Contents
1. Preface ............................................... 4
2. Inspection ............................................. 5
3. Specifications and Optional Parts.......................... 6
3.1 Specifications ............................................... 6
3.2 Products Series Introduction .................................... 8
3.2.1 HV950 Models ........................................ 8
3.2.2 Ordering information of HV950 series ...................... 8
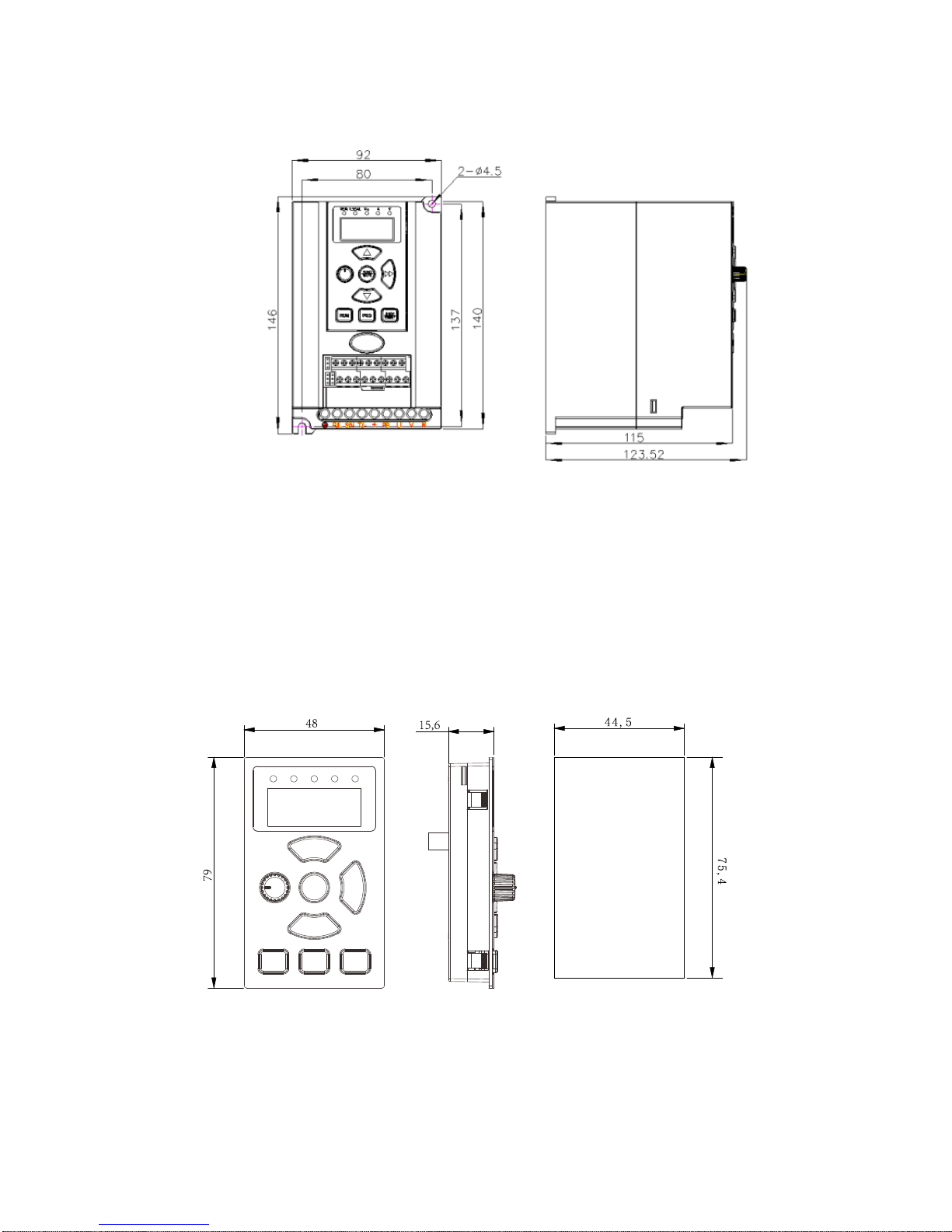
3.2.3 Demision............................................. 9
3.2.4 LED Keypad Display Unit Size............................ 9
4. Installation and Wiring ................................. 11
4.1 Installation................................................. 11
4.2 Wiring .................................................... 12
4.2.1 Overview............................................ 12
4.2.2 Power Terminals ...................................... 13
4.2.3 Control Circuit Wiring.................................. 13
5. Operation Procedures .................................. 20
5.1 Operation Guide ............................................ 20
5.1.1 LED Keypad ......................................... 20
5.1.2 Keypad Function Explanation............................ 20
5.1.3 Indicator Description................................... 21
5.1.4 Parameter Setting Method............................... 21
5.1.5 Motor parameters self-learning ........................... 22
5.1.6 Password setting ...................................... 23
6. Parameters ......................................... 24
6.1 Basic Parameters(F0)...................................... 24
6.2 Motor Parameter(F1)...................................... 27
6.3 Start/Brake Parameter(F2).................................. 28
6.4 Flux vector control parameters(F3)........................... 30
6.5 Current vector control parameter(F4).......................... 32
6.6 Multi-function terminal(F5)................................. 32
6.7 Output terminal control parameters(F6)........................ 38
6.8 Close-loop PID control(F7)................................. 43
6.9 MS parameters(F8)........................................ 45
6.10 Enhanced function(F9).................................... 45