Safety Information
The products described in this manual can fail in a variety of modes due to misuse, age, or malfunction. Systems
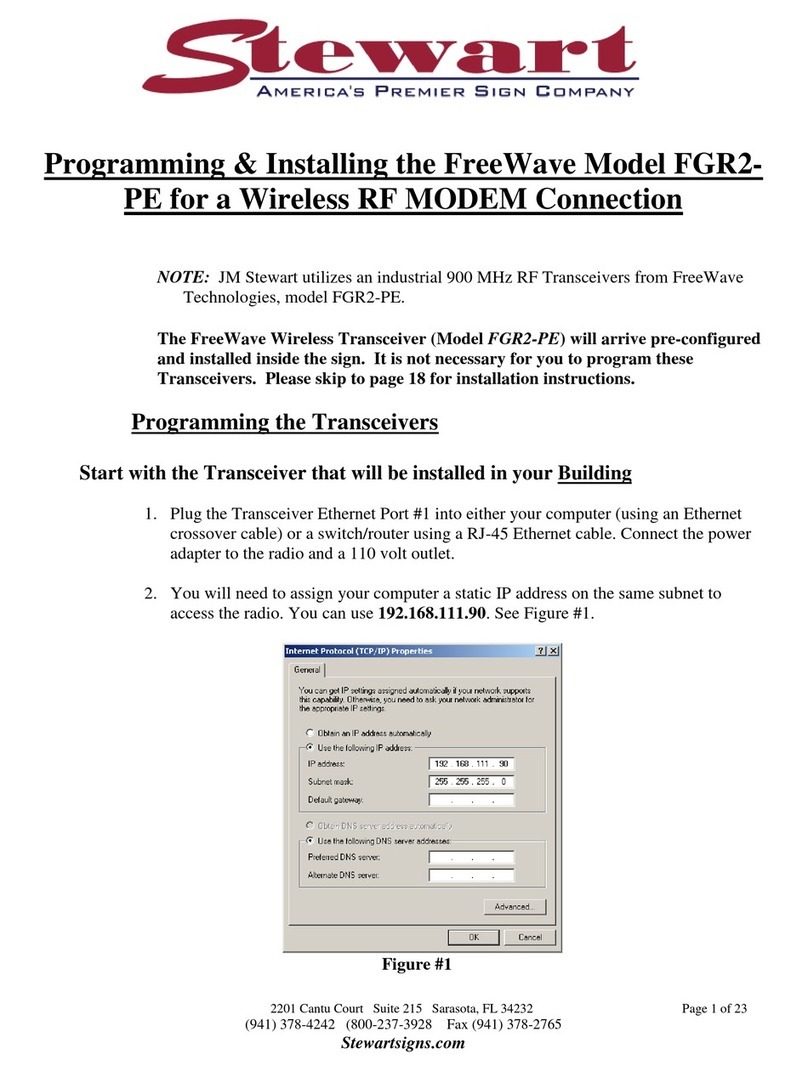
with these products must be designed to prevent personal injury and property damage during product operation
and in the event of product failure.
Warning! Do not remove or insert diagnostics cable while circuit is live unless the areais
known to be free of ignition concentrations of flammable gases or vapors.
Warranty
FreeWave Technologies, Inc. warrants your FreeWave® Wireless Data Transceiver against defects in materials
and manufacturing for a period of two years from the date of shipment. In the event of a Product failure due to
materials or workmanship, FreeWave will, at its option, repair or replace the Product. The Product must be returned
to FreeWave upon receiving a Return Material Authorization (RMA) for evaluation of Warranty Coverage.
In no event will FreeWave Technologies, Inc., its suppliers, and its licensors be liable for any damages arising from
the use of or inability to use this Product. This includes business interruption, loss of business information, or other
loss which may arise from the use of this Product. Please be advised that OEM customer’s warranty periods may
vary.
Warranty Policy may not apply:
1. If Product repair, adjustments or parts replacements is required due to accident, neglect, unusual
physical, electrical or electromagnetic stress.
2. If Product is used outside of FreeWave specifications.
3. If Product has been modified, repaired, or altered by Customer unless FreeWave specifically
authorized such alterations in each instance in writing. This includes the addition of conformal coating.
Special Rate Replacement Option
A special rate replacement option is offered to non-warranty returns or upgrades. The option to purchase the
replacement unit at this special rate is only valid for that RMA. The special replacement rate option expires if not
exercised within 30 days of final disposition of RMA.
Restricted Rights
Any product names mentioned in this manual may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
companies and are hereby acknowledged. Information in this manual is subject to change without notice and is
proprietary and confidential to FreeWave Technologies, Inc..
This manual is for use by purchasers and other authorized users of FreeWave® tranceivers.
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, or
for any purpose without the express written permission of FreeWave Technologies, Inc.. FreeWave reserves the
right to make changes to this manual without notice. Unless otherwise agreed to in writing,FreeWave assumes no
responsibility or liability for the use of this manual or the infringement of any copyright or other proprietary
right.FreeWave shall deem nothing contained in this manual as warranty or guarantee.
FreeWave's Wireless Data Transceivers are designed and manufactured in the United States of America.
FreeWave Technologies, Inc.
1800 South Flatiron Court
Boulder, CO 80301
303.444.3862
Toll Free: 1.866.923.6168
Printed in the United States of America. 303.786.9948
Copyright © 2011 by FreeWave Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. www.freewave.com
LUM0024AB Rev A ii