Contents
Leuze electronic RS4 4
6.5.3 Protective field contour and reference boundary........................................................................................................36
6.6 Mobile danger zone guarding on DTSs ......................................................................................................................36
6.6.1 Basic requirements.....................................................................................................................................................37
6.6.2 Minimum distance D ...................................................................................................................................................37
6.6.3 Protective field dimensions ........................................................................................................................................39
6.6.4 Test mode for MotionMonitoring.................................................................................................................................39
6.7 Mobile side guarding on DTSs....................................................................................................................................40
7 Technical data ............................................................................................................................................................41
7.1 Safety..........................................................................................................................................................................41
7.2 Optics..........................................................................................................................................................................41
7.3 Protective field ............................................................................................................................................................42
7.4 Warning field...............................................................................................................................................................42
7.5 Measured data............................................................................................................................................................42
7.6 Electrical power supply ..............................................................................................................................................43
7.7 Software......................................................................................................................................................................44
7.8 Ambient conditions .....................................................................................................................................................44
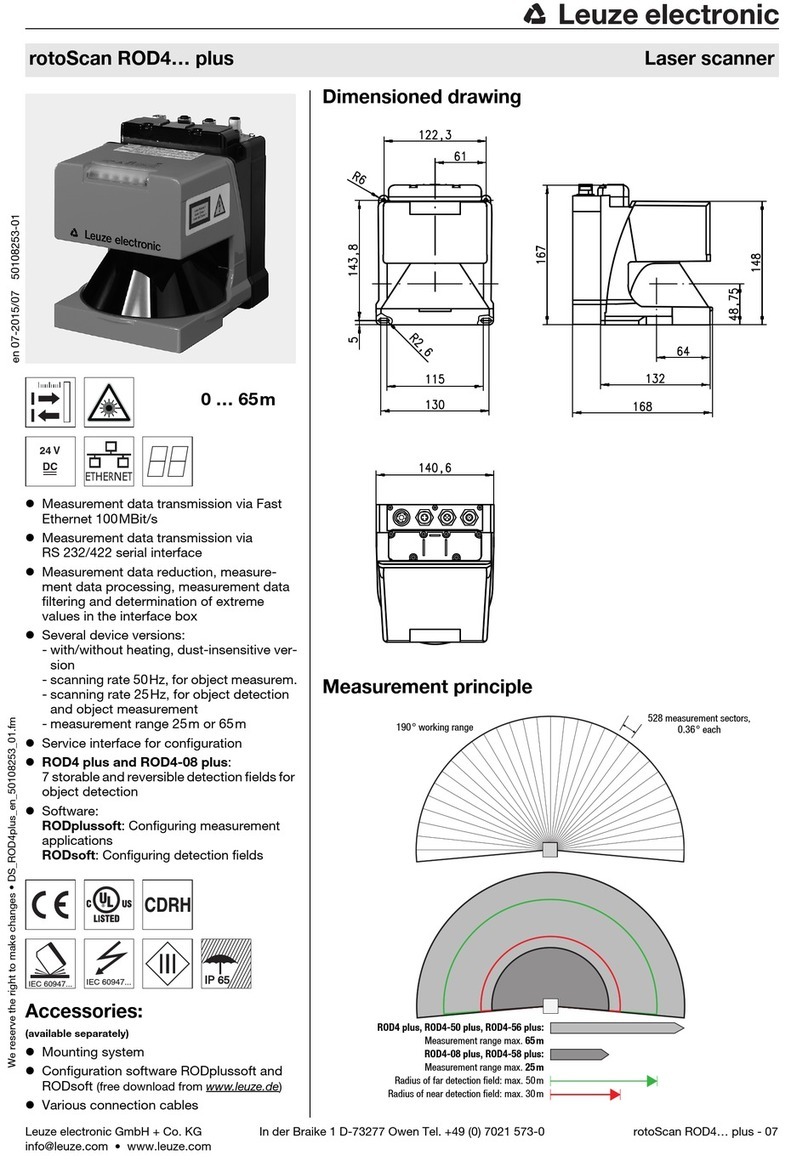
7.9 Dimensions, weight.....................................................................................................................................................45
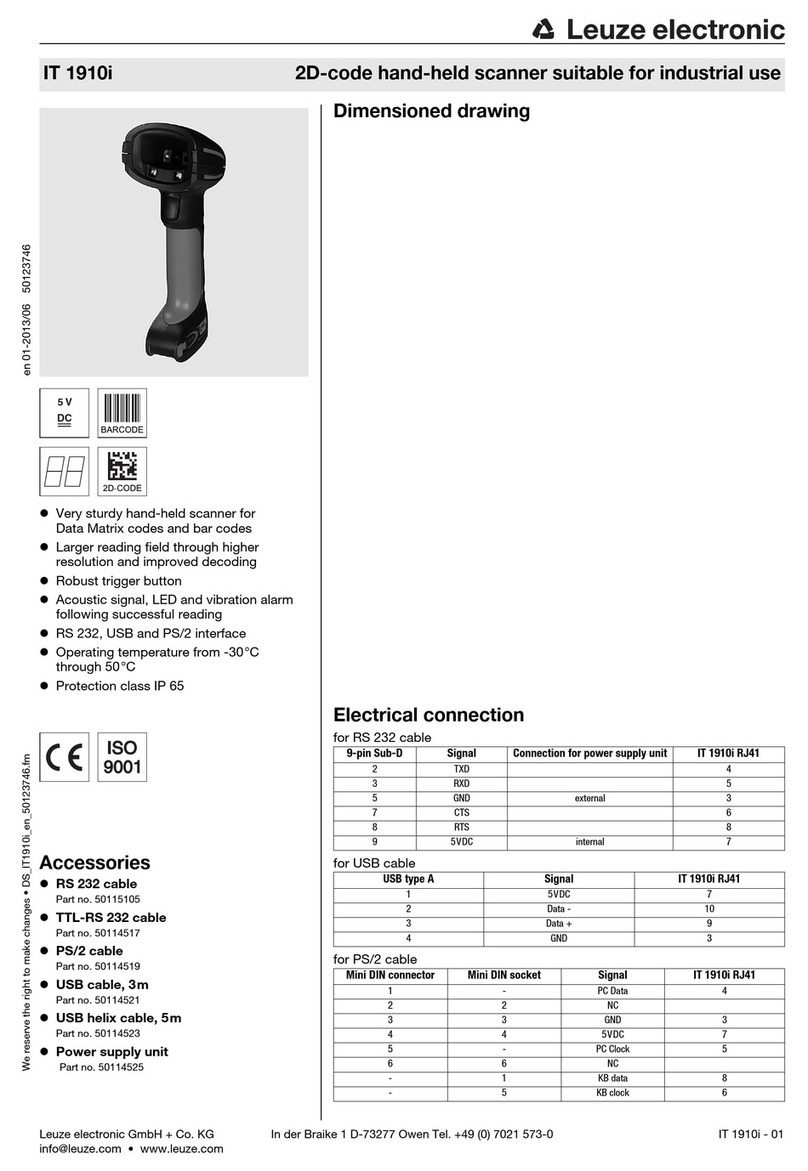
8 Electrical connection...................................................................................................................................................47
8.1 Electrical power supply...............................................................................................................................................47
8.2 Interfaces....................................................................................................................................................................47
8.2.1 X1 plug interface assignment .....................................................................................................................................48
8.2.2 Interface assignment, plug X2....................................................................................................................................49
8.3 Assemble cables.........................................................................................................................................................50
8.4 Integrating the safety sensor into machine control system.........................................................................................51
8.4.1 Downstream safety circuit with start/restart interlock, contactor monitoring, without field pair switchover.................51
8.4.2 Programmable logic controller (PLC) with corresponding safety level and field pair switchover................................51
9 Parameters .................................................................................................................................................................53
9.1 Administrative parameters..........................................................................................................................................53
9.1.1 Safety Laser Scanner name.......................................................................................................................................53
9.1.2 Description..................................................................................................................................................................53
9.1.3 Start segment output ..................................................................................................................................................53
9.1.4 Stop segment output...................................................................................................................................................53
9.1.5 Output resolution ........................................................................................................................................................53
9.1.6 Serial interface baud rate............................................................................................................................................54
9.1.7 Alarm incident.............................................................................................................................................................54
9.1.8 Precalculated measured values output.......................................................................................................................54
9.1.9 2nd measured value calculation segment ..................................................................................................................54
9.1.10 3rd measured value calculation segment ...................................................................................................................54
9.2 Safety-relevant parameters ........................................................................................................................................55
9.2.1 Application ..................................................................................................................................................................55
9.2.2 Response times..........................................................................................................................................................55
9.2.3 Dust suppression........................................................................................................................................................55
9.2.4 Applicable field pair selection with scanner start ........................................................................................................56
9.2.5 Permitted field pair switchovers..................................................................................................................................56
9.3 Field pair.....................................................................................................................................................................56
9.3.1 Protective field/description..........................................................................................................................................56
9.3.2 Warning field/description ............................................................................................................................................56
9.4 MotionMonitoring ........................................................................................................................................................56
9.4.1 Vehicle width...............................................................................................................................................................56
9.4.2 Protective field side additional distance......................................................................................................................56
9.4.3 Laser scanner installation point..................................................................................................................................57
9.4.4 Warning field prerun time............................................................................................................................................57
9.4.5 Vehicle response time ................................................................................................................................................57
9.4.6 Brake wear and tear additional distance.....................................................................................................................57
9.4.7 Ambient influences additional distance.......................................................................................................................57
9.4.8 Speed with PF ............................................................................................................................................................58
9.4.9 Braking distance with PF ............................................................................................................................................58
9.4.10 Standstill monitoring ...................................................................................................................................................58
9.4.11 Creep and reverse......................................................................................................................................................58