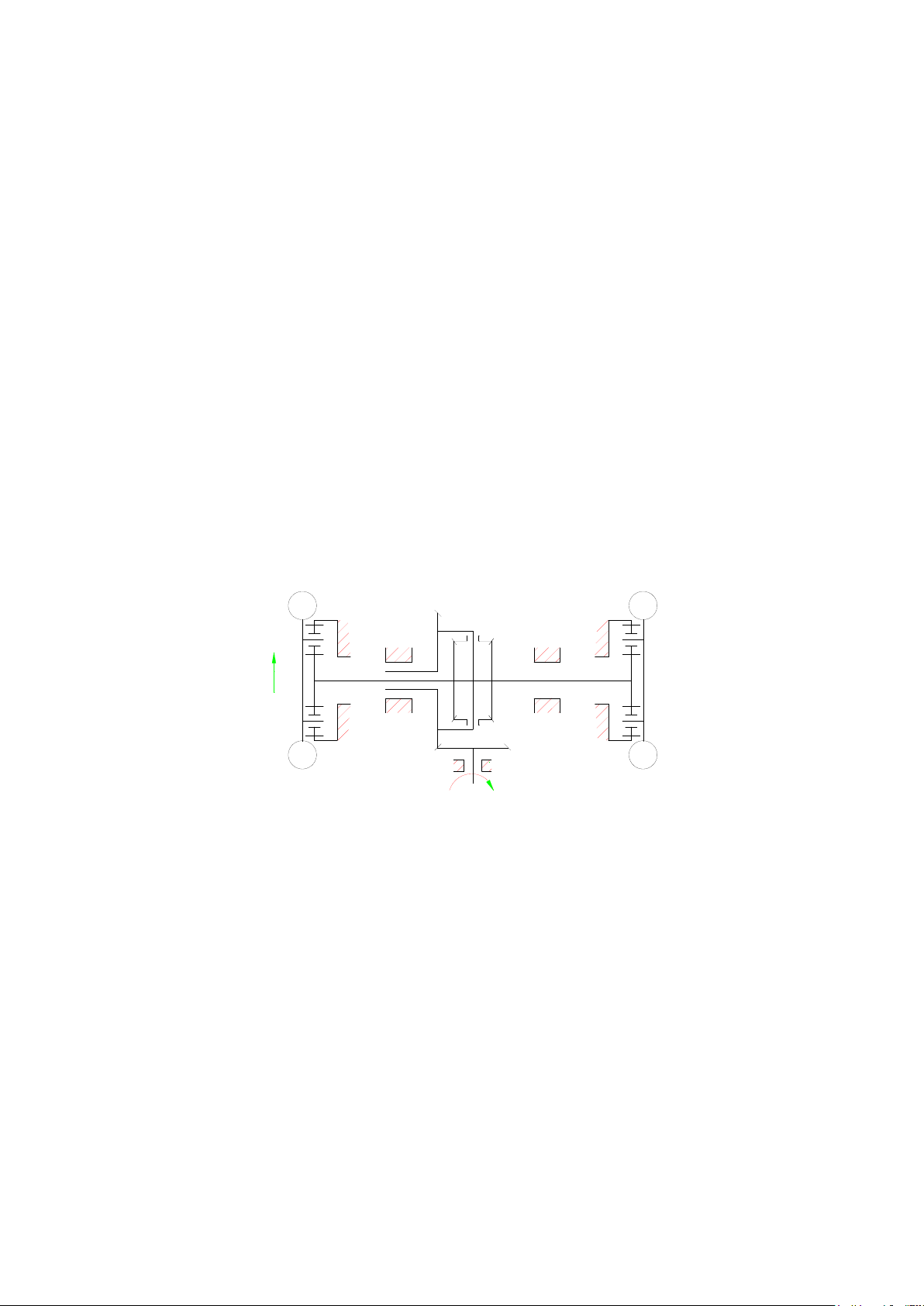CONTENT
Ⅰ.Power System ..................................................................................................................... 1
1.Engine for Forklift........................................................................................................... 1
Ⅱ.Drive system ....................................................................................................................... 2
1.Summarize..................................................................................................................... 2
2. Hydrodynamic power transmission gear-box ................................................................ 4
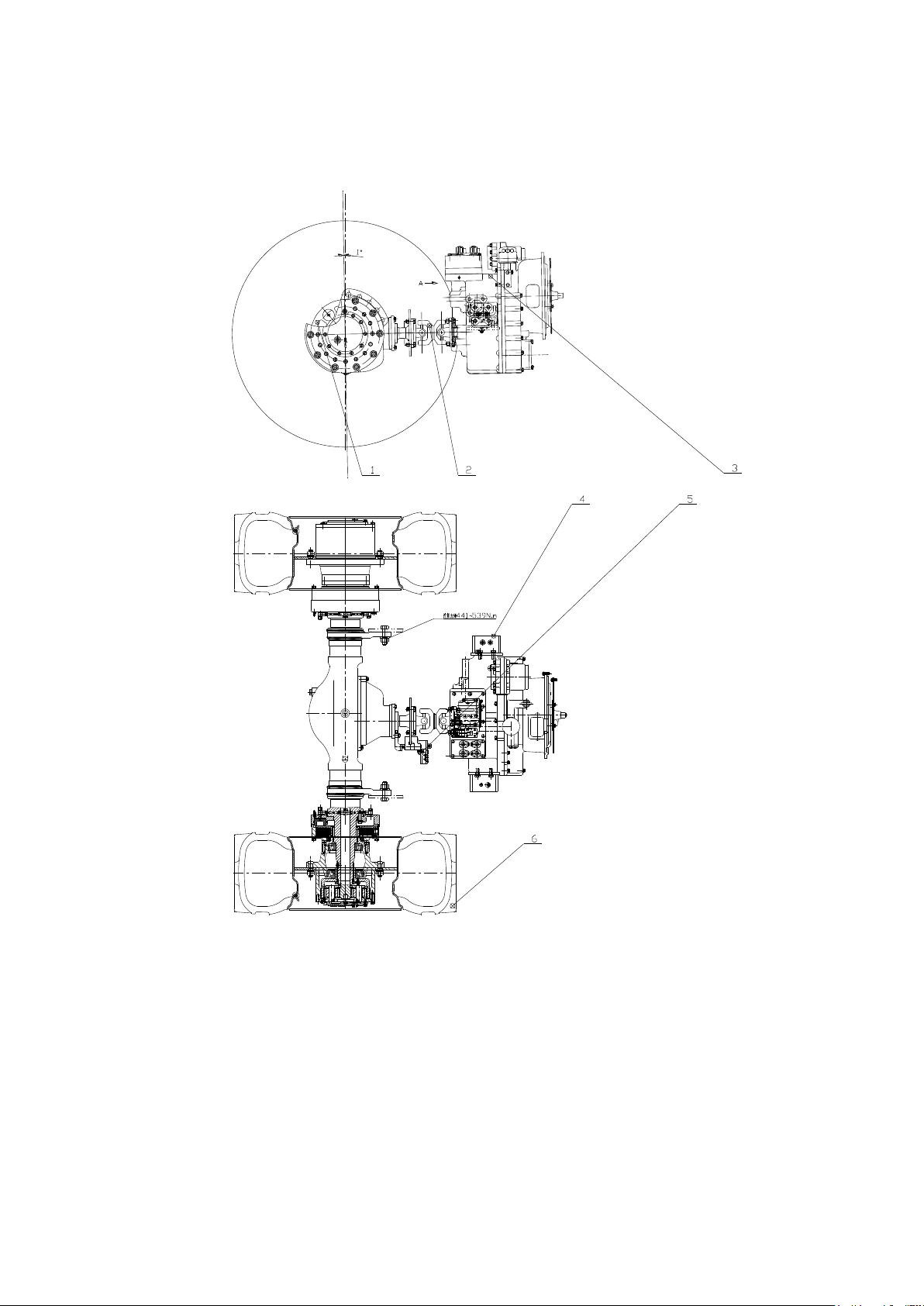
3. Driving axle..................................................................................................................... 6
ⅢSteering system.................................................................................................................. 13
1 Structure introduction ................................................................................................. 13
Ⅳ.Brake system...................................................................................................................... 26
1.Data............................................................................................................................... 26
2.Fault diagnoses and corrections................................................................................... 27
3.Brake inching pedal adjustment.................................................................................... 29
4.Brake valve and accumulator........................................................................................ 30
5.Hand brake.................................................................................................................... 32
6.Service brake................................................................................................................ 38
7.Hydraulic brake malfunction diagnosis......................................................................... 40
8.Exhaust of air in the hydraulic system.......................................................................... 40
Ⅴ.Hydraulic system ................................................................................................................ 40
1.Oil pump........................................................................................................................ 40
2.Multiple directional control valve................................................................................... 42
3.Rotary type piping filter ................................................................................................. 50
4.One-way governor valve............................................................................................... 50
5.Lifting cylinder............................................................................................................... 50
6.Tilting cylinder ............................................................................................................... 51
7.Air exhaust in hydraulic system .................................................................................... 51
8.Hydraulic system fault diagnosis and corrections......................................................... 52
9.Hydraulic system schematic diagram........................................................................... 53
Ⅵ. Lifting system..................................................................................................................... 54
1.Assemble debugging data ............................................................................................ 55
2.Fault diagnosis and corrections.................................................................................... 56
3.Summary....................................................................................................................... 61
4.Mast dismantle and install adjustment.......................................................................... 62
5.Disassembly and installation of lifting cylinder ............................................................. 67
6.Disassembly and installation of tilting cylinder ............................................................. 68
7.Noticing proceeding of debugging................................................................................ 69
Ⅶ.Electrical system ................................................................................................................ 70
1.Control box assembly.................................................................................................... 70
2.Instrument,sensor and relay ......................................................................................... 71
3.Lighting system............................................................................................................. 74
4.Electrical system diagram............................................................................................. 80