Shenzhen Hpmont Technology Co., Ltd. Chapter 1 Safety Information and Precautions
HD-PFT-A User Manual V1.1 -1-
Chapter 1 Safety Information and Precautions
1.1 Design Precautions
Make sure to have safety circuits outside of the PFC to ensure safe system operation even during
external power supply problems or PFC failure. Otherwise, malfunctions may cause serious accidents.
•1) Most importantly, have the following: an emergency stop circuit, a protection circuit, an interlock
circuit for movements (such as normal vs. reverse rotation), and an interlock circuit (to prevent
damage to the equipment at the upper and lower positioning limits).
•2) Note that when the PFC CPU detects an error, such as a watchdog timer error, during self-
diagnosis, all outputs are turned off. Also, when an error that cannot be detected by the CPU occurs
in an input/output control block, output control may be disabled. External circuits and mechanisms
should be designed to ensure safe machinery operation in such a case.
•3) Note that the output current of the service power supply for sensors varies depending on the
model and the absence/presence of extension blocks. If an overload occurs, the voltage
automatically drops, inputs in the PLC are disabled, and all outputs are turned off. External circuits
and mechanisms should be designed to ensure safe machinery operation in such a case.
•4) Note that when an error occurs in a relay, triac or transistor output device, the output could be
held either on or off. For output signals that may lead to serious accidents, external circuits and
mechanisms should be designed to ensure safe machinery operation in such a case.
•To maintain the safety of the programmable controller system against unauthorized access from
external devices via the network, take appropriate measures. To maintain the safety against
unauthorized access via the Internet, take measures such as installing a firewall.
1.2 Wiring Precautions
For installation, wiring, etc., be sure to turn off all power.
Avoid wiring in the live state, plugging and unplugging the cable, otherwise it may cause electric
shock or damage to the circuit.
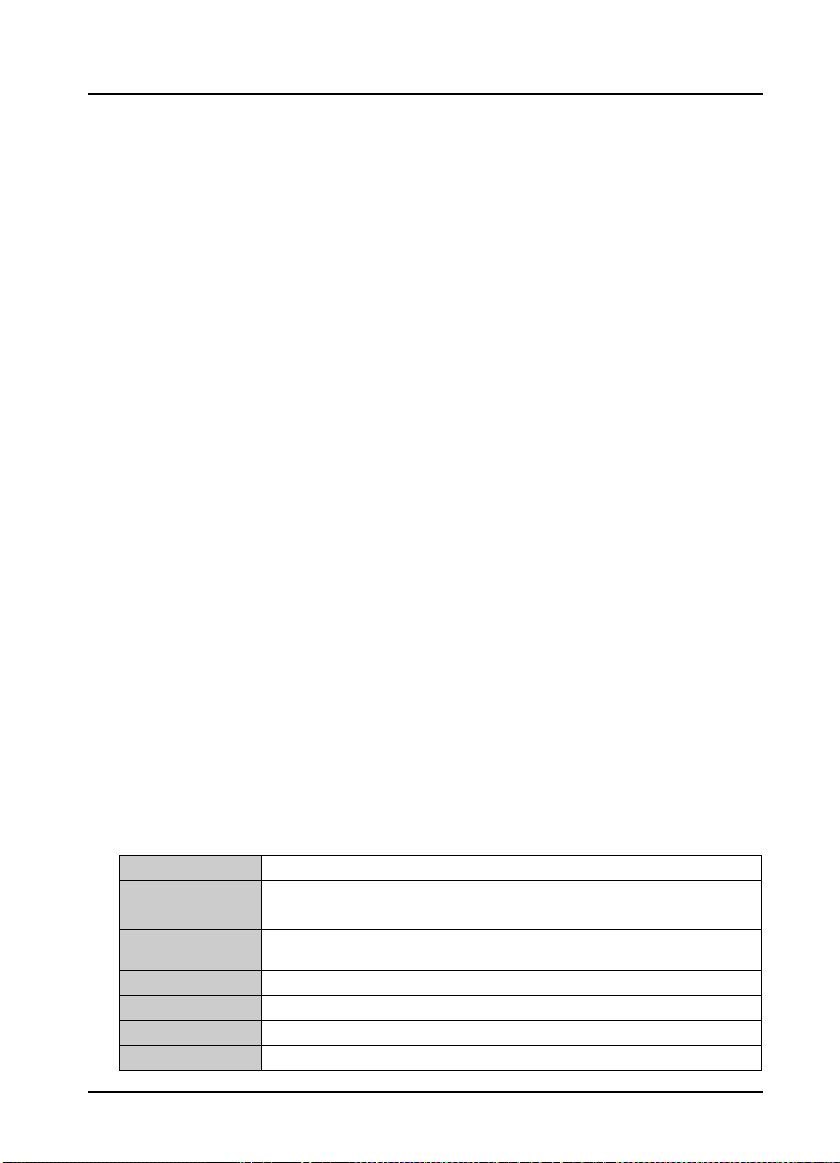
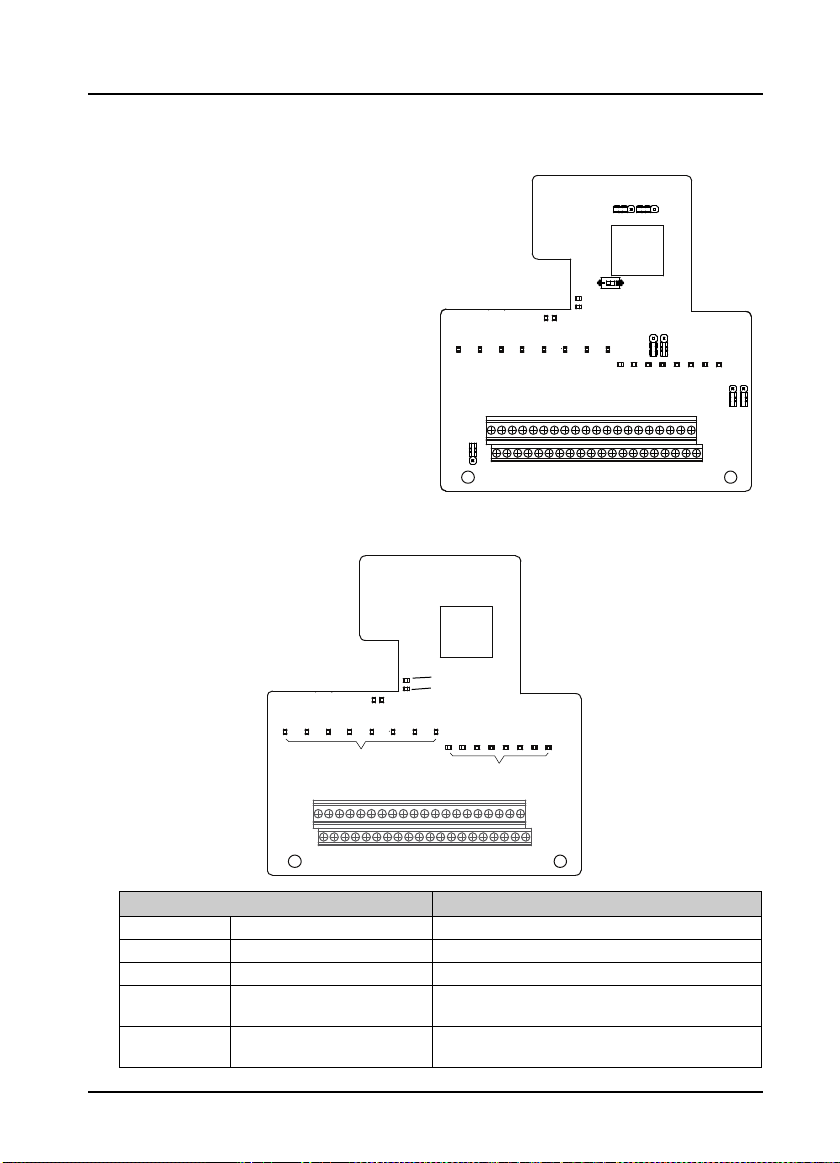
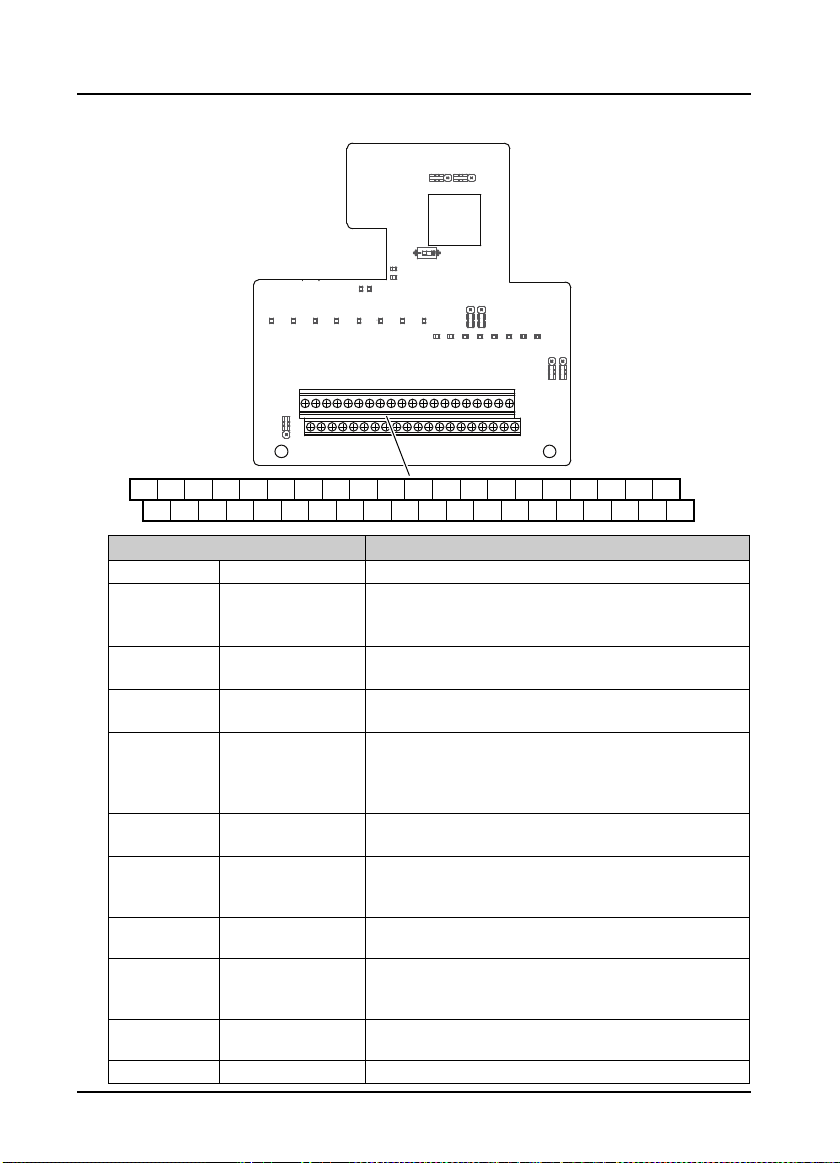
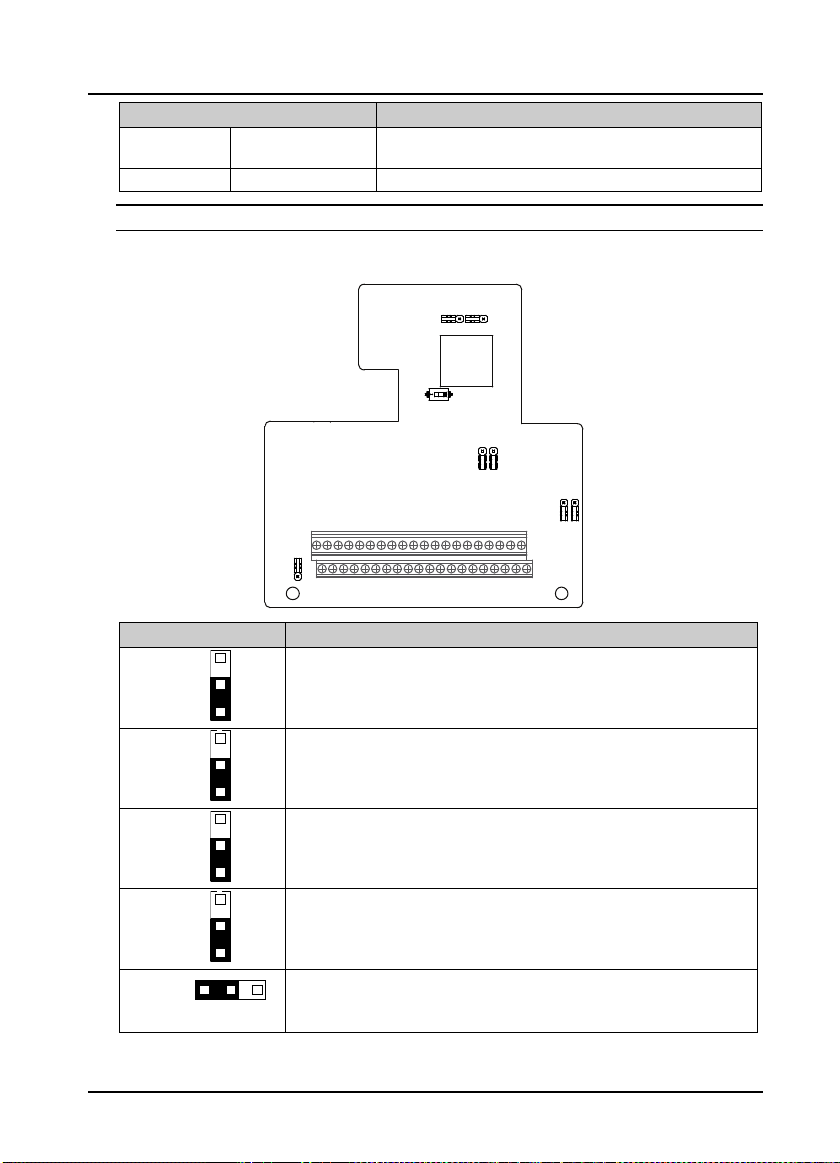
Do not supply power from the outside of the P24 terminal of the process card.
1.3 Environment Requirement
The environment should meet the following requirements:
Working temperature -10 - +50℃, air temperature change is less than 0.5℃/min
Storage environment
temperature -40 - +70℃
Operation place Indoor, not exposed to direct sunlight, no dust, soot, conductive dust, corrosive gas,
flammable gas, etc
Humitidy Less than 95%RH, no water condenses
Vibration resistance 3.5m/s2in 2 - 9Hz,10m/s2in 9 - 200Hz (IEC60721-3-3)
Level of protection IP20
Cass of pollution Level 2 (dry, non-conductive dust pollution)