material
is a blend of PEEK polymer and carbon fiber.
EMSTAT AR+
EMSTAT AR+ is a blend of high-purity
polypropylene with milled carbon fiber.
STAT-PRO 100 Material
STAT-PRO 100 black static dissipative polyprop-
ylene is a blend of polypropylene and pure inert
carbon powder.
Blue Polypropylene
Blue polypropylene is standard polypropylene
with an additive to make the material blue.
MATERIAL PROPERTIES OVERVIEW
Rank Material
Dimensional
Stability
Static
Protection
Moisture
Absorption General Interface Comments
1STAT-PRO 9000 Excellent Exceptional Low The best material available for
reliable interface.
2STAT-PRO 3000 Excellent Excellent Low The next best material available
for reliable interface.
3EMSTAT AR+ Poor Very good Very low Good material for reliable
interface.
4STAT-PRO 100 Poor Very good Very low Poor material for interface, still
widely used.
5 Blue
polypropylene
Poor None Very low Very poor material for
interface.

200 MM WAFER CARRIER INTERFACE
ENTEGRIS, INC. INSTALLATION AND USE MANUAL 13
Process Wafer Carriers
Process wafer carriers are used in processes
that require chemical resistance. PFA material
(translucent perfluoroalkoxy) is used as it
offers superior chemical resistance. PFA
materials provide:
• Excellent chemical compatibility
• Poor dimensional stability
• No static protection
• Minimal moisture absorption
Detailed Material Properties
Static Protection
• Surface resistivity test method ASTM D-257
Material Surface Resistivity Static Decay
STAT-PRO 9000 104–106ohms/sq <0.02 sec
STAT-PRO 3000 105–1010 ohms/sq <0.01 sec
EMSTAT AR+ 105–1010 ohms/sq <0.01 sec
STAT-PRO 100 10 3–108ohms/sq 0.01 sec
Blue polypropylene <1013 ohms/sq <30 sec
Natural PFA <1013 ohms/sq Not applicable
Moisture Absorption
• Test method ASTM 570
Material Water Absorption
STAT-PRO 9000 0.04%
STAT-PRO 3000 0.05%
EMSTAT AR+ 0.01%
STAT-PRO 100 0.02%
Blue polypropylene 0.02%
Natural PFA < 0.03%
Temperature Limits
Material
Maximum
Continuous
Use Temperature
Maximum
Wafer
Insertion
Temperature
STAT-PRO 9000 120°C (248°F) 340°C (644°F)
STAT-PRO 3000 120°C (248°F) 340°C (644°F)
EMSTAT AR+ 55°C (131°F) 70°C (158°F)
STAT-PRO 100 55°C (131°F) 70°C (158°F)
Blue polypropylene 55°C (131°F) 70°C (158°F)
Natural PFA 180°C (356°F) 250°C (482°F)
Flammability
• Test method UL94
Material Flammability
STAT-PRO 9000 V-O
STAT-PRO 3000 V-O
EMSTAT AR+ HB
STAT-PRO 100 HB
Blue polypropylene UL94
Natural PFA UL94

Entegris®, the Entegris Rings Design®, Creating a Material Advantage®and STAT-PRO®are registered trademarks of Entegris, Inc.
PEEK
™
is a trademark of Victrex PLC.
ENTEGRIS, INC.
Corporate Headquarters | 129 Concord Road | Billerica, MA 01821 USA
Customer Service Tel. +1 952 556 4181 | Customer Service Fax +1 952 556 8022
In North America 800 394 4083 | www.entegris.com
©2001–2015 Entegris, Inc. All rights reserved Printed in USA 1210-0469ENT-1215
For More Information
Please call your Regional Customer Service
Center today to learn what Entegris can do
for you. Visit www.entegris.com and select the
Customer Service link for the center nearest you.
Terms and Conditions of Sale
All purchases are subject to Entegris’ Terms
and Conditions of Sale. To view and print
this information, visit www.entegris.com and
select the Legal Notices link from the footer.
Product Warranties
For Product Warranties, visit www.entegris.com
and select the Legal Notices link from the footer.
This manual suits for next models
7
Table of contents
Other entegris Industrial Equipment manuals