5
GYSPOT ALU 66 FR
RECOMMANDATIONS POUR EVALUER LA ZONE ET L’INSTALLATION DE SOUDAGE
Généralités
L’utilisateur est responsable de l’installation et de l’utilisation du matériel de décharge capacitive suivant les instructions du fabricant.
Si des perturbations électromagnétiques sont détectées, il doit être de la responsabilité de l’utilisateur du matériel de décharge
capacitive de résoudre la situation avec l’assistance technique du fabricant. Dans certains cas, cette action corrective peut être aussi
simple qu’une mise à la terre du circuit de soudage. Dans d’autres cas, il peut être nécessaire de construire un écran électromagnétique
autour de la source de courant de soudage et de la pièce entière avec montage de filtres d’entrée. Dans tous les cas, les perturbations
électromagnétiques doivent être réduites jusqu’à ce qu’elles ne soient plus gênantes.
Evaluation de la zone de soudage
Avant d’installer un matériel de décharge capacitive, l’utilisateur doit évaluer les problèmes électromagnétiques potentiels dans la
zone environnante. Ce qui suit doit être pris en compte:
a) la présence au-dessus, au-dessous et à côté du matériel de décharge capacitive d’autres câbles d’alimentation, de commande, de
signalisation et de téléphone;
b) des récepteurs et transmetteurs de radio et télévision;
c) des ordinateurs et autres matériels de commande;
d) du matériel critique de sécurité, par exemple, protection de matériel industriel;
e) la santé des personnes voisines, par exemple, emploi de stimulateurs cardiaques ou d’appareils contre la surdité;
f) du matériel utilisé pour l’étalonnage ou la mesure;
g) l’immunité des autres matériels présents dans l’environnement.
L’utilisateur doit s’assurer que les autres matériels utilisés dans l’environnement sont compatibles. Cela peut exiger des mesures de
protection supplémentaires;
h) l’heure du jour où le soudage ou d’autres activités sont à exécuter.
La dimension de la zone environnante à prendre en compte dépend de la structure du bâtiment et des autres activités qui s’y
déroulent. La zone environnante peut s’étendre au-delà des limites des installations.
Evaluation de l’installation de soudage
Outre l’évaluation de la zone, l’évaluation des installations de matériel de décharge capacitive peut servir à déterminer et résoudre les
cas de perturbations. Il convient que l’évaluation des émissions comprenne des mesures in situ comme cela est spécifié à l’Article 10
de la CISPR 11. Les mesures in situ peuvent également permettre de confirmer l’efficacité des mesures d’atténuation.
RECOMMANDATIONS SUR LES METHODES DE REDUCTION DES EMISSIONS ELECTROMAGNETIQUES
a. Réseau public d’alimentation: Il convient de raccorder le matériel de décharge capacitive au réseau public d’alimentation selon
les recommandations du fabricant. Si des interférences se produisent, il peut être nécessaire de prendre des mesures de prévention
supplémentaires telles que le filtrage du réseau public d’alimentation. Il convient d’envisager de blinder le câble d’alimentation dans
un conduit métallique ou équivalent d’un matériel de décharge capacitive installé à demeure. Il convient d’assurer la continuité
électrique du blindage sur toute sa longueur. Il convient de raccorder le blindage à la source de courant de soudage pour assurer un
bon contact électrique entre le conduit et l’enveloppe de la source de courant de soudage.
b. Maintenance du matériel de décharge capacitive : Il convient que le matériel de décharge capacitive soit soumis à l’entretien
de routine suivant les recommandations du fabricant. Il convient que tous les accès, portes de service et capots soient fermés et
correctement verrouillés lorsque le matériel de décharge capacitive est en service. Il convient que le matériel de décharge capacitive
ne soit modifié en aucune façon, hormis les modifications et réglages mentionnés dans les instructions du fabricant.
c. Câbles de soudage : Il convient que les câbles soient aussi courts que possible, placés l’un près de l’autre à proximité du sol ou
sur le sol.
d. Liaison équipotentielle : Il convient d’envisager la liaison de tous les objets métalliques de la zone environnante. Toutefois,
des objets métalliques reliés à la pièce à souder accroissent le risque pour l’opérateur de chocs électriques s’il touche à la fois ces
éléments métalliques et l’électrode. Il convient d’isoler l’opérateur de tels objets métalliques.
e. Mise à la terre de la pièce à souder : Lorsque la pièce à souder n’est pas reliée à la terre pour la sécurité électrique ou en
raison de ses dimensions et de son emplacement, ce qui est le cas, par exemple, des coques de navire ou des charpentes métalliques
de bâtiments, une connexion raccordant la pièce à la terre peut, dans certains cas, et non systématiquement, réduire les émissions.
Il convient de veiller à éviter la mise à la terre des pièces qui pourrait accroître les risques de blessure pour les utilisateurs ou
endommager d’autres matériels électriques. Si nécessaire, il convient que le raccordement de la pièce à souder à la terre soit
fait directement, mais dans certains pays n’autorisant pas cette connexion directe, il convient que la connexion soit faite avec un
condensateur approprié choisi en fonction des réglementations nationales.
f. Protection et blindage : La protection et le blindage sélectifs d’autres câbles et matériels dans la zone environnante peuvent
limiter les problèmes de perturbation. La protection de toute la zone de soudage peut être envisagée pour des applications spéciales.
TRANSPORT ET TRANSIT DE LA SOURCE DE COURANT DE SOUDAGE
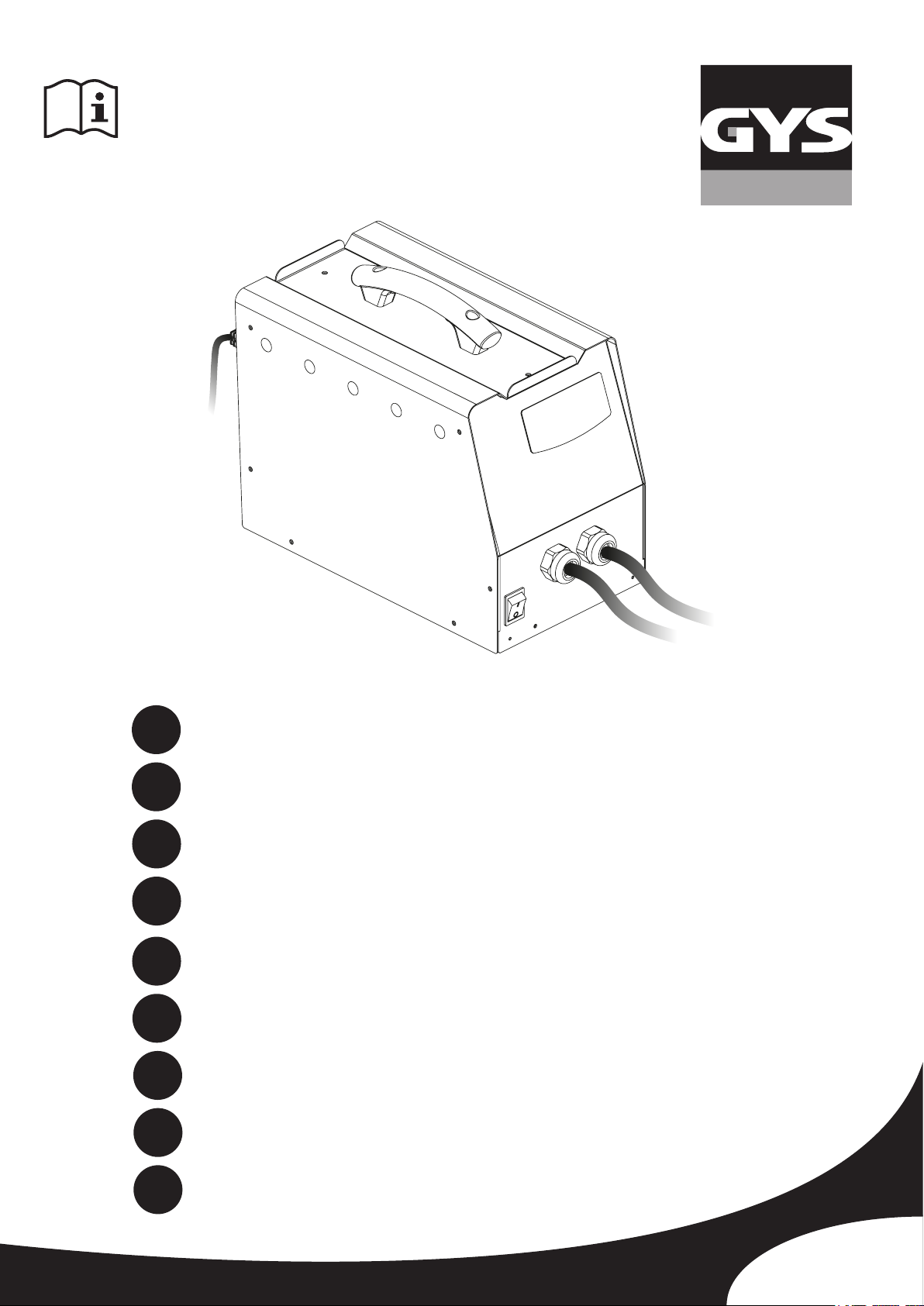
La source de courant de soudage est équipée d’une (de) poignée(s) supérieure(s) permettant le portage / déplacement
à la main. Attention à ne pas sous-évaluer son poids. La (les) poignée(s) n’est (ne sont) pas considérée(s) comme un
moyen d’élingage.
Ne pas utiliser les câbles pour déplacer la source de courant de soudage.
Ne pas faire transiter la source de courant au-dessus de personnes ou d’objets.