UK
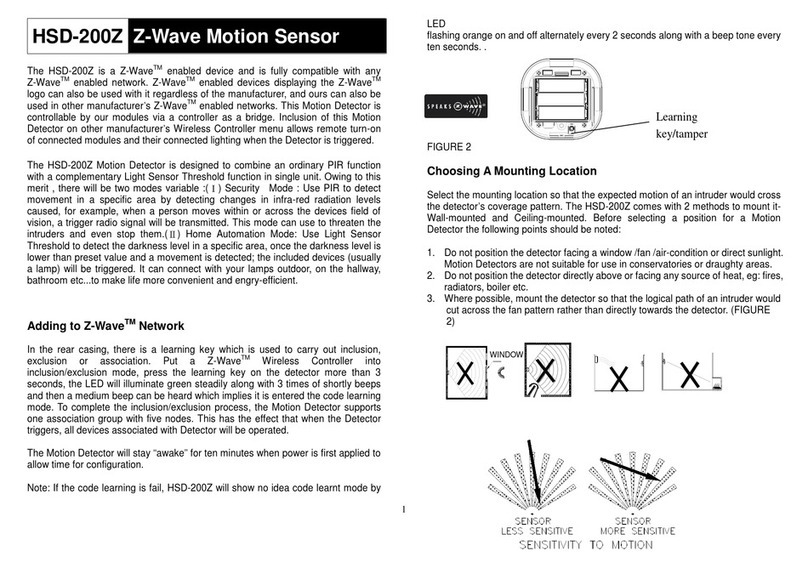
Info card
Inductive sensors
21
Operating voltage The voltage range in which the sensor functions reliably. A stabilised and smoothed
direct voltage should be used! Take into account residual ripple!
Utilisation category AC units: AC-140 (control of small electromagnetic loads with holding currents
< 200 mA)
DC units: DC-13 (control of solenoids)
Hysteresis Difference between the switch-on and the switch-off point.
Short-circuit protection ifm sensors which are protected against excessive current by means of a pulsed
short-circuit protection. The inrush current of incandescent lamps, electronic relays
and low resistance loads may cause this protection to cut in and turn the sensor off!
Standard target Square-shaped steel plate (e.g. S235JR) of a thickness of 1 mm with a side length
equal to the diameter of the sensing face or 3 x S
n
, depending on which value is the
highest.
Product standard IEC 60947-5-2
Repeatability Difference between any two S
r
measurements. Max. 10 % of S
r
.
Leakage current Current for the internal supply of 2-wire units; also flows through the load when the
output is blocked.
Switch point drift The shifting of the switch point owing to changes in the ambient temperature.
Switching frequency Damping with standard target at half S
n
. The
ratio damped to undamped (tooth to gap) = 1 : 2.
2a
a
a
S
n
2
Protection rating IPxy According to IEC 60529
IP68 Test condition: 1 m water depth for 7 days
IP69K To ISO 20653 (replacement for DIN 40050-9)
Current consumption Current for the internal supply of 3-wire DC units.
Transport and
storage conditions
Unless otherwise indicated in the data sheet, the following applies:
Transport and storage temperature:
Min. = - 40 °C.
Max. = max. ambient temperature according to the data sheet.
The relative air humidity (RH) must not exceed 50 % at +70 °C.
At lower temperatures, a higher air humidity is permissible.
Shelf life: 5 years.
Transport and storage height: no restrictions.
Degree of soiling Inductive proximity sensors are designed for degree of soiling 3.
Maintenance, repair and disposal If used correctly, no maintenance and repair measures are necessary.
Only the manufacturer is allowed to repair the unit.
After use dispose of the unit in an environmentally friendly way in accordance with
the applicable national regulations.
i
This info card is to be regarded as a supplement to the main position sensors catalogue and to the individual data
sheets. For further information and contact addresses please visit our homepage at www.ifm.com.
Intended use
While in use the products are exposed to influences which may have an effect on function, life, quality and reliability of
the product.
It is the customer’s responsibility to ensure that the products are suitable for the intended application. This applies in
particular to applications in hazardous areas and with adverse environmental influence such as pressure, chemicals,
temperature fluctuations, moisture and radiation as well as mechanical stress, especially if the products are not installed
properly.
Using the products in applications where the safety of people depends on the function of the product is not permitted.
Non-compliance may result in death or serious injuries.
Operating principle of an inductive proximity switch
Coil and capacitor form an LC resonant circuit, also called
basic sensor.
Eddy current losses in electrically-conductive materials are
used for a switching signal.
①
Connection
⑤
Coil
②
Housing
⑥
Alternating electromagnetic field = active zone
③
Downstream electronics
⑦
Target = electrically conductive material
④
Capacitor
Important Glossary
Active zone / active face Area above the sensing face in which the sensor reacts to the approach of the target.
Output function Normally open: object within the active zone
> output is switched.
Normally closed: object within the active zone
> output is blocked.
Programmable: choice between normally closed or normally open.
Positive switching: positive output signal (to L-).
Negative switching: negative output signal (to L+).
Rated insulation voltage AC units depending on UB: 140 V AC or 250 V AC
DC units with protection class II: 250 V AC
DC units with protection class III: 60 V DC
Rated short-circuit current for short-circuit-proof units: 100 A
Rated impulse withstand voltage AC units depending on UB: 140 V AC = 2.5 kV or 250 V AC = 4 kV
(≙ overvoltage category III)
DC units with protection class II: 4 kV (≙ overvoltage category III)
DC units with protection class III: 0.8 kV (≙ overvoltage category II)
Power-on delay time The time the sensor needs to be ready for operation after application of the operating
voltage (in the millisecond range).
1D2226 / 06 11 / 2018