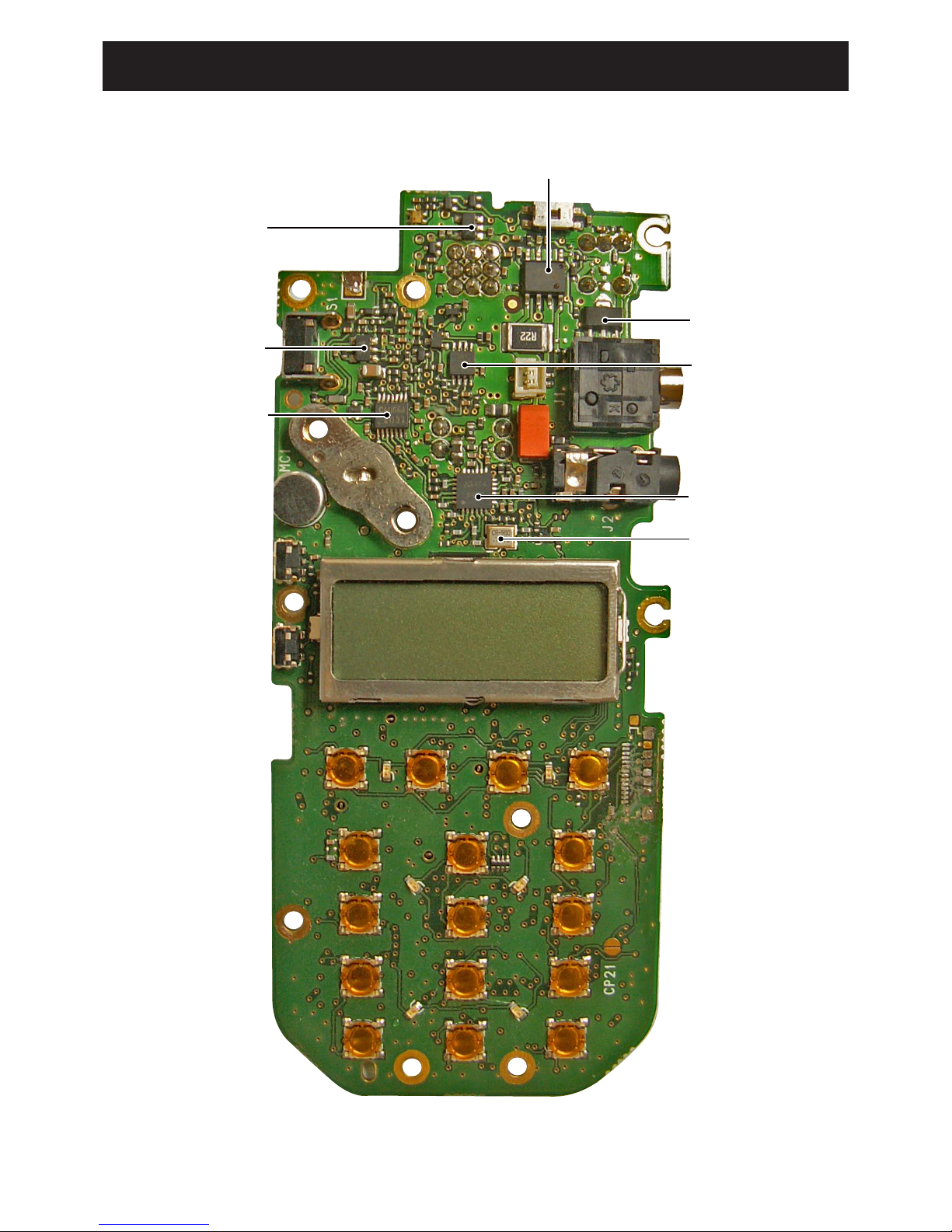
11,D12,D33
FREQUENCY
MODULATION
D13
BUFF
Q31
BUFF
Q30
TX VCO
From the TX AF circuits
To the TX AMP circuits
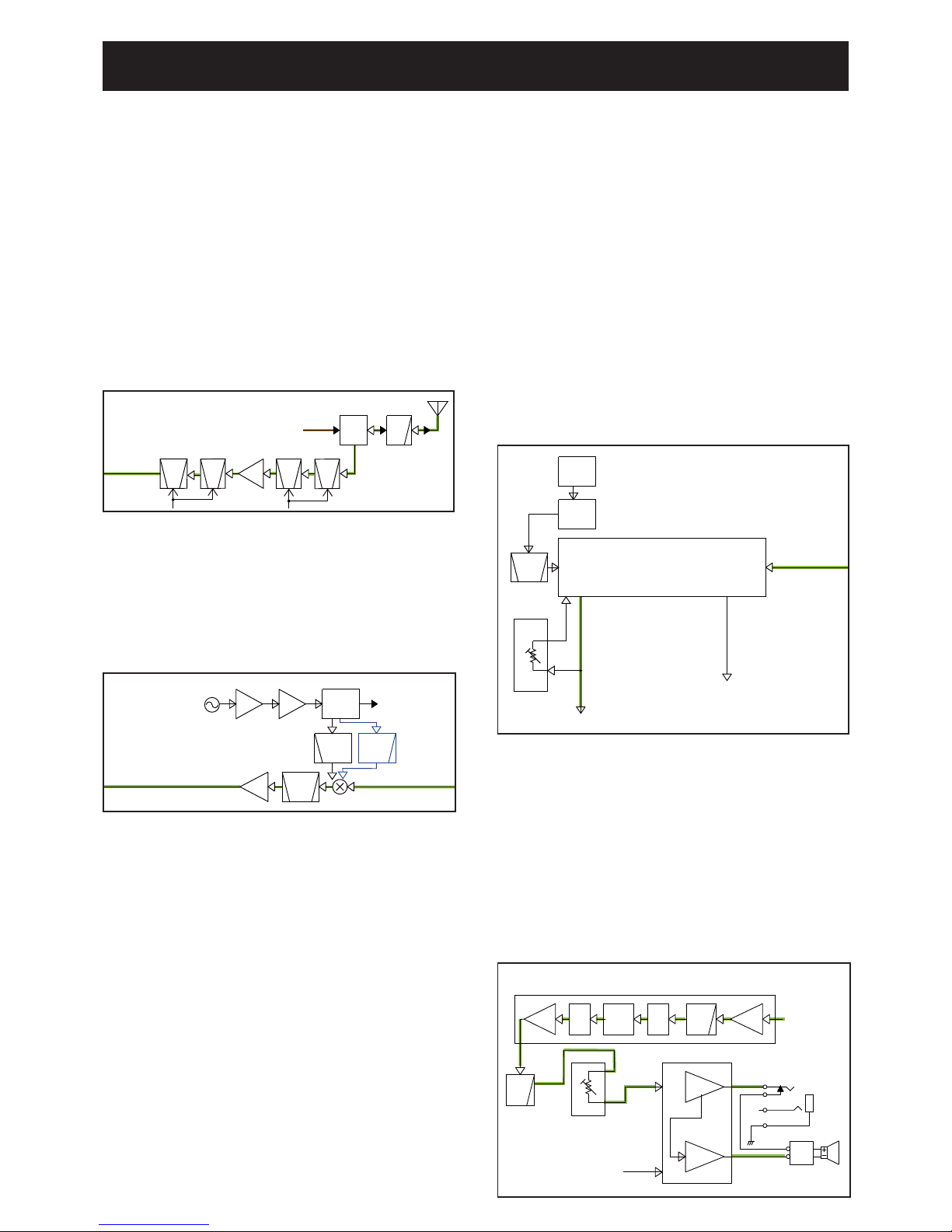
4-2 TRANSMIT CIRCUITS
TX AF CIRCUIT
The audio signal from the internal or external microphone
(MIC signal) is passed through the MIC gain SW (IC2) and
applied to the baseband IC (IC4).
The processed AF signal is passed through the AF
SW (IC2) and LPF (IC11), and then applied to the D/A
converter (IC10), which adjusts its level (=deviation). The
level-adjusted MIC signal is applied to the TX VCO as the
modulation signal.
MODULATION CIRCUIT
The modulation signal from the TX AF circuits is applied
to D13 of the TX VCO (Q27, D11 to D13 and D33). The
frequency-modulated signal from is amplified by two buffers
(Q30 and Q31), and then applied to the TX AMP circuit,
through the TX/RX SW (D16).
• TX AMPLIFIERS AND APC CIRCUIT
LPF
PWR
DET
D22,D23
ANT
SW
D19,D27
PWR
AM P
Q38
APC
AMP
IC17
DRIVE
AM P
Q36
ANT
From the
TX VCO
To the RX circuits
AMP
PRE
Q34
TX AMP CIRCUIT
The buffer amplified signal from the TX/RX SW (D16)
is sequentially amplified by the pre-AMP (Q34), drive
AMP (Q36) and power AMP (Q38). The power amplified TX
signal is passed through the antenna SW (D19) and LPF
(L29 to L31, C333, C347 to C350, C352 and C403), and
then applied to the antenna.
APC CIRCUITS
At the TX output power detector, the RF signal at the LPF
(L26, C303, C330, C353 and C355) is rectified by the
diodes (D22 and D23), and it is used as the TX power sens-
ing voltage.
The voltage is applied to the APC AMP (IC17), and the
output voltage controls the bias voltages of the drive AMP
(Q36) and power AMP (Q38) to keep the TX output power
constant.
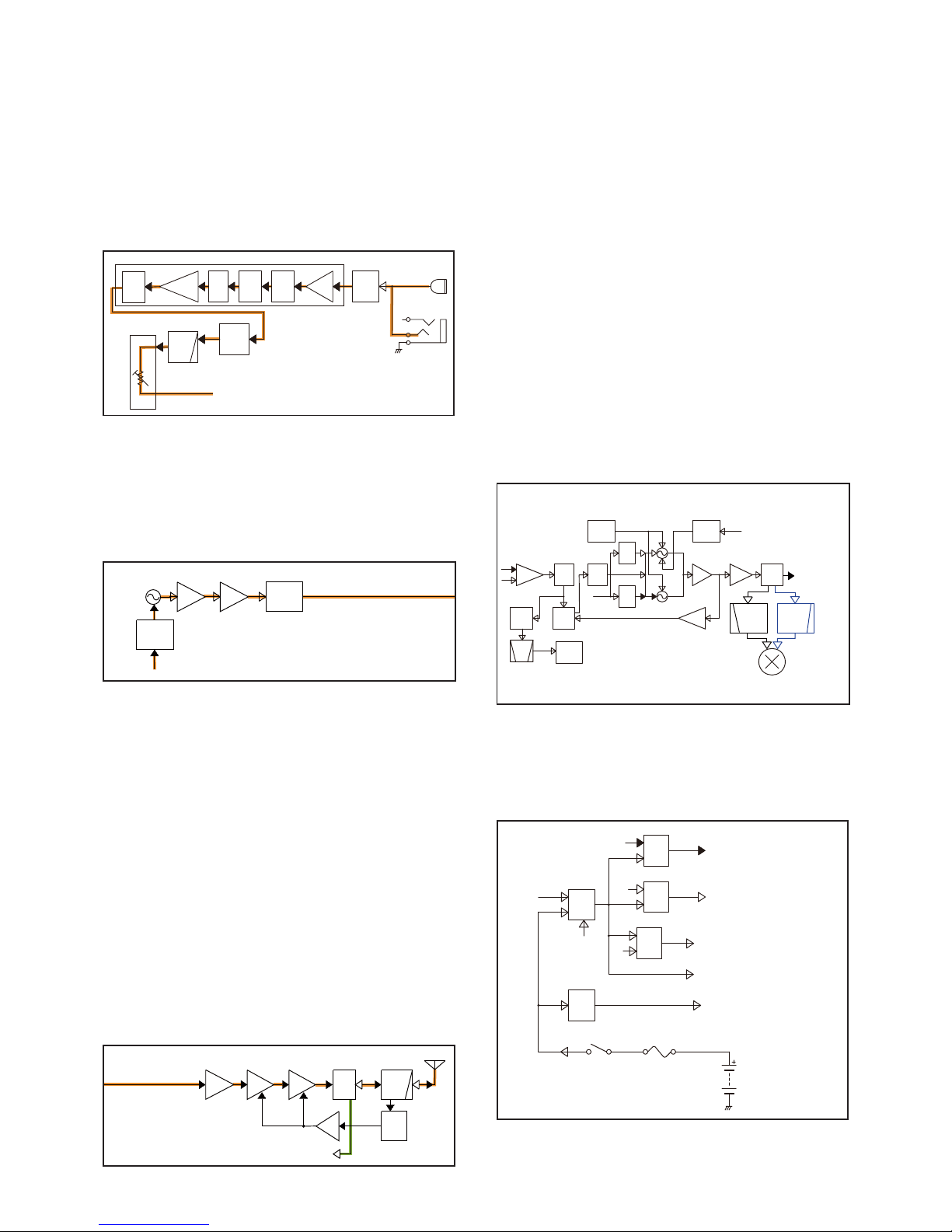
• FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER CIRCUITS
4-4 VOLTAGE BLOCK DIAGRAM
1st IF mixer
TX/RX
SW
D16
D17
Q25
D9,D10
Q27
D11,D12
FIL
RIPPLE
Q23
VCO
SW
Q29
FIL
LOOP
PLL
IC IC15
X3
Q26
Q37
BPF
BUFF
Q31
BUFF
Q30
BUFF
Q32
X3
CR-794
TCXO
LV
ADJ
D11
LV
ADJ
D10
BUFF
IC7
IF IC
R5V
RX VCO
TX VCO
IC16
REF
BAL
15.3MHz
45.9MHz
LV
LVA
×2
To the TX AMPs
HPF** LPF*
To the TX circuits
To the RX circuits
To both RX and TX circuits
To both RX and TX circuits
To the logical circuits
F1
12
T5
REG
Q17
REG
+5V
IC20
REG
S5
Q15
BATTERY_1
BT1
S5
REG
R5
Q16
CPU5
REG
IC6
S5C
VCC
R5C
+5V
T5C
S5V
R5VPWON
VCC
CPU5
T5V
4-3
FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER CIRCUITS
The RX VCO is composed of Q25, D9, D10 and D32. The
output signal is amplified by two buffers (Q31 and Q31) and
applied to the 1st IF mixer (Q37), through the LO SW (D17)
and LO filter (LPF*: L41, C296 and C441, or HPF**: L21,
L42 and C293).
The TX VCO is composed of Q27, D11 to D13 and D33.
The output signal is amplified by two buffers (Q30 and Q31)
and applied to the pre-AMP (Q34), through the LO SW (D16).
A portion of oscillated VCO output signal from each VCO is
fed back to the PLL IC (IC15), through the buffer (Q32) and
LPF (L11, C210 and C231).
The applied VCO output signal is divided and phase-
compared with a 15.3 MHz reference frequency signal from
the TCXO (X3), which is also divided. The resulting signal
is output from the PLL IC (IC15), and DC-converted by the
loop filter, and then applied to the VCO as the lock voltage.
When the oscillation frequency drifts, its phase changes
from that of the reference frequency, causing a lock voltage
change to compensate for the drift in the VCO oscillating
frequency.
*:For [EUR] and [UK] versions.
**:For except [EUR] and [UK] versions.