Output Module CR2011
2
Contents
1 Preliminary note � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 3
2 Safety instructions � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 3
3 Function and features� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 3
4 Function � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 4
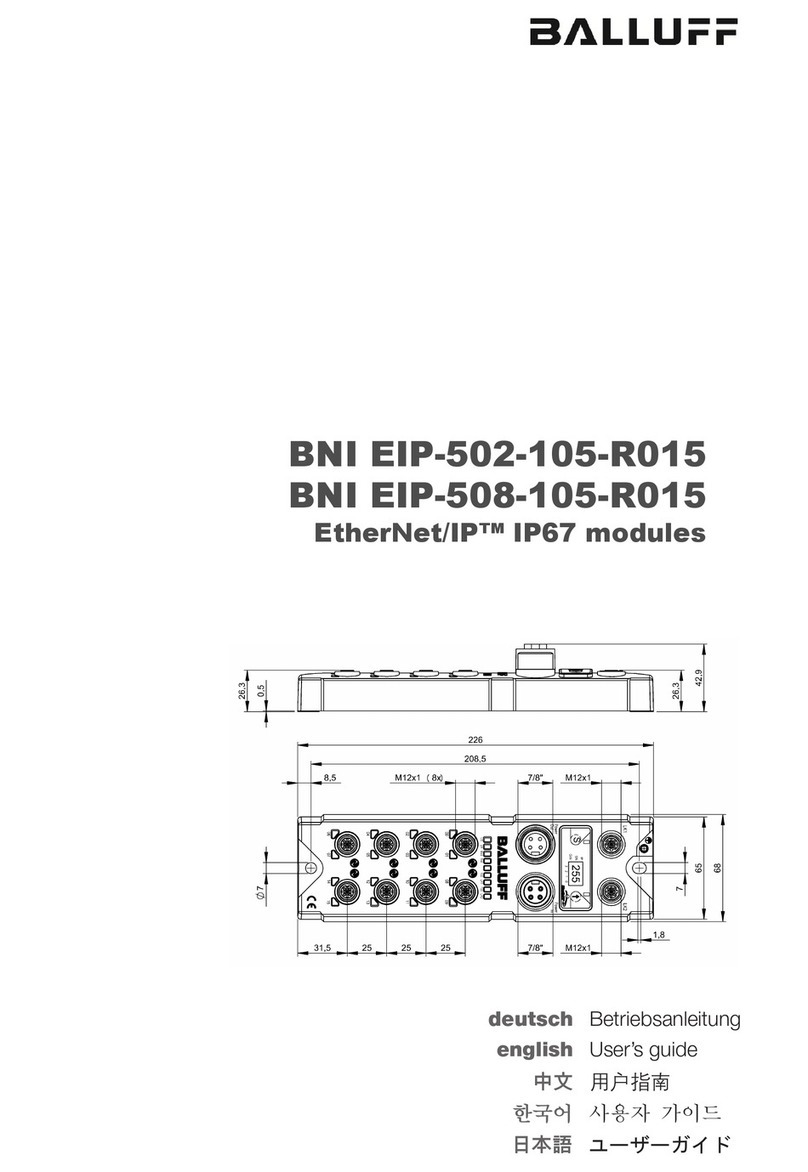
5 Dimensions and mounting � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5
6 Electrical connection� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5
6�1 Wiring � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5
6�2 Outputs without current monitoring � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5
6�3 Outputs with current monitoring � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 6
7 Operating indicators � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 6
8 Set-up � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 7
8�1 PLC configuration in CODESYS 2�3 � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 7
8�2 PLC configuration in CODESYS 3�5 � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 8
8�2�1 Heartbeat configuration � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 8
8�2�2 SyncMonitoring � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 9
8�3 Electronic Data Sheet� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 9
9 Parameter setting � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 10
9�1 Parameter list � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 10
10 Technical data� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � �11
10�1 Characteristics of the outputs� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � �11
10�1�1 Digital outputs � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � �11
10�1�2 PWM outputs � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 12
10�1�3 Current outputs � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 12
11 Object directory� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 13
11�1 Manufacturer Specific Profile Area; index 2000 to 5FFF � � � � � � � � � � � � 13
11�2 Communication Profile Area; index 1000 to 1FFF � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 15
12 Fault correction� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 18
12�1 EMCY Object � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 18
13 Maintenance, repair and disposal� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 19
14 Declaration of conformity � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 19
15 Terms and abbreviations� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 19