3 - 3
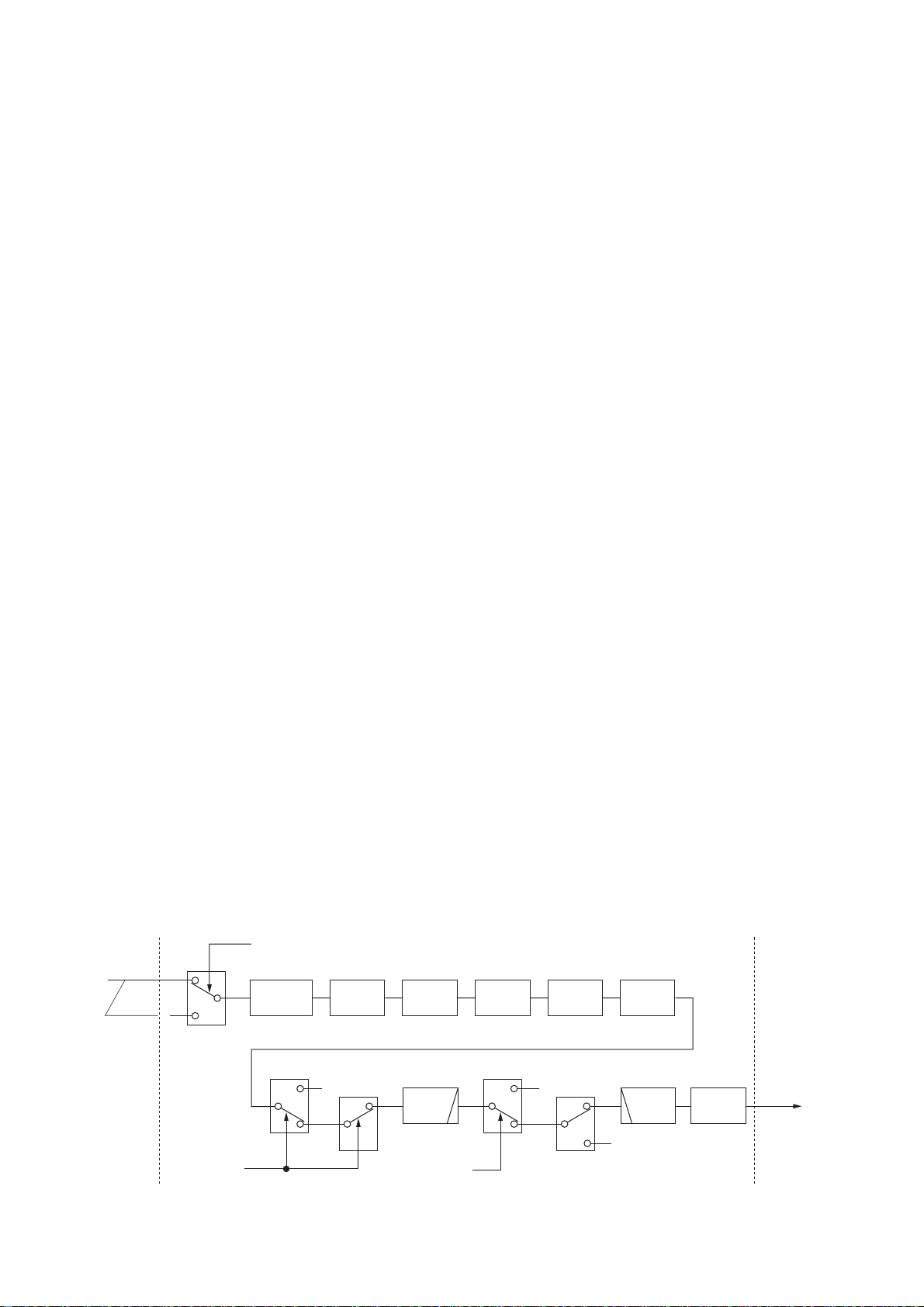
The converted signal is changed from a 5 V level signal to
a 3.3 V signal in the level converter (IC2051), and is then
applied to the DSP IC (IC2001) for 36 kHz digital IF filter,
demodulation, automatic notch and noise reduction, etc.
The output signal from the DSP IC (IC2001) is changed
from a 3.3 V level signal to a 5 V level signal in the level
converter (IC2502), and is applied to the D/A converter
(IC2351) to convert into the analog audio signals.
The converted audio signals are passed through the active
filter (IC2371a), AF amplifier (IC2371b), analog switches
(IC2372, pins 13, 14 and pins 1, 15) then applied to the
low-pass filter (IC2401, pins 5, 11). The filtered signals are
passed through the analog switches (IC2372, pins 3, 4 and
IC2473, pins 1, 7), high-pass filter (IC2441A) and mixer
amplifier (IC2471A), and then applied to the MAIN-A unit
via J2001 (pin 13) as the DRAF signal.
3-1-11 TWIN PBT CIRCUIT (DSP-A BOARD)
General PBT (Passband Tuning) circuit shifts the center fre-
quency of IF signal to electronically narrow the passband
width. The IC-756PROIII uses the DSP circuit for the digital
PBT function and actually shifts the both lower and higher
passbands of 3rd IF filter within ±1.8 kHz.
The twin PBT circuit in DSP IC (IC2001) controlled by the
[TWIN PBT] controller adjusts the 3rd IF passband width
and rejects interference.
3-1-12 AGC CIRCUIT (DSP-A BOARD)
The AGC (Automatic Gain Control) circuit reduces IF ampli-
fier gain and attenuates IF signal to keep the audio output
at a constant level.
The receiver gain is determined by the voltage on the
AGC line (IC2461, pin 4). The D/A converter (IC2461) for
AGC supplies control voltage to the AGC line and sets the
receiver gain with the [RF/SQL] control.
The 3rd IF signal from the level converter (IC2051) is
detected at the AGC detector section in DSP IC (IC2001),
and is applied to the D/A converter for AGC via the level
converter (IC2052). The AGC voltage is amplified at the
buffer amplifier (IC2471b), and is then applied to the
MAIN-A unit via J2001 (pin 16) to control the AGC line.
When receiving strong signals, the AGC voltage decreases
via the buffer amplifier (IC2471b). As the AGC voltage is
used for the bias voltage of the IF amplifier (RF-B unit;
Q1751), and IF amplifier gain is decreased.
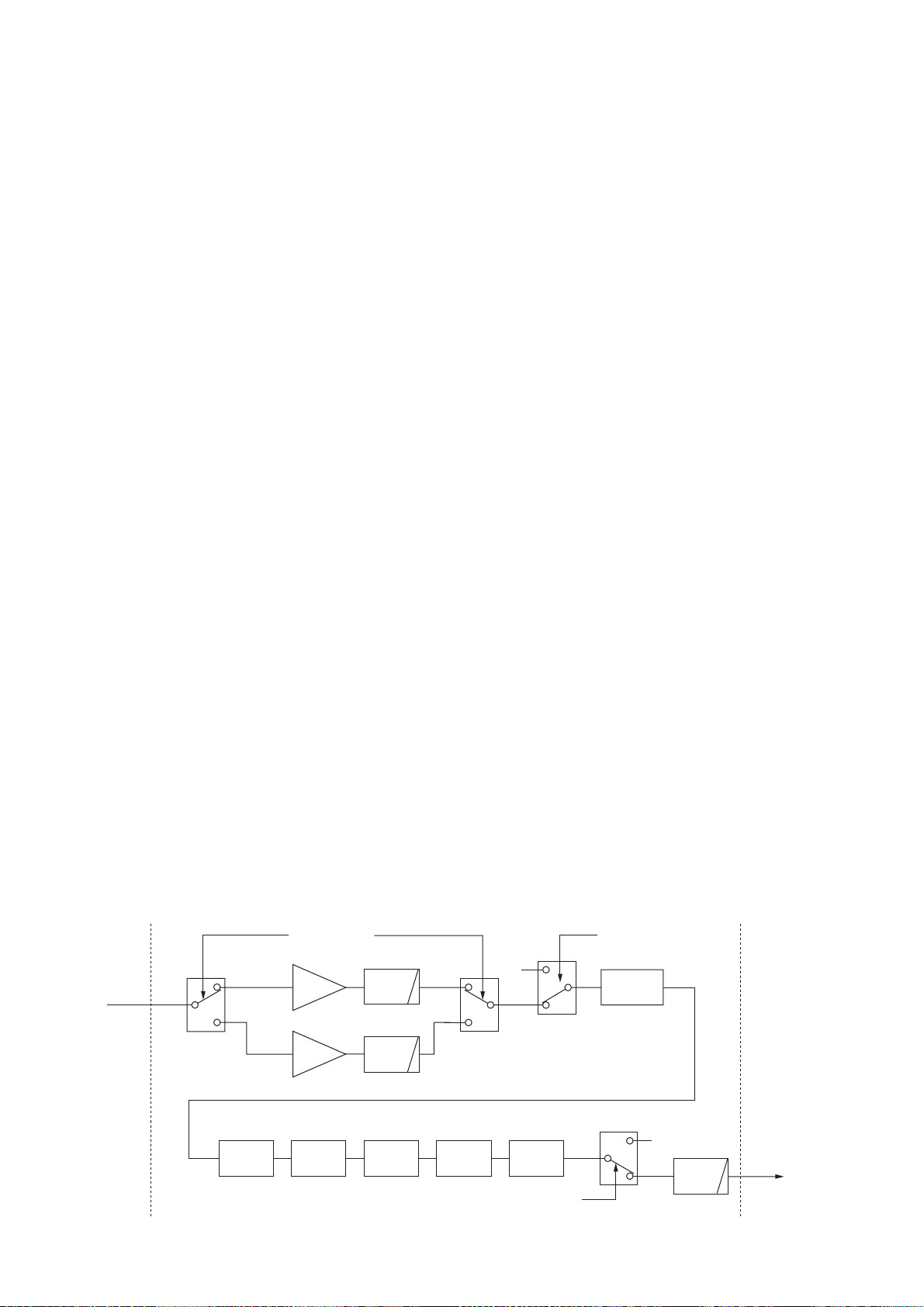
3-1-13 S-METER CIRCUIT (MAIN-A UNIT)
The S-meter circuit indicates the relative received signal
strength while receiving by utilizing the AGC voltage which
changes depending on the received signal strength.
A portion of the AGC bias voltage from the DSP-A board
is applied to the differential amplifier (IC101a, pin 2) where
the difference between the AGC and reference voltage is
detected.
The detected voltage is passed through the analog switch
(IC3631, pins 12, 14) as the SML signal and applied to the
main CPU (IC3501, pin 108) to activate the S/RF meter via
the sub CPU (DISPLAY board, IC401).
3-1-14 SQUELCH CIRCUIT (MAIN-A UNIT)
The squelch circuit mutes audio output when the S-meter
signal is lower than the [RF/SQL] setting level.
The S-meter signal is applied to the main CPU (IC3501, pin
108) and is compared with the threshold level set by the
[RF/SQL] control. The [RF/SQL] setting signal is applied to
the main CPU via the sub CPU (DISPLAY board; IC401,
pin 91). The main CPU analyzes the compared signal and
outputs control signal to the squelch gate (IC301, pin 5)
via the interface IC (IC3653, pin 19) to open or close the
squelch as the SQLS signal.
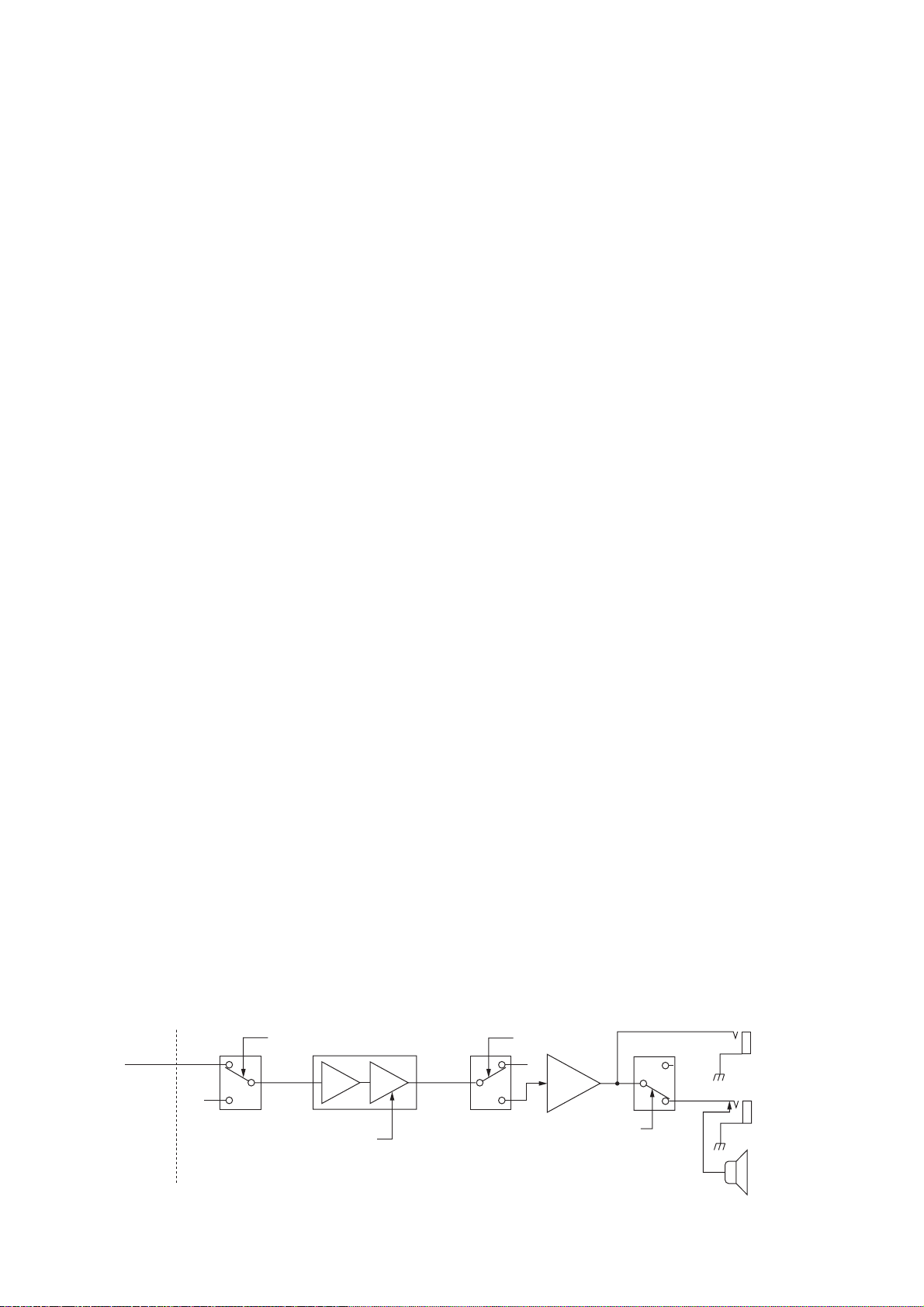
3-1-15 AF AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT (MAIN-A UNIT)
The AF amplifier amplifies the audio signals to a suitable
driving level for the speaker.
The AF signals (DRAF) from the DSP-A board are passed
through the squelch gate (IC301, pins 1, 7) and amplified
at the AF amplifier section of IC311 (pins 2, 4), and volume
is controlled by the AFGV signal at the VCA section (pins 7
–9). The volume controlled AF signals are passed through
the AF mute gate (IC331, pins 1, 7), then applied to the AF
power amplifier (IC332, pins 1, 4).
The amplified audio signals are passed through the SP
mute switch (RL351) and [EXT SP] jack then applied to the
internal speaker when no plug is connected to the jack.
The AF mute gate is controlled by the [AF] control via the
sub and main CPUs.
When headphones are connected, the SP mute signal from
the main CPU (IC3501, pin 56) is applied to the SP mute
switch (RL351) via the BUS driver (IC3654, pins 8, 13) as
the SPS signal.
[PHONES]
[EXT SP]
Int. speaker
IC332
AF
power
amp.
DRAF
• AF amplifier circuit
7
6
129
IC301 IC311
Mute switchSquelch gate
MAIN-A unitDSP-A board
“SQLS” signal
“AFGV” signal
56
7
1
IC331 RL351
“AFMS” signal
“SPS” signal
2
AMP VCA