- 5 -
gone beyond or is obstructed by a vise/bed mount,
then use the following procedures.
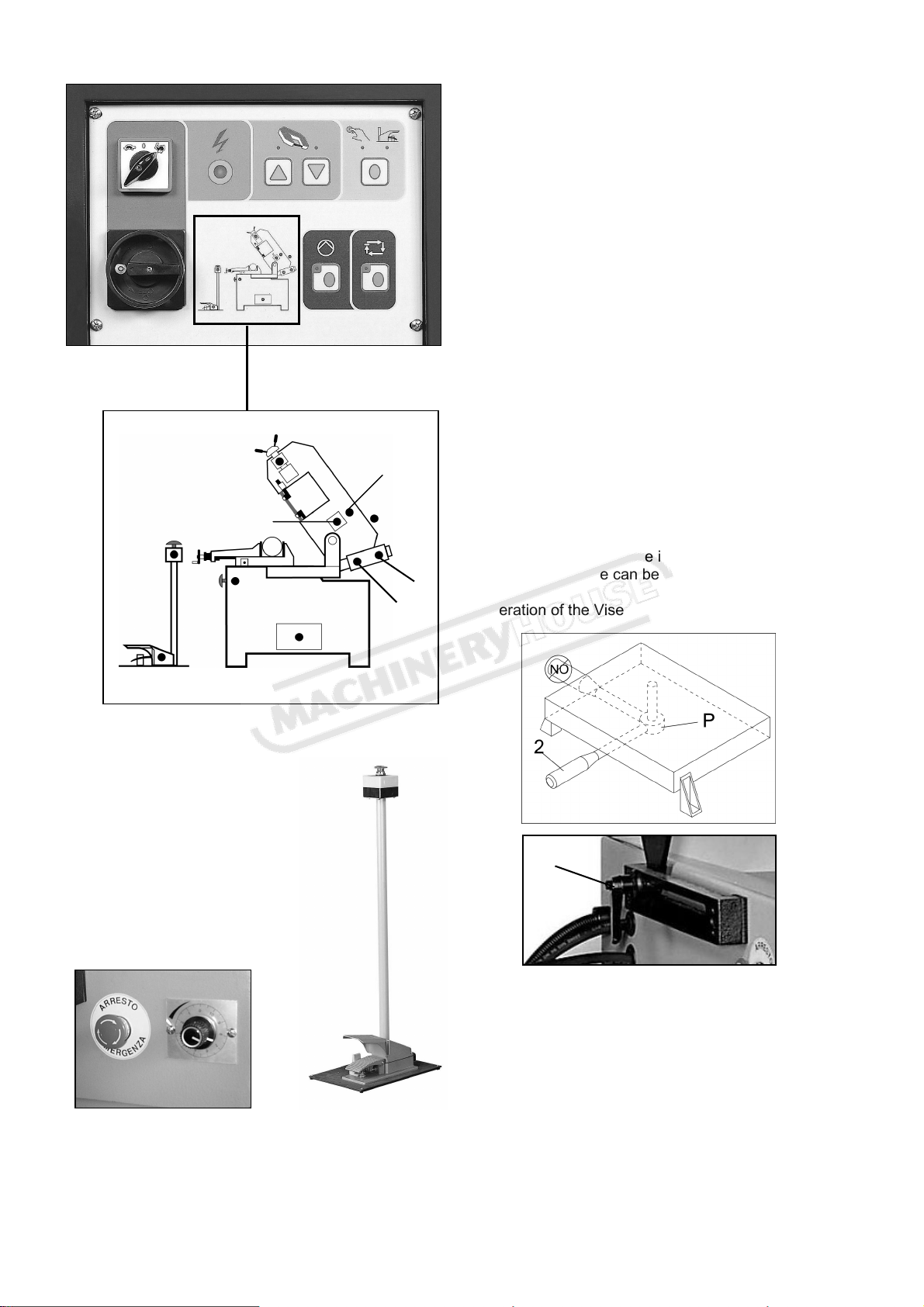
- Adjust the lever (2) by grasping at the pivot point (P)
and lowering it, which may assist in the adjustment.
The lever can now be freely rotated into a more
convenient position. Some movement of the vise
jaw may be required. Raise the lever (2) then move to
the right to lock.
- Lock the track support (1) by turning handle
clockwise.
3.4 Cutting angle adjustment
Cutting at angles
- Angle can be cut up to 60°.
- Unlock lever (L) by pushing it to the left side.
- Rotate the saw arm to the desired angle by
following the index on the scale.
- Lock lever (L) by pushing to the right side.
3.5 The base
- A structure supporting the SAW ARM (revolving arm
for gradual cutting and respective blocking system),
the VISE, the BAR STOP, the ROLLER for the support
of the material. The base houses the cooling liquid
TANK, PUMP, and the DEVICE CONTROLLING THE
AUTOMATIC HYDRAULIC LOWERING AND RISING
OF THE SAW FRAME.
The main connect switch is designed with a lock hole.
A lock can be attached to the lock hole to prevent
machine operation for safety and security purposes.
- To use the footpad switch (J), first use the side of the
foot to push aside the plastic clip that blocks the foot
pad. Be careful not to damage the clip by using
excessive force or stomping on the footpad. Next,
step down on the footpad to start operation.
3.6 The operation cycle
- Make sure the voltage indicated on machine motor is
the same as power source voltage. Connect the
machine to the power source, and Press the main
connect switch (B). If power indicator light (1) is on,
it means the voltages are okay.
-Select the cutting speed on switch (A).
*Note: While selecting the cutting speed indicator
light will blink.
-Press hydraulic flow control start switch (G). *Note: If
the hydraulic flow control fails to activate, then switch
(C), (D), and (F) cannot operate. Indicator light (7)
will blink if any are pressed, indicating that start switch
(G) has failed to activate.
-Check the hydraulic oil level. If oil rises up, it means
the motor is running in the right direction. If not,
rewire the plug.
- Check that the saw arm is properly set. Press saw
bow switches (C) or (D) to adjust the bow height to
help when setting the workpiece.
-Place the workpiece in the vise and clamp securely.
-Select the speed using speed selector switch (A).
The turtle indicates low speed and the rabbit indicates
high speed. “O” is for neutral.
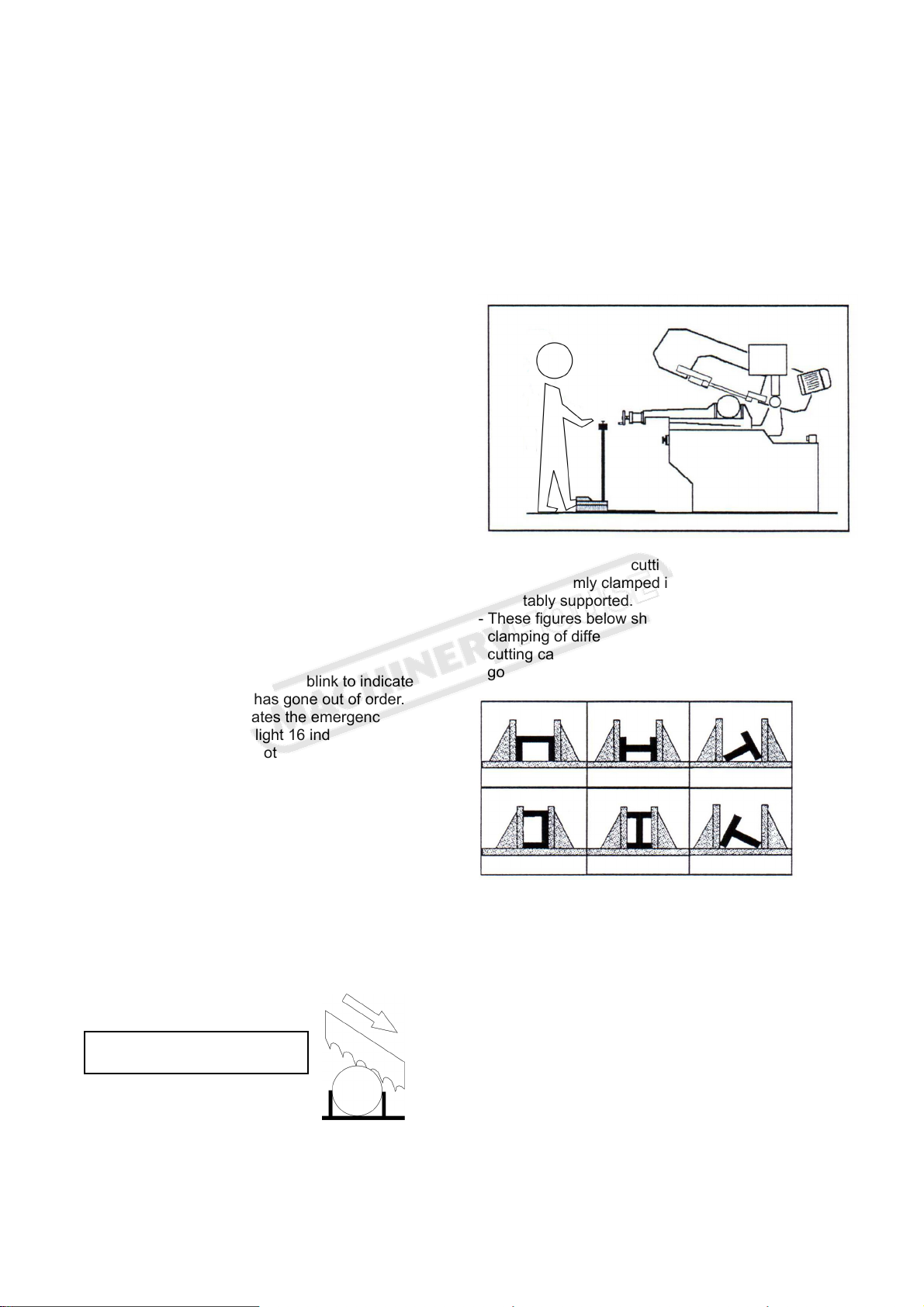
-Be sure to stand in a safe location while operating.
There are two ways to start the machine. Press the
switch (C) to let the saw bow return to the highest
position and then using the first method, select hand
operation on selector (E) and press cycle start switch
(F) to start operation. Using the second method,
Select footpad operation on selector (E) and step on
start footpad (J) to start operation.
- In general, start cuts by slightly turning hydraulic flow
regulation switch (K) counter-clockwise from 2 to 3 to
control the saw arm descent rate. If the arm
descends too quickly, turn hydraulic flow regulation
switch (K) clockwise all the way back to stop its
descent - When cutting different material use the
hydraulic flow regulation switch (K) to control saw
arm’s rate of descent.
*Note: A saw arm dropping too quickly can cause the
blade to stall on the work piece and the machine will
J
Instruction Manual for EB-270DSA (B066)