— 1 —
Solenoid Valve F Series
EtherNet/IP Compliant
1 Contents
1 Contents..............................................................................................................1
2 Revision History....................................................................................................3
3 Glossary ..............................................................................................................3
4 Major Parts and Functions ......................................................................................5
4-1 Power, communications, and FG connectors ........................................................5
4-2 Indicator panel ...............................................................................................5
4-3 Hardware switch settings .................................................................................6
4-3-1 Network address setting switch, HOLD/CLEAR switch......................................6
4-3-2 Host address setting switch ........................................................................6
5 EDS file ...............................................................................................................7
6 IP address settings................................................................................................7
6-1 Specify using the host address switches .............................................................7
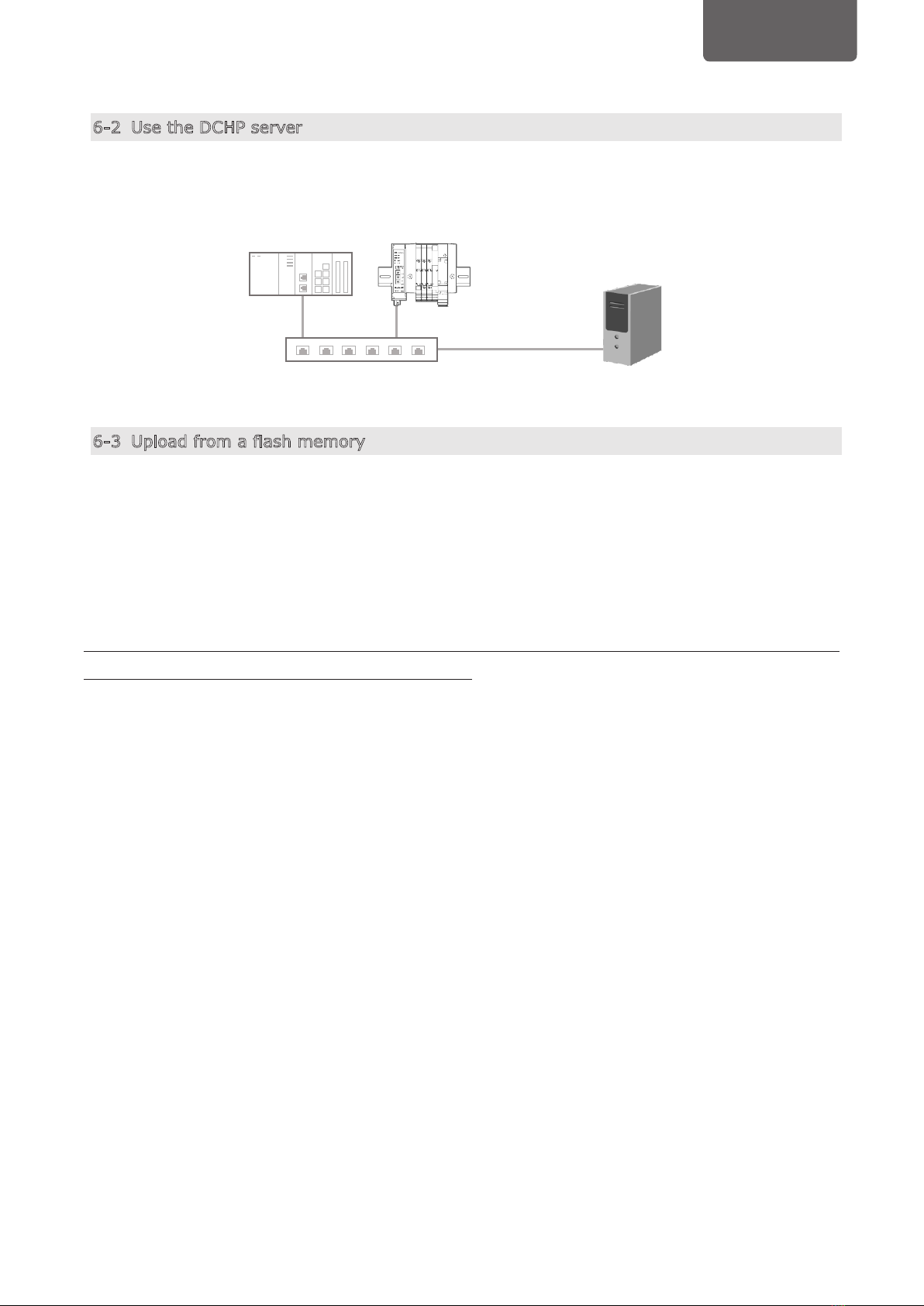
6-2 Use the DCHP server .......................................................................................8
6-3 Upload from a flash memory.............................................................................8
7 Relationship between I/O data allocation and solenoid valves ......................................9
8 Network topology................................................................................................10
8-1 Line format .................................................................................................. 10
8-2 Star format .................................................................................................. 10
8-3 Device level ring format ................................................................................. 11
9 CIP class objects.................................................................................................11
9-1 Identity (class code: 01 hex) .......................................................................... 11
9-1-1 Service code........................................................................................... 11
9-1-2 Attribute ................................................................................................ 12
9-1-3 Reset service .......................................................................................... 12
9-2 TCP/IP interface (class code: F5 hex)............................................................... 13
9-2-1 Service code........................................................................................... 13
9-2-2 Attribute ................................................................................................ 13
9-3 Ethernet Link (class code: F6 hex)................................................................... 15
9-3-1 Service code........................................................................................... 15
9-3-2 Attribute ................................................................................................ 15
9-4 Device Level Ring (class code: 47 hex)............................................................. 16
9-4-1 Service code........................................................................................... 16
9-4-2 Attribute ................................................................................................ 16
9-5 Quality of Service (class code: 48 hex)............................................................. 17
9-5-1 Service code........................................................................................... 17
9-5-2 Attribute ................................................................................................ 17
9-6 Discrete Output Point (class code: 09 hex) ....................................................... 17