Industrial Scientific DSX-L User guide

Start-up
Guide
DSX-L Local Server Mode
Edition: 9
January 24, 2020
Part Number: 17156008

ii
Industrial Scientific Corporation.
Pittsburgh, PA USA
Shanghai, China
© 2015, 2016, 2017, 2019, 2020 Industrial Scientific Corporation
All rights reserved. Published 2020
Revision 9
DSXDocking Station is a trademark of Industrial Scientific Corporation.
iNet Instrument Networkis a trademark of Industrial Scientific Corporation.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Industrial Scientific Corporation Phone: 412-788-4353
1 Life Way Toll Free: 1-800-DETECTS (338-3287)
Pittsburgh, PA 15205-7500 USA Fax: 412-788-8353
Service: 1-888-788-4353
Web: www.indsci.com
Although every effort is made to ensure accuracy, the specifications of this product and the
content herein are subject to change without notice.

iii
Warnings and Cautionary Statements
WARNING: Failure to perform certain procedures or note certain conditions may impair the
performance of this product. For maximum safety and optimal performance, please read and
follow the procedures and conditions listed below.
•Use of this product in areas where it may be subject to large amounts of electromagnetic
interference may affect the reliable operation of this device and should be avoided.
•Sources of large amounts of interference could be and are not limited to:
oOperation near high radio frequency fields (near 2-way radio transmission
antennas where the RF fields may greatly exceed 10 V/M, etc.).
oAC Power Mains that may have excessive power surges / spikes /
transients (from large AC motors operating heavy loads which may induce
voltage sags and, etc.).
NOTE: This product has been tested to, and passes all EMC requirements to EN 61326:1998
Electrical Equipment for Measurement, Control and Laboratory Use for Type 2 (Industrial)
Apparatus, as well as FCC Part 15, Class A emissions levels when installed to the requirements
outlined within this manual. Mandatory compliance to these standards help to ensure controlled,
reliable operation of this device when exposed to typical levels of electromagnetic interference
as well as ensuring that this device is not source of emissions that might interfere with other
equipment installed nearby.
NOTE: Per 30 CFR 75.320(b), the DSX docking station tests for oxygen deficiency of MSHA
approved oxygen detectors compatible with the DSX that can detect 19.5% oxygen with an
accuracy of ± 0.5%.
NOTE: Per 30 CFR 22.7(d)(2)(i), the acceptable limit during calibration and bump testing with
2.5% methane must be 10% for MSHA approved instruments using Industrial Scientific certified
calibration gas.
NOTE: The DSX has an internal pump that controls the flow of gas being delivered to the
system. As a result of the internal pump, a demand flow regulator must be used in conjunction
with this calibration and bump test station.
NOTICE: The software associated with this product contains open source components. To
obtain licensing and related information about these components, click here.

iv

Table of Contents
ABOUT THIS MANUAL............................................................................................................................................3
1.1. DOCUMENT OVERVIEW...............................................................................................................................3
INTRODUCTION .......................................................................................................................................................5
2.1. OVERVIEW ..................................................................................................................................................5
2.2. FEATURES ...................................................................................................................................................5
2.3. COMPONENTS OF THE DOCKING STATION NETWORK..................................................................................6
2.3.2. Docking Station Server Admin Console (DSSAC) Overview.................................................................6
2.3.3. Instrument Docking Station (IDS) Overview .........................................................................................6
2.4. REQUIRED NETWORK CONNECTIONS ..........................................................................................................7
2.5. BEFORE GETTING STARTED.........................................................................................................................9
GETTING STARTED...............................................................................................................................................11
3.1. INTRODUCTION..........................................................................................................................................11
3.2. REQUIREMENTS FOR SOFTWARE INSTALLATION .......................................................................................11
3.2.1. Server Requirements............................................................................................................................11
3.2.2. Browser Requirements.........................................................................................................................14
3.2.3. SQL Server Requirements....................................................................................................................14
3.2.4. Additional Requirements and Warnings ..............................................................................................15
3.3. INSTALLING MICROSOFT INTERNET INFORMATION SERVICES (IIS) AND MICROSOFT MESSAGE QUEUING
(MSMQ) .................................................................................................................................................................16
3.3.1. Overview..............................................................................................................................................16
3.3.2. IIS and MSMQ on Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012, and Windows Server 2012 R2 ......16
3.3.3. Installing IIS and MSMQ on Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2............................22
3.3.4. Installing IIS and MSMQ on Windows 7, Windows 8, and Windows 10 .............................................27
3.4. INSTALLING THE DOCKING STATION SERVER (DSS) SOFTWARE...............................................................31
3.5. LOADING THE INSTALLER SOFTWARE .......................................................................................................31
3.6. INSTALLATION WIZARD FOR DSS .............................................................................................................34
3.7. DATABASE PREPARATION OPTIONS FOR FIRST TIME INSTALLATIONS.......................................................36
3.7.1. Overview..............................................................................................................................................36
3.7.2a. Install SQL Server/SQL Server Express Instance and a New DSS Database on This Machine ..........39
3.7.2b. Install New DSS Database to an Existing SQL Server/SQL Server 2008 Express Instance on This
Machine39
3.7.2c. Attach to an Existing DSS Database Available on My Network..........................................................41
3.8. CONTINUING INSTALLATION (OR INSTALLATION AFTER UNINSTALLING A PREVIOUS VERSION)...............42
3.8.1a. Use SQL Server/SQL Server Express on this Machine and Connect to the Existing DSS Database...43
3.8.1b. Attach to an Existing DSS Database Available on My Network..........................................................44
3.9. SELECTING THE DATABASE OPTION..........................................................................................................45
3.9.1a. Install SQL Server Express on This Machine and Use Existing DSS Database ..................................46
3.9.1b. Attach to an Existing DSS Database Available on My Network..........................................................47
3.10. ACCESSING THE DOCKING STATION SERVER ADMIN CONSOLE (DSSAC) THROUGH A BROWSER............49
3.11. THE DOCKING STATION CONFIGURATOR ..................................................................................................51
3.11.1. Installing the Docking Station Configurator Software ........................................................................51
3.11.2. Running the Docking Station Configurator Software ..........................................................................53
3.12. ASSIGNING A STATIC IP ADDRESS TO A SEVER OR PC ..............................................................................53
3.13. DISABLING THE DS2 BROADCASTER.........................................................................................................56
3.14. CONFIGURING THE FIREWALL ...................................................................................................................57
3.14.1. Windows Firewall Settings for SQL Server............................................................................................57
CONFIGURING THE DOCKING STATION .......................................................................................................63
4.1. INTRODUCTION..........................................................................................................................................63
4.2. INSTRUMENT DOCKING STATION HARDWARE OVERVIEW ........................................................................63
4.3. SETTING UP AN INSTRUMENT DOCKING STATION .....................................................................................66

4.4. INSTRUMENT DOCKING STATION STATUS AND PROPERTIES......................................................................67
4.5. REMOVING AN INSTRUMENT DOCKING STATION.......................................................................................74
4.6. CONFIGURING GAS CYLINDERS.................................................................................................................74
4.7. ADDING GAS FROM INDUSTRIAL SCIENTIFIC.............................................................................................78
4.8. ADDING GAS FROM A THIRD PARTY..........................................................................................................80
4.9. CHANGING GAS CYLINDERS......................................................................................................................81
4.10. SUPPORTED SENSORS................................................................................................................................83
4.11. USING IGAS...............................................................................................................................................84
6.12 MANIFOLD INSTRUCTIONS...............................................................................................................................86
BASIC OPERATION................................................................................................................................................89
5.1. INTRODUCTION..........................................................................................................................................89
5.2. MENU OPTIONS .........................................................................................................................................89
5.3. LED AND ALARM SIGNALS.......................................................................................................................91
5.4. FORCED BUMP TESTS................................................................................................................................94
5.5. CALIBRATION............................................................................................................................................95
5.5.1. Forced Calibrations.............................................................................................................................95
5.5.2. O2 Sensor Failures..............................................................................................................................96
5.6. DOWNLOAD AND CLEARING DATALOG DATA...........................................................................................96
5.6.1. Forced Datalog Download ..................................................................................................................96
5.6.2. Clearing Datalog Data........................................................................................................................97
5.7. IDS DIAGNOSTICS.....................................................................................................................................98
5.8. INSTRUMENT DOCKING STATION OPERATING GUIDELINES.......................................................................99
5.8.1. General................................................................................................................................................99
5.8.2. Cleaning.............................................................................................................................................100
5.8.3 Explanation of Symbols Used on Unit ...............................................................................................100
5.8.4 Specifications.....................................................................................................................................101
5.8.5. Regulatory Notices.............................................................................................................................101
5.8.6. Wiring Requirements .........................................................................................................................102
EVENT SCHEDULING..........................................................................................................................................103
6.1. INTRODUCTION........................................................................................................................................103
6.2. GLOBAL EVENTS.....................................................................................................................................104
6.2.1. Global Instrument Docking Station Events........................................................................................104
6.2.2. Global Instrument Events ..................................................................................................................107
6.3. SPECIAL EVENTS .....................................................................................................................................110
6.4. DSX-L DEFAULTS FOR SCHEDULED EVENTS..........................................................................................113
WARRANTY...........................................................................................................................................................114
Limitation of Liability ......................................................................................................................................114
CONTACT INFORMATION .......................................................................................................................................116

About This Manual
Chapter
1
1.1. Document Overview
This documentation is designed to assist with the start-up of the DSX-L Local Server Mode. For
day-to-day operation and detailed information about using the features of the docking station,
please see the manual included on the CD provided with the DSX-L.
This start-up guide contains the following main sections:
•Chapter 2: Introduction - Begin with this section to learn about the main components and
an overview of the functionality.
•Chapter 3: Getting Started - This section provides an introduction to the Docking Station
Server Admin Console (DSSAC), the web-based user interface through which
administrative tasks are performed by the safety team. It also provides minimum server
and browser requirements for proper installation and operation of the DSS and DSSAC
software. An overview of the Broadcaster is also provided, as well as how to enable and
disable this feature.
•Chapter 4: Configuring the Docking Station –This section explains how to setup the
docking station for operation. It includes explanations of status, properties, setup and
removal, , manifold instruction, gas cylinder configuration, and connections using iGas.
•Chapter 5: Basic Operation –This section explains the basic operation of the docking
station. It includes topics such as user interface menu options, LED and alarm signals,
forced bump tests, forced calibrations, downloading and clearing datalog data, IDS
diagnostics, and operating guidelines.
•Chapter 6: Event Scheduling –This section provides an overview of global and special
events, and explains how they are used in the docking station system.
For information about installing the DSX-L, please see Administrator’s Guide, DSX-L Local
Server Mode.
NOTE: Throughout this document, the term server –when used alone –refers to either a PC or
server running the DSS software.


Introduction
Chapter
2
2.1. Overview
DSX-L provides the capabilities for fleet management and the scheduling and automatic
performance of testing, calibration, and battery charging for the following Industrial Scientific
instruments:
•Tango™TX1 Single-Gas Monitor
•Ventis™ Pro4 Multi-Gas Monitor
•Ventis™ Pro5 Multi-Gas Monitor
•SafeCore™ Module
•Ventis™ MX4 Multi-Gas Monitor
•Ventis™ LS Multi-Gas Monitor
•MX6 iBrid™ Multi-Gas Monitor
•GasBadge® Pro
DSX-L and its software are installed to function as a system where data reside on a
company’s internal computer network (or PC). The remainder of this guide refers to this
type of installation.
2.2. Features
Features of the docking station system include the following.
•Ability to operate from a server or stand-alone PC.
•Ability to handle up to 100 Instrument Docking Stations (IDS) with one docking station.
•One fresh air input and two or five gas inputs.
•Built-in Smart charger on each IDS for rechargeable instruments.
•Simplified feedback on the IDS via 3 LEDs (red, yellow, and green), and an audible
alarm.
•A graphical user interface tool (DSSAC) that allows an administrator to view operations
on each IDS from a network computer.
•Ability to schedule calibrations, bump tests, diagnostic tests and datalog data downloads
globally for all IDSs, or on an instrument-specific basis.
•Multilingual user interface (English, French, Spanish, or German) on the IDS display as
well as in the DSSAC application.
•Storage of instrument data in a central database.
•Option to use the Industrial Scientific supplied run-time database or the customer’s own
existing MicrosoftSQL Server.
•Option to implement Industrial Scientific Corporation’s iNet solution, gas detection as a
service.
•Optional iGas configuration for automatic configuration of gas cylinders on an IDS.
6
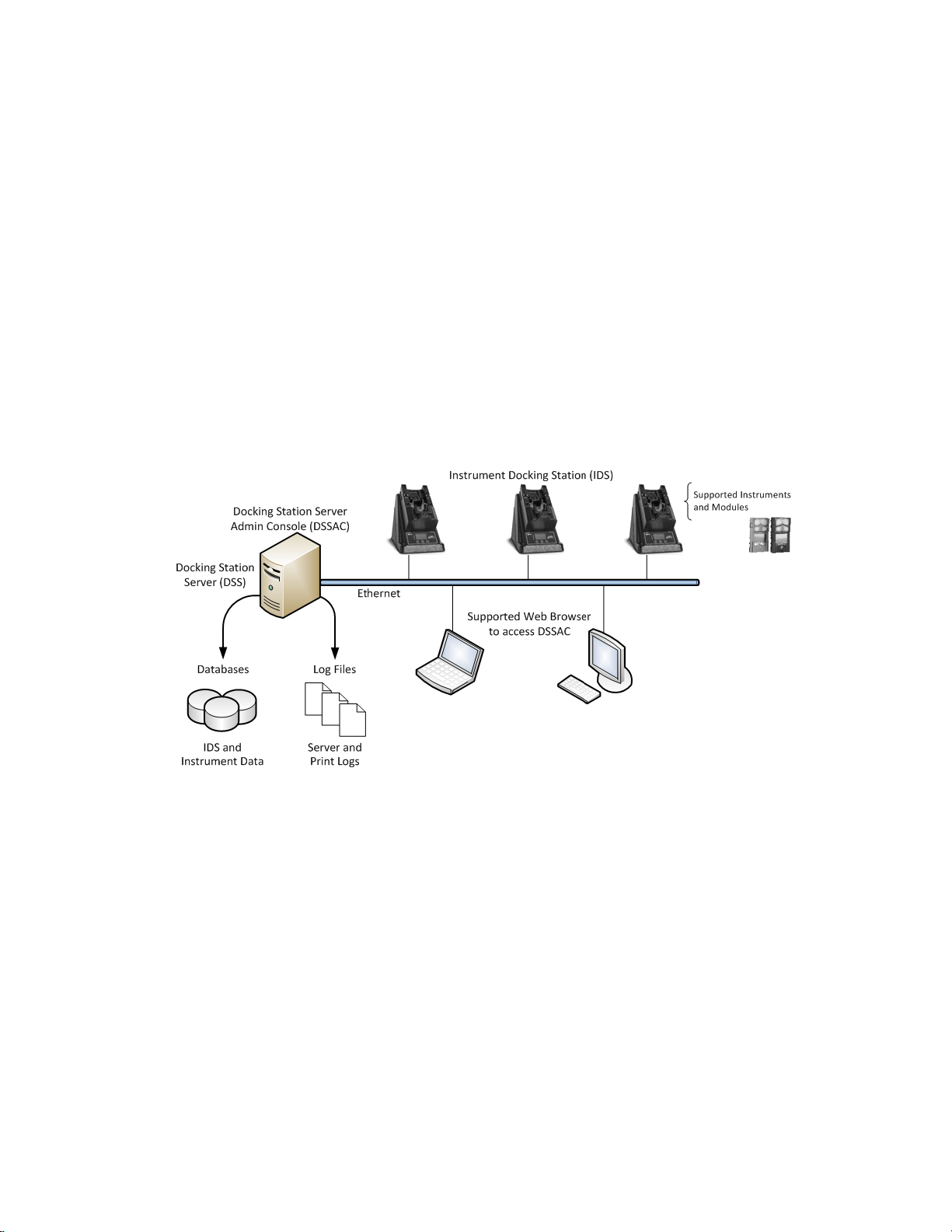
2.3. Components of the Docking Station Network
The DSX-L network consists of at least three (3) components:
•a Docking Station Server (DSS)
•the Docking Station Server Admin Console (DSSAC) application
•multiple Instrument Docking Stations (IDSs).
Refer to Figure 2-1. An introduction to each of these components can be found in the next three
sections.
2.3.1. Docking Station Server (DSS) Overview
The Docking Station Server (DSS) is a computer (server of PC) that controls the entire docking
station network. The DSS sends information to—and retrieves information from—IDSs and the
instruments docked in them. IDS and instrument data, such as calibration and bump test results,
are stored in databases that are controlled by the DSS. Refer to Figure 2-1.
Figure 2-1. Sample Docking Station Network
2.3.2. Docking Station Server Admin Console (DSSAC) Overview
The DSS is administered using the Docking Station Server Admin Console (DSSAC) web
application. DSSAC is used by the safety team to manage instrument data, view IDS status, and
manage DSS configurations.
Before using the DSSAC for the first time, read Chapter 3 Getting Started for an overview of the
application’s user interface. Chapter 4 contains information about setting up and using IDSs.
2.3.3. Instrument Docking Station (IDS) Overview
An Instrument Docking Station (IDS) is the device into which an instrument is placed for use in
the DSS. When docked, an instrument is ready for automatic calibrations, bump tests, diagnostic
tests, and datalog data downloads, all of which are controlled by the DSS. An IDS also serves as
a battery charger for instruments with rechargeable batteries.
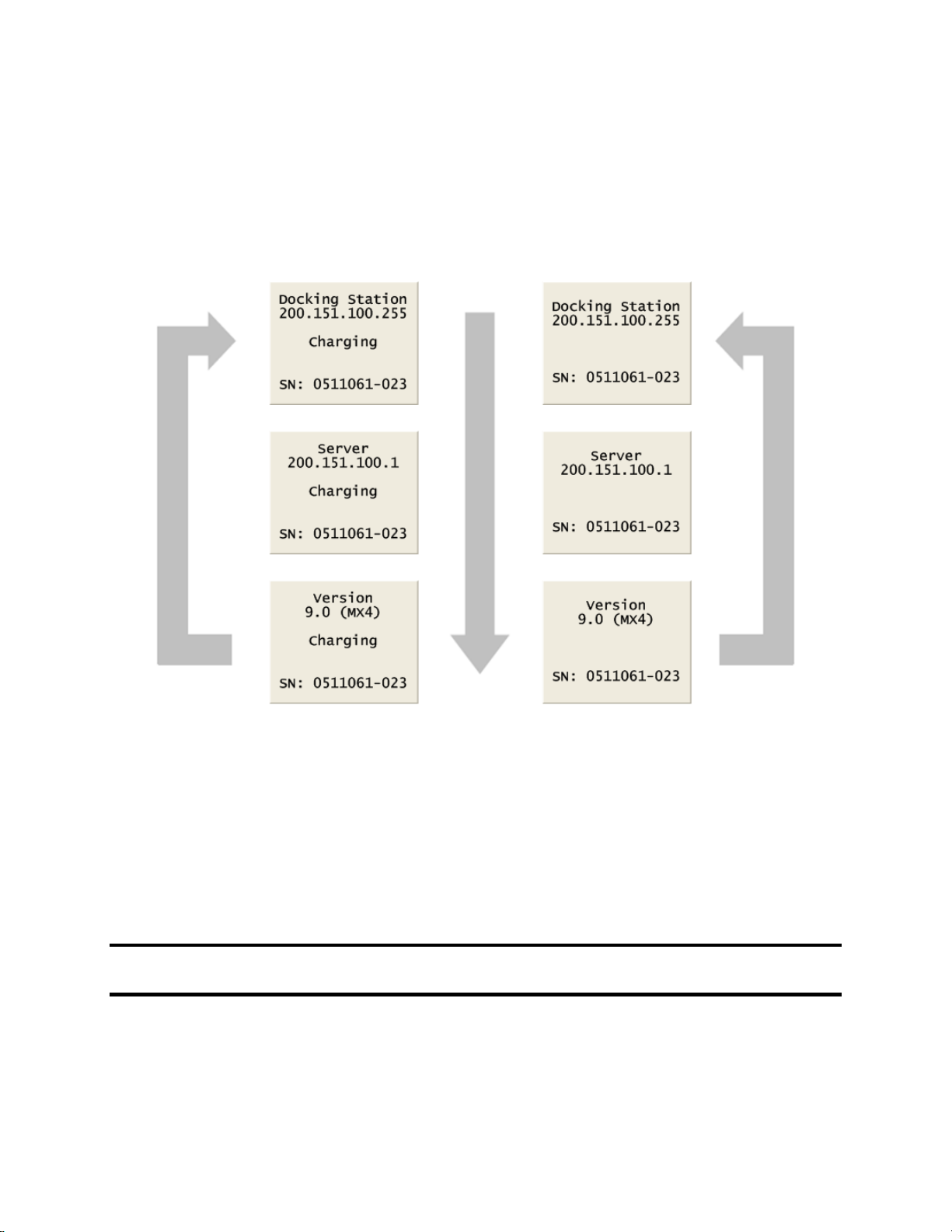
7
An IDS contains an LCD panel that displays a menu used to perform tasks on an instrument or
on the IDS itself. The menu is controlled using a keypad on the IDS. When the menu is not in
use, the LCD panel shows the current activity of the IDS. The IDS also contains LED lights and
an audible alarm to provide you with additional feedback about current activity and status of the
IDS.
When idle, the IDS cycles through three screens of information, as shown below. Each screen is
shown for 10 seconds.
Figure 2-2. Sample LCD Panel Idle Displays (While and While Not Charging)
Additional details about how to use the features of an IDS are covered in the following sections:
•Chapter 4: Configuring the Docking Station
•Chapter 5: Basic Operation
2.4. Required Network Connections
Below is a summary of the required network connections needed for the DSX-L to function.
NOTE: Throughout this document, the term server—when used alone—refers to either a PC or
server running the DSS software.

8
Table 2-1. Required Network Connections
Connection
Requirements
Browser to
DSSAC web
application
Open the web browser. Supported web browsers include:
•Internet Explorer 10 (or above)
•Google Chrome (latest)
•Mozilla Firefox (latest)
•Apple Safari (latest)
Navigate to the following URL:
http://<server_name_or_ip_address>/dssws
or
https://<server_name_or_ip_address>/dssws
Server to SQL
Server
The DSS server uses ODBC to access the SQL Server databases it uses.
This ODBC connection is established using the server names, users, and
passwords in the web.config file.
There are a total of 3 databases the DSS needs access to: DSS, DSSDL, and
DSSUSERDIR.
These databases can be local or remote.
The database can use SQL Server 2014 Express SP1 Edition or SQL Server.
To verify that the server machine can reach the database, try establishing an
ODBC connection using the user, password, and server name from the
web.config file.
Each IDS must be able to reach the server, and the server must be able to
reach the IDS(s).
To IDS(s)
This communication is XML over http, using TCP/IP.
This takes place on port 80.
The IDS posts XML to an ASP.NET page running under IIS. The ASP.NET
page used by the IDSs is shown below.
http://<server_ip_address>/DSSWS/Server.aspx
or
https://<server_ip_address>/DSSWS/Server.aspx
Each IDS contacts the server once each minute, unless the IDS is in the
middle of a long operation, in which case it contacts the server after the
operation is over.
The IDS learns the server IP address either by listening for the broadcaster (if
you are using it), or by being programmed with the server IP using
DS.Config.
The Server learns of the IDS IP when the IDS contacts the server (the server
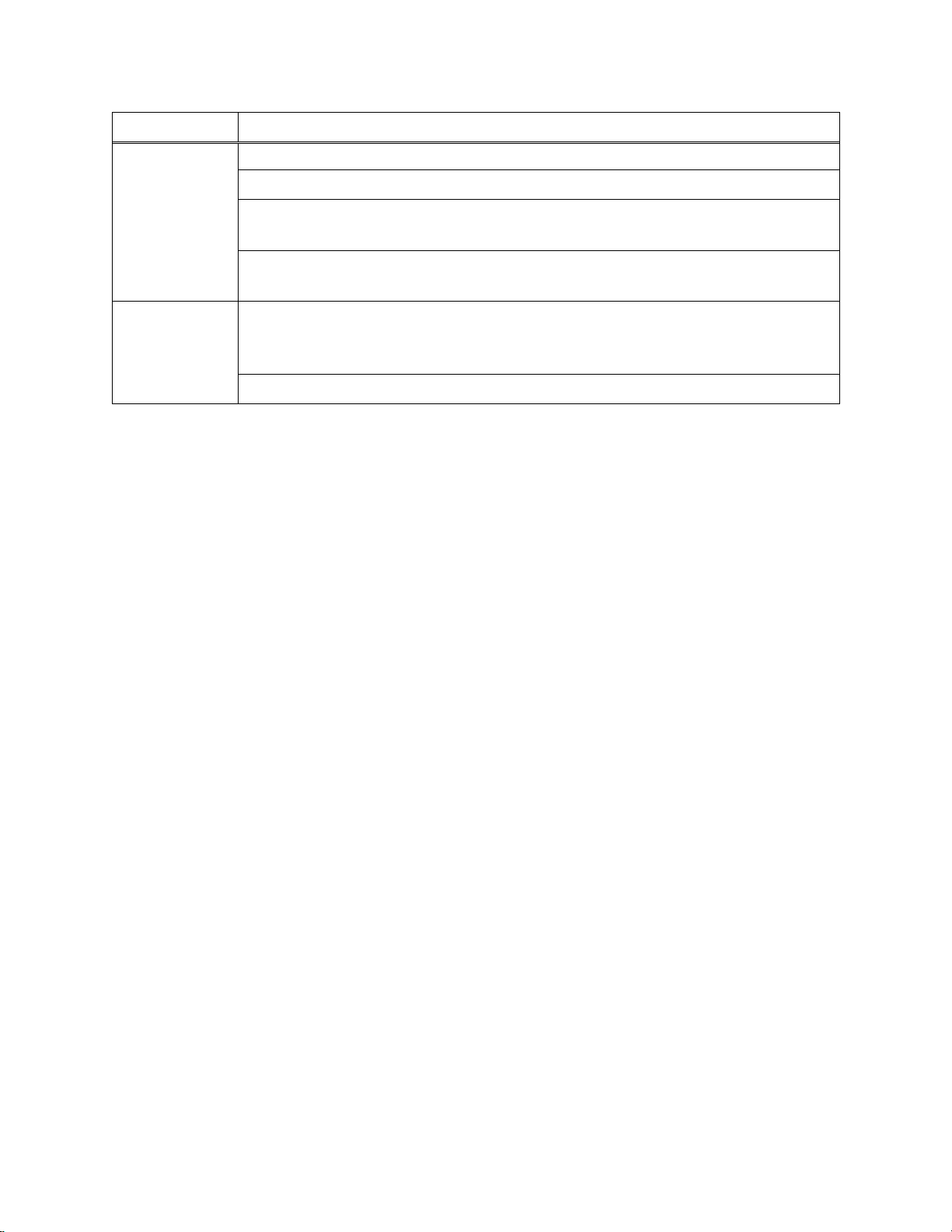
9
Connection
Requirements
merely replies).
The IDS can have either a dynamic or static IP address.
If a static IP address is used, you must set the address on the IDS using
HyperTerminal and a serial cable.
To verify the IDS is reaching the server, turn on the tracelog and look for
messages from the IDS in question. If there are any, it is reaching the server.
Broadcaster to
Network
The “DS2 Broadcaster” is a service that runs on the DSS server, broadcasting
the IP address of the DSS server, to be received by any IDS and/or DSSAC
running on the network.
The broadcasts take place from the server via UDP on port 55555.
2.5. Before Getting Started
Before getting started, please note the following:
1. The DSSAC windows client has been replaced with a web interface starting with v9.6.
2. The DSSAC web interface does not need to be installed separately; it is part of the DSS
installation.
3. DSSAC v9.5 windows client or earlier users can log in to the DSSAC web interface with
their existing DSSAC credentials. However, on first login into DSSAC web, DSSAC
web forces users to update their password. Once a user’s password has been updated,
that user will no longer be able to login with the DSSAC windows client.
4. If users are running DSSAC v9.5 or earlier to connect to DSS v9.6 or above, they cannot
create, update, or delete user accounts in the system.
Below is a list of features that are currently supported in DSSAC v9.5 or below, and have been
discontinued starting with DSSAC v9.6:
•Adding instruments manually to the system is no longer supported.
•Adding or removing bump and calibration records manually is no longer supported.
•Adding or removing components on legacy instruments is no longer supported.


Getting Started
Chapter
3
3.1. Introduction
This chapter explains how to install the DSS Software package onto a computer system to be
used on either a server-based operating system or a PC-based system. It also explains how to
begin using the DSSAC application to administer your DSX-L system.
This chapter is divided into the following topics:
•Requirements for software installation
•Installing Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS)
•Installing Microsoft Message Queuing (MSMQ)
•Installing the Docking Station Server (DSS) software
•Loading the installer software
•Installation wizard for DSS
•Database preparation options for first time installations
•Selecting the database option
•Accessing the Docking Station Server Admin Console (DSSAC)
•Installing and running the Docking Station Configurator software
•Assigning a static IP address to a sever or PC
•Disabling the DS2 Broadcaster
•Configuring Windows firewall
•Specifying the DSS IP address
Each of these topics is explained in the sections that follow.
3.2. Requirements for Software Installation
Before installing the software make sure that your PC and Server meet the following minimum
requirements.
3.2.1. Server Requirements
•Processor: 1.4 GHz (or higher)
•Memory: 4 GB RAM (or higher)
•Hard disk: 20 GB free disk space
•Supported operating systems:
oWindows 7 SP1

12
oWindows Server 2008* SP2 with Windows Hotfix KB980368 (upgrades only;
new installations not supported)
oWindows Server 2008 R2 SP1
oWindows 8(.x)
oWindows 10
oWindows Server 2012
oWindows Server 2012 R2
oWindows Server 2016
*NOTE:If opening DSSAC in a web browser results in a “Server Error” page, navigate to:
Support > Windows Server 2008>Hotfix KB980368 and install the Hotfix.
•Supported operating system languages (for installation and running):
oEnglish
oFrench
oGerman
oSpanish
oCzech
oPolish
oRussian
oOther Western Europe Latin-based languages (i.e., “Latin-1” languages per
Windows) should also work, but have not been specifically tested. These include:
Afrikaans, Basque, Catalan, Danish, Dutch, Faeroese, Finnish, Galician (Spain),
Icelandic, Indonesian, Italian, Malay, Norwegian, Portuguese, Swahili, and
Swedish.
oThe SQL Server (or SQL Server 2014 Express SP1 Edition) database must be
configured to use a Collation type within the Windows Latin codepage of 1252.
(NOTE: If the DSX-L database has any other collation type, it prevents the DSS
software from functioning properly.) The SQL Server (or SQL Server 2014
Express SP1 Edition) will automatically default to “collation type” within the
proper codepage of 1252 if installed under the Latin-based languages listed above.
Installing SQL Server under a non-Latin-based operating system may result in a
non-Latin collation type for the DSX-L database. Database administrators also
have the ability to change a database’s collation type. Changing the collation type
of the DSX-L database to anything other than a Latin collation type is not
supported.
•Internet Information Services (IIS) must be installed to the operating system if not
already present (may require the Operating System CD)
•Message Queuing (MSMQ) must be installed to operating system (may require the
operating system CD).
NOTE: Server software is supported on English, French, German, Spanish, Czech, Polish, or
Russian operating systems. Other Latin-based language operating systems may work, but they
have not been fully tested.
13
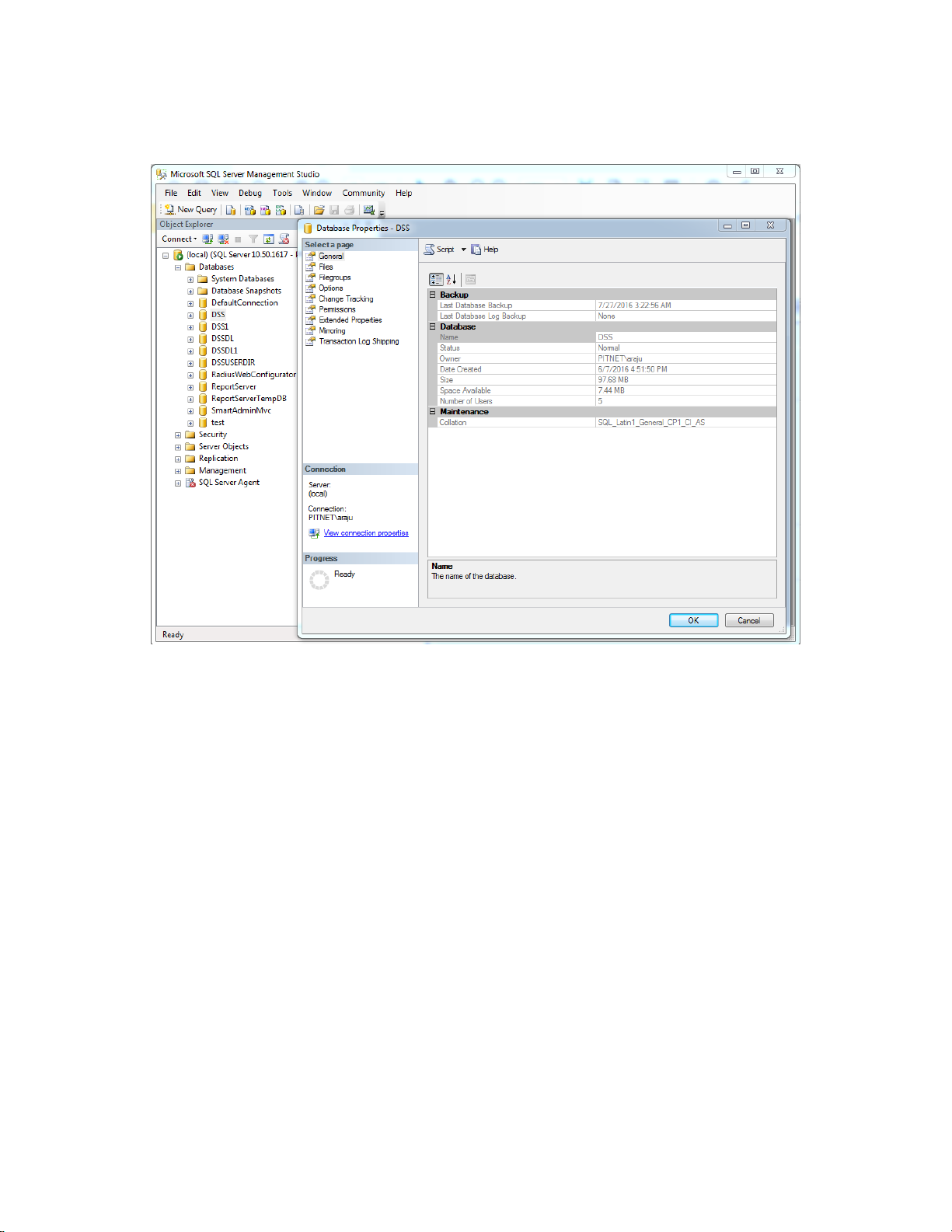
The collation type of the database can be seen using SQL Server Enterprise manager and
examining the Properties of a database as in the screenshot below.
Figure 3-1. Determining the Collation Type of a Database
Although the DSS may run under non-English operating systems as described above, for it to
successfully communicate data back and forth between docking stations necessitates that the
English-US regional settings for Number formatting remain in their default state. That is, even if
the DSS is running under a non-English-US language, it is necessary that the settings for
English-US remain at their defaults. The default Number settings are shown below. If any of
these defaults are modified, then the DSS may be unable to properly communicate data with
docking stations.

14
Figure 3-2. Default English-US Regional Options for “Numbers”
3.2.2. Browser Requirements
The DSSAC application is best viewed with the following browsers:
•Internet Explorer (10 or above)
oRequires ActiveX scripting to be enabled
•Google Chrome (latest version)
•Mozilla Firefox (latest version)
•Apple Safari (latest version)
3.2.3. SQL Server Requirements
•Installation Type 1 “Install new SQL Express and a new DSS Database on this machine”:
SQL server 2014 SP1 will be installed as a part of DSX-L software installation. No prior
database is needed.
•Installation Type 2 “Install new DSS to an existing SQL/ Server/SQL Express on this
machine”: SQL server 2008 R2 and above is required.

15
•Installation Type 3 “Attach to an existing DSS database available on my network”: SQL
server 2008 R2 and above is required.
•Upgrades, where SQL server is already running with Databases attached: SQL 2005 and
above is required.
3.2.4. Additional Requirements and Warnings
WARNING: When connecting a single IDS to either a server or PC, an Ethernet cross over
cable must be used. If you are connecting multiple IDSs to a network, standard Ethernet cables
must be used.
WARNING: If you are installing the DSS software on a server or PC, any network device must
be connected to the PC via an Ethernet Cable, for the software to install. Simply connecting a
DSX-L or any other network device such as a hub or router to the server or PC will be adequate.
If no devices are connected to the computer, the DSS will not install.
NOTE: Throughout this document, Internet Information Services will be referred to as IIS, and
Message Queuing will be referred to as MSMQ.
Prior to installing the DSS software, IIS must be installed to the Operating System if it is not
already present. Installing this Windows service requires the Operating System CD.
The DSS installer will check for “prerequisite” programs during DSS installation. If prerequisite
programs are not found in the machine, DSS installer will display the message below:
For Windows versions starting from v6.1 (Windows 7)
At this time, the user can go back and install the IIS using the procedures outlined on the
following pages.

16
3.3. Installing Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS) and
Microsoft Message Queuing (MSMQ)
3.3.1. Overview
Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS) and Microsoft Message Queuing (MSMQ) must be
installed before installing the DSX-L software. The procedures for installing IIS and MSMQ
differ based on the version of the operating system that is used, namely:
•Windows Server 2016
•Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2
•Windows 7, Windows 8, and Windows 10
•Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2 with Windows Hotfix KB980368
Separate sections are provided for explaining the IIS and MSMQ installation processes under
each of these systems. Refer to the appropriate section below.
3.3.2. IIS and MSMQ on Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012, and
Windows Server 2012 R2
Step
Instruction
1.
Navigate to Server Manager.
2.
Click on Manage; choose Add Roles and Features.
Other manuals for DSX-L
1
Table of contents
Other Industrial Scientific Docking Station manuals