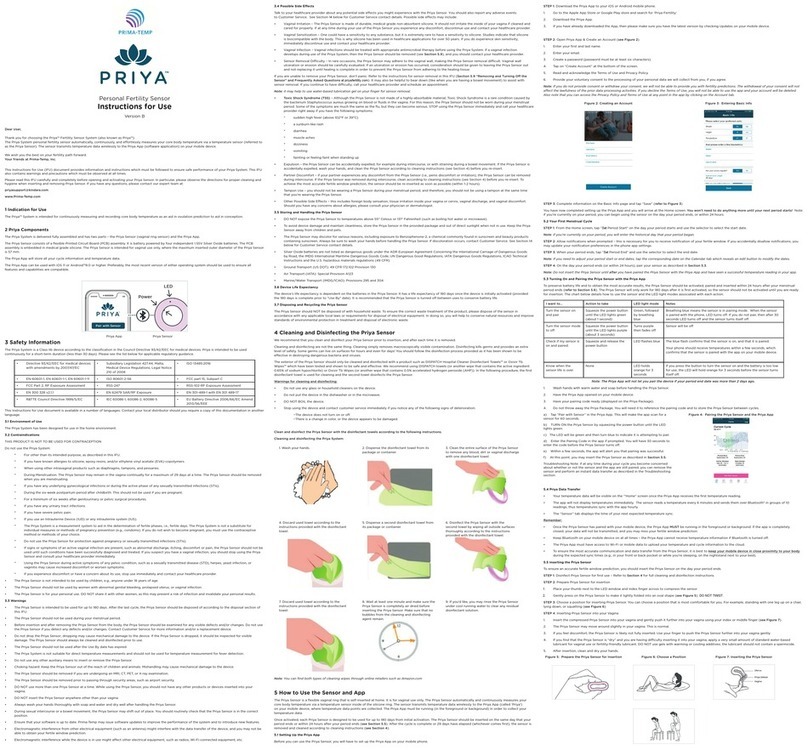
Livox Mid-70 User manual

Livox Mid-70
v1.2
2021.02
User Manual

2
©2020 Livox Tech. All Rights Reserved.
Using this Manual
Legend
Warning Important Hints and Tips Explanation
Downloading Documents
Visit the link below to download the latest Livox Mid-70 User Manual and other documents related to the
Livox Mid-70.
www.livoxtech.com/mid-70
Downloading Livox Viewer
Visit the link below to download Livox Viewer and the Livox Viewer User Manual.
www.livoxtech.com/mid-70
Downloading Livox SDK
Visit the link below to download the Livox SDK:
https://github.com/Livox-SDK
Searching for Keywords
Search for keywords such as “FOV” and “mount” to nd a topic. If you are using Adobe Acrobat Reader to read
this document, press Ctrl+F on Windows or Command+F on Mac to begin a search.
Navigating to a Topic
View a complete list of topics in the table of contents. Click on a topic to navigate to that section.
Printing this Document
This document supports high resolution printing.

©2020 Livox Tech. All Rights Reserved.
3
Contents
Using this Manual 2
Legend 2
Downloading Documents 2
Downloading Livox Viewer 2
Downloading Livox SDK 2
Product Prole 4
Introduction 4
Product Characteristics 4
Overview 6
Connectors 7
M12 Aviation Connector 7
Power Cable and Sync Cable 8
Ethernet Port 9
Mounting the Livox Mid-70 9
Effective Field of View (FOV) Range 9
Mounting Notice 10
Dimensions 10
Getting Started 12
External Power Supply 12
Connection 13
Usage 15
Coordinates 15
Output Data 15
Working States & Working Modes 18
Dual Return Mode 18
Livox Viewer 19
Software Development Kit (SDK) 19
Storage, Transportation, and Maintenance 19
Storage 19
Transportation 19
Maintenance 20
Troubleshooting 20
After-Sales Information 21
Appendix 21
Appendix 1 21
Appendix 2 22
Appendix 3 23
Specications 23

4
©2020 Livox Tech. All Rights Reserved.
Product Prole
Introduction
The Livox Mid-70 is a high-performance LiDAR sensor that can be used for multiple applications including autonomous
driving, industrial robots, indoor and outdoor service robots, or any robots used in special applications. Specically,
the Mid-70 can be used with automated guided vehicles (AGV), autonomous mobile robots (AMR), automated trucks,
medical logistics robots, cleaning robots, terminal delivery robots, and intelligent security robots. The Livox Mid-70 can
detect objects as close as 0.05 meters away, and has a detection range of up to 260 meters.
Wide FOV: Compared with Mid-40, the Mid-70 has a larger circular eld of view (FOV) of 70.4°, increasing its
ability to detect both near and distant objects.
Small Blind Zone: The blind zone of the Mid-70 is 5 cm, and the detection precision from 0.2 to 1 m is 3 cm.
Users can adjust the Mid-70 angle to completely eliminate the blind zone. It is recommended to embed the
Mid-70 in an automotive device before adjusting the angle.
Non-Repetitive Scanning Technology: Livox’s unique non-repetitive scanning technology ensures a high-
density point cloud, and can precisely detect every detail inside the FOV.
High Reliability: The Mid-70 oers enhanced reliability as the cutting-edge optoelectronic system design works
normally without rotating internal electronic devices such as a transmitter and receiver. The Mid-70 has undergone
rigorous reliability testing required by the automotive industry. In addition, the Mid-70 has achieved an IP67
waterproof and dustproof rating under GB 4208-2008 and IEC 60529 standards. Note the included cables and
mounting bracket do not meet the same standards.
User-Friendly Livox Viewer: Livox Viewer is a software specially designed for Livox LiDAR sensors. It displays
and records real-time point cloud data, replays point cloud videos, and analyzes the 3D point cloud data. Users
can set product parameters and calibrate extrinsics using Livox Viewer. The simple interface makes Livox
Viewer easy to use.
Open Source Livox SDK: a software development kit (SDK) is provided to help develop customizable applications
using the data acquired from the point cloud data. Livox SDK supports Windows/Linux/Mac OS/ROS.
• The Mid-70 has a detection range of up to 260 m, which can be reached when the target object reects
80% or more of light. For reference, grey concrete walls and roads have a reectivity range from 15%
to 30%, while white plaster walls have a reectivity range from 90% to 99% in an environment with a
temperature of 25° C (77° F).
• Before using for the first time, remove the screen protector from the optical window.
Product Characteristics
The Livox Mid-70 has a high coverage ratio due to its unique non-repetitive scanning technology. Over time, the
coverage inside the FOV increases signicantly and reveals more detailed information of the surroundings.
Figure 1.2.1 displays the typical point cloud patterns of the Livox Mid-70 over an extended period.
Figure 1.2.2 displays the FOV coverage of Mid-70 compared with traditional mechanical LiDAR sensors that
use common mechanical scanning methods. The diagram shows that when the integration time is 0.2 seconds,
the FOV coverage of the Livox Mid-70 is similar to a 32-line LiDAR sensor. As the integration time increases,
however, the FOV coverage of the Livox Mid-70 increases signicantly. After 1.5 seconds, the FOV coverage
approaches 86%, so almost all areas would be illuminated by laser beams. In this way, more details in the FOV
can be revealed.
Figure 1.2.1 Point cloud patterns of the Livox Mid-70 accumulated over an extended period
Azimuth/ deg
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
130
Zenith/ deg
-30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40-40
Azimuth/ deg
Zenith/ deg
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
130
-30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40-40
Azimuth/ deg
Zenith/ deg
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
130
-30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40-40
Azimuth/ deg
Zenith/ deg
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
130
-30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40-40

Livox Mid-70 User Manual
©2020 Livox Tech. All Rights Reserved.
5
The performance of the scanning method is defined by the FOV coverage, which is calculated as
the fraction of FOV illuminated by laser beams. The FOV coverage (C) can be calculated with the
following formula:
Refer to the official Livox website for more information about how the FOV coverage is calculated.
C = Total area in FOV
Total area illuminated by laser beams
×100%
00.2 0.40.6 0.811.21.4 1.5
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
Livox-Mid-70
Integration time (s)
FOV Coverage (%)
64 Lines
32 Lines
16 Lines
Figure 1.2.2 The FOV coverage of the Mid-70 and non-Livox LiDAR sensors using common mechanical scanning
methods. The 16-line non-Livox LiDAR sensor has a vertical FOV of 30°, the 32-line non-Livox LiDAR sensor is 41°, and
the 64-line non-Livox LiDAR sensor is 27°.
Laser Wavelength 905 nm
Laser Safety Class 1 (IEC 60825-1:2014) (Safe for eyes)
Detection Range (@ 100 klx) 90 m @ 10% reectivity;
130 m @ 20% reectivity;
260 m @ 80% reectivity
Close Proximity Blind Zone 0.05 m
FOV 70.4° (circular)
Distance Random Error 1σ (@ 20 m) ≤ 2 cm
1σ (@ 0.2~1 m) ≤ 3 cm
Angular Random Error 1σ < 0.1°
Beam Divergence 0.28° (Vertical) × 0.03° (Horizontal)
Point Rate 100,000 points/s (rst or strongest return)
200,000 points/s (dual return)
False Alarm Ratio (@100 klx) < 0.01%
Table 1.2.1 Point cloud specications

Livox Mid-70 User Manual
6
©2020 Livox Tech. All Rights Reserved.
• Close Proximity Blind Zone: Target objects within 0.05 to 0.2 m from the Mid-70 can be detected and
point cloud data can be recorded. However, since the detection precision cannot be guaranteed, the data
should be taken as a reference only.
• Tested in an environment at a temperature of 25° C (77° F) with a target object that has a reectivity of
30% and is 20 meters away from the Livox Mid-70. The actual environment may dier from the testing
environment. The gure listed is for reference only.
• Tested in an environment at a temperature of 25° C (77° F) with a target object that has a reectivity of
30% and is within the range of 0.2 to 1 meters from the Livox Mid-70. The actual environment may dier
from the testing environment. The gure listed is for reference only.
• The performance may decrease in extreme environments such as those with foggy weather, that cause
strong vibration, or where the temperature is -20° C (-4° F) or 65° C (149° F).
Overview
Livox Mid-70
1. Optical Window
The laser passes through the optical window and
scans objects in the FOV.
2. M3 Mounting Holes
Make sure to use the correct screws when
mounting.
3. Locating Hole
The locating hole makes it easy for users to find
the correct location to mount a fixed support for
the Mid-70. Refer to the Dimensions section for
more information.
4. M12 Aviation Connector
Used with the conversion cable, the M12 aviation
connector connects to the Livox Converter 2.0 to
implement a quick performance test of the Mid-70.
Used with the conversion cable, the M12 aviation
connector connects to the Livox Converter 2.0
to carry out a quick performance test of the Mid-
70. If users wish to improve the waterproof and
dustproof protection of their system, they can
replace the conversion cable with a cable of
their own. Refer to the Cables section for more
information.
5. Conversion Cable
The Livox Mid-70 includes a conversion cable. To
connect the Livox Mid-70 to the Livox Converter
2.0, users can use this cable or a cable of their
own. Refer to the Cables section for more
information.
5
1
2
3
4

Livox Mid-70 User Manual
©2020 Livox Tech. All Rights Reserved.
7
Livox Converter 2.0
1. LiDAR Connector Port
A JAE MX34012NF1 type connector port is used
to connect to the Mid-70. The mating connector is
JAE MX34012SF1 LiDAR.
2. Power Port
Connects to an external power supply. When the
Mid-70 is connected to the Livox Convertor 2.0,
users can use a power supply of 9 to 30 V. The
connector type is MOLEX 1053313-1102. The
mating connector is MOLEX 105307-1202.
3. Ethernet Port
An RJ45 type Ethernet connector is used to
connect to Ethernet cables.
4. Sync Port
The 3-pin sync port supports 3.3V LVTTL sync
signal input. Refer to Table 2.2.2 for more
information. The mating connector of the sync
port connector is Famfull 9.510A0-003-1R0. JST
GHR-03V-S is also compatible.
1
2 3 4
Connectors
M12 Aviation Connector
The Mid-70 uses the high-reliability M12 aviation connector (male). It is a M12 12P A-code fully
shielded male connector that meets the IEC61076-2-101 standard. The connector type is Finecables
MA12MAHD12STXXXB14 and its mating connector is Finecables MA12FAHD12STXXXB14, both of which meet
the IP rating of IP67. When the M12 aviation connector is used with the conversion cable, users can connect
the Mid-70 to the Livox Connector 2.0 for connecting power and transmitting control signals and data. If users
wish to improve the waterproof and dustproof protection of their system, they can replace the conversion cable
with a cable of their own.
765
4
3
2
1
9
812 11
10

Livox Mid-70 User Manual
8
©2020 Livox Tech. All Rights Reserved.
LiDAR Connector
Pin
M12 Aviation
Connector Pin Signal Type Description Color
1 1 Power+ Power DC10V-15V Blue/white
79Power+ Power DC10V-15V Blue
2 2 Ground Power Ground Silver bare wire
83Ground Power Ground Silver bare wire
3 4 Ethernet-TX+ Output 100BASE-TX, TX+ Orange/white
4 5 Ethernet-TX- Output 100BASE-TX, TX- Orange
96Ethernet-RX+ Input 100BASE-TX, RX+ Green/white
10 7 Ethernet-RX- Input 100BASE-TX, RX- Green
58 Ground Power Ground Silver braided wire
11 10 Ground Power Ground Silver braided wire
12 11 Sync- Input RS485_B, Pulse Per Second Grey
6 12 Sync+ Input RS485_A, Pulse Per Second Grey/white
Table 2.1.1 Conversion Cable description
Power Cable and Sync Cable
The Mid-70 cables package includes a power cable and sync cable.
Power Cable
Connect “A” to the power port of the Livox Converter 2.0 and connect “B” to an external DC power supply. The
connector type of this power cable is MOLEX 105307-1202.
Figure 2.2.1 Power cable
Figure 2.1.1 Conversion Cable
2
1
A B
500±25 mm
Conversion Cable
To connect the Mid-70 to the Livox Converter 2.0, users can use this cable or a cable of their own.
Below is more information on the Livox Mid-70 M12 aviation connector and the aviation and converter
connector cable.
121110987
4321 5 6
10
6
7
8
9
12
3
4
5
11 12
LiDAR Connector M12 Aviation
Connector (Female)

Livox Mid-70 User Manual
©2020 Livox Tech. All Rights Reserved.
9
Pin Signal Type Description Color
1 Power+ Power DC 10 - 30 V (max 30 V) Red
2Ground Power Ground Black
Table 2.2.1 Power cable description
Pin Signal Type Description Color
1Ground Power Ground Black
2 Sync+ Input 3.3 V LVTTL, Pulse Per Second Blue
3Reserved Reserved Undened White
Table 2.2.2 Sync cable description
Sync Cable
Connect “A” into the sync port of the Livox Converter 2.0 and connect “B” to the sync signal. The sync cable
has a 3-pin connector. The connector type is Famfull 9.510A0-003-1R0, which is compatible with JST GHR-
03V-S type connectors. Refer to the Data Synchronization section for more information.
Figure 2.2.2 Sync cable
Ethernet Port
The Livox Converter 2.0 supports a 100BASE-TX standard RJ45 Ethernet port. The Mid-70 uses two twisted
pairs to send and receive data.
1AB
2
3
500±25 mm
Mounting the Livox Mid-70
Effective Field of View (FOV) Range
As shown below, the Mid-70 has a circular FOV of 70.4°. When mounting a Livox LiDAR sensor, make sure that
the FOV is not blocked by any objects. Go to www.livoxtech.com/mid-70 to download the 3D models of the
Mid-70 and its FOV.
Figure 3.1.1 Effective FOV of the Mid-70
Vertical
Horizontal
70.4°
35.2° 35.2°
32.4
70.4°
Unit: mm

Livox Mid-70 User Manual
10
©2020 Livox Tech. All Rights Reserved.
As shown above, when an object with a reectivity of 10% is placed in the center of the FOV, the object can be
detected as far as 90 m. However, as the object moves towards the edge of the FOV, the distance at which it
can be detected shortens accordingly. Pay attention to the eective detection range when the Mid-70 is in use.
Mounting Notice
Read and understand the following warnings before mounting the Mid-70.
1. Before use, remove the screen protector from the optical window.
2. Signicant dust and stains on the optical window will aect the performance of the Mid-70 sensor. Follow
the instructions in the Maintenance section to clean the optical window using compressed air, isopropyl
alcohol, or a lens cloth.
3. When mounting the Mid-70, the eld of view must not be blocked by an object, including glass. Refer to
Figure 3.1.1.
4. There are no restrictions on which direction the Mid-70 can be installed. The top or bottom surface can be
used to mount the Mid-70. It is recommended that the surface is parallel to the ground when mounting.
5. The Mid-70 cannot bear any extra payload. Otherwise, the reliability of the product cannot be guaranteed.
Dimensions
Mounting the Mid-70 without Mounting Bracket
The bottom surface of the Mid-70 has four M3 mounting holes with a depth of 5 mm. Refer to the dimensions
and the mounting holes in the diagrams below to mount or embed the Mid-70 to or in an appropriate place on
the target base.
Figure 3.1.2 Effective FOV of the Mid-70
Note that the eective detection range of the Livox Mid-70 varies based on where the object is within the FOV.
The closer to the edge of the FOV, the shorter the eective detection range is. The closer to the center of the
FOV, the farther the eective detection range. Refer to the diagrams below:
10% reectivity
100
80
60
40
20
0
100
80
60
40
20
0
120°
105°
90°
75°
60° -30°
-15° 0° 15°
30°
70 70
90
70 70
90
Unit: m
35.5 35.5
61.0
64.0
46.0
62.7
6.0
1.0
4.0 1.3
4-M3 4.8
4.0 1.3
4-M3 5
46.0
61.0
6.0
1.0
35.5 35.5
4.0 1.5
4.0 1.5
15.4
18.2
32.4
97.0
15.8
12.5°
21.7
Vertical Horizontal

Livox Mid-70 User Manual
©2020 Livox Tech. All Rights Reserved.
11
Table 3.2.1 The Mid-70 Weight & Dimensions
Table 3.2.2 The Mounting Bracket Weight & Dimensions
Weight (with cable) Approx. 580 g
Dimensions 97×64×62.7 mm
Weight Approx. 76 g
Dimensions 100×97×5.7 mm
Figure 3.2.1 The Mid-70 Dimensions
(refer to Appendix 1)
Unit: mm
Unit: mm
35.5 35.5
61.0
64.0
46.0
62.7
6.0
1.0
4.0 1.3
4-M3 4.8
4.0 1.3
4-M3 5
46.0
61.0
6.0
1.0
35.5 35.5
4.0 1.5
4.0 1.5
15.4
18.2
32.4
97.0
15.8
12.5°
21.7
Mounting the Mid-70 with Mounting Bracket
It is recommended to rst attach the Mid-70 to the mounting bracket using the M3 mounting hole and then
mount the Mid-70 using the M6 mounting hole on the mounting bracket. There is one 1/4 inch mounting hole
available on the center of the mounting bracket to help mount the Mid-70 based on your requirements.
85.0
100.0
80.0
22.2
97.0
12.8
26.0
8.5
4.0- 6.6
6- 3.4
6.4
2- 4.0
1/4-20UNC
4.0
2.0
46.0
4.5
5.7
14.0
2-3.4 Through
2-6.4 3.2
3.2
36.0
14.0
11.0
0
+0.08
4.0
70.0
9.0
12.0
2.2
2- 4.00
+0.08 2.2
-0.06
0

Livox Mid-70 User Manual
12
©2020 Livox Tech. All Rights Reserved.
Weight Approx. 88 g
Dimensions 74×52×23 mm
Table 3.2.3 Livox Converter 2.0 Weight & Dimensions
Livox Converter 2.0
Refer to the dimensions below to mount the Livox Converter 2.0.
Unit: mm
74
52 22.9 37
66
4-M2 2.5
Getting Started
External Power Supply
The working voltage range of the Mid-70 is from 10 to 15 V, with a recommended working voltage of 12 V.
The minimum working voltage should be increased in a low-temperature environment. When the Mid-70 is
connected to an external power source directly, make sure the output voltage range of the external power
source is within the working voltage range of the Mid-70. When an extension cable is required, make sure to
increase the output voltage of the external power source due to the extra voltage reduction. Make sure the
maximum voltage does not exceed 15 V. Note that the power cable may generate voltage uctuation where
the voltage exceeds 15 V in some scenarios such as if the power cable is interfered with or other devices
connected to another power source in the parallel circuit suddenly power o. In such scenarios, the Mid-70
may not work normally or even be damaged.
Normally, the working power of the Mid-70 is 8 W. In an environment where the temperature is from -20° to 0°
C (–4° to 32° F), the Mid-70 will rst enter self-heating mode automatically, which lasts at least three minutes. In
self heating mode, the working power of the Mid-70 may reach up to 40 W. The working power of the Mid-70
varies at dierent temperature. Below shows the relationship between the temperature of the environment and
the working power of the Mid-70. Make sure the power supply is suitable based on the peak power of the Livox
Mid-70. The value is for reference only. In normal conditions, the peak power varies depending on each sensor.
Figure 4.1.1 The working power of the Mid-70 at varying temperatures
Temperature (℃)
Startup Power
Operating Power
Power (W)
20 30 40 50 60 650
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
温度 (°C)
功率 (W)
-20 -10 10

Livox Mid-70 User Manual
©2020 Livox Tech. All Rights Reserved.
13
Connection
The Mid-70 uses M12 aviation connector for power supply as well as control signal and data transmission.
Refer to the Cables section for more information about the connector. The Livox Converter 2.0 integrates
a LiDAR port, a sync port, a power port, and an Ethernet port. For temporary use or to ensure optimal
performance, it is recommended to always use a Livox Converter 2.0 and a conversion cable.
The Mid-70 uses an Ethernet cable for data transmission and supports user datagram protocol (UDP). Both
static and dynamic IP address congurations are supported. All Mid-70 sensors are set to static IP address
mode by default with an IP address of 192.168.1.1XX (XX stands for the last two digits on the serial number of
the Mid-70 sensor). The default subnet masks of the Mid-70 sensors are all 255.255.255.0, and their default
gateways are 192.168.1.1. Directly connect the Mid-70 to the computer when using for the rst time.
The static and dynamic IP addresses are connected in dierent ways. 1. The static IP address is connected by
default and in this mode, the Mid-70 can be connected to a computer directly. 2. To connect to the dynamic
IP address, make sure the Mid-70 is switched to dynamic IP mode by using Livox Viewer or the Livox SDK. In
dynamic address mode, the addresses are assigned to the Mid-70 using dynamic host conguration protocol
(DHCP).
Static IP address:
1. Follow the steps to set the IP address of your computer to static IP address:
Windows system
a. Click to enter the Network and Sharing Center under Control Panel.
b. Click the network you are using and click “Properties”.
c. Double click “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)”.
d. Set the static IP address of the computer to 192.168.1.50 and the subnet mask to 255.255.255.0. Click
“OK” to complete.
Ubuntu-16.04 system
The IP address of the computer can be configured by using ifconfig command at the terminal. The
conguration code is as below:
~$ sudo ifcong enp4s0 192.168.1.50 (replace “enp4s0” with the network port name of the computer)
2. Connect the Mid-70, Livox Converter 2.0, external power source, and computer by following Figure 4.2.1.
Figure 4.2.1 Connecting using static IP address
Livox Converter 2.0
Livox Mid-70
External Power Source
Ethernet Cable

Livox Mid-70 User Manual
14
©2020 Livox Tech. All Rights Reserved.
• If necessary, use the sync cable to connect with the sync port of Livox Converter 2.0 and sync source.
• If multiple Mid-70 sensors are set to static IP addresses, make sure all the Mid-70 sensors have dierent
IP addresses and use a switchboard to connect them to the computer.
• If more than six Mid-70 sensors are required, use a kilomega router or switchboard.
• The broadcast number for each LiDAR sensor can be viewed in the Device Manager of Livox Viewer or
the Livox SDK. For the Mid-70, the broadcast number will be its serial number ending in an additional “1”.
• Launch Livox Viewer after the Mid-70 is connected. Click the device with the static IP address that
should be altered. Click to open the settings page and set the static IP address of the Mid-70.
a. Connect the Mid-70 to the 1.5m aviation connector and converter connector cable. Next, connect the
1.5m cable to the Livox Converter 2.0.
b. Connect the computer and the Livox Converter 2.0 to the router using Ethernet cables. Make sure both
the Livox Converter 2.0 and the computer are connected to the LAN port on the router.
c. Connect the Livox Converter 2.0 to an external power source.
Dynamic IP address:
1. Follow Figure 4.2.1 to connect the Mid-70, conversion cable, Livox Converter 2.0, external power source,
and computer.
2. Run Livox Viewer, click to open the settings page, and set the IP address of the Mid-70 to dynamic IP
address.
3. Disconnect the Mid-70, conversion cable, Livox Converter 2.0, external power source, and computer.
4. Follow the steps to set the IP address of your computer to dynamic IP address:
Windows system
a. Click to enter the Network and Sharing Center under Control Panel.
b. Click the network you are using and click “Properties”.
c. Double click “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)”.
d. Select “Obtain an IP address automatically” and “Obtain DNS server address automatically”, then click “OK”
to complete.
Ubuntu-16.04 system
a. Click to open “Network”.
b. Click “IPv4”, and then click “Automatic (DHCP)”. Click “Apply” to complete.
5. Connect the Mid-70, conversion cable, Livox Converter 2.0, router, computer, and external power supply by
following Figure 4.2.2.
Livox Mid-70
External Power Supply
Router with DHCP
Ethernet Cable
Figure 4.2.2 Connecting using dynamic IP address

Livox Mid-70 User Manual
©2020 Livox Tech. All Rights Reserved.
15
• If necessary, use the sync cable to connect with the sync port of Livox Converter 2.0 and sync source.
• If more than six Mid-70 sensors are required, use a kilomega router or switchboard.
• The broadcast number for each LiDAR sensor can be viewed in the Device Manager of Livox Viewer or
the Livox SDK. For the Mid-70, the broadcast number will be its serial number ending in an additional “1”.
a. Connect the Mid-70 to the 1.5m aviation connector and converter connector cable. Next, connect the
1.5m cable to the Livox Converter 2.0.
b. Connect the computer and the Livox Converter 2.0 using an Ethernet cable.
c. Connect the Livox Converter 2.0 to an external power source.
Usage
Coordinates
The Cartesian coordinates O-XYZ of Mid-70 is dened as below:
Output Data
The output information of the Mid-70 sensors includes point cloud data, which have timestamp, status codes,
target reectivity, coordinates, and tag information.
Point Cloud Data
A point cloud is the collection of the points where the surface of an object was detected in the FOV
of the LiDAR sensor. Each point contains the following information.
Target reflectivity: 0 to 255. 0 to 150 corresponds to the reflectivity within the range of 0 to 100%
in the Lambertian reflection model. 151 to 255 corresponds to the reflectivity of target objects with
retroflection properties. When the target is less than 2 m from the Mid-70, it may result in a large
reflectivity error. The data should be taken as a reference only.
Coordinates: can be expressed as Cartesian coordinates (x, y, z) and Spherical coordinates (r, θ, φ).
The relationship between Cartesian and Spherical coordinates is shown in the figure below. When
there is no object within the detection range or the object is placed outside the detection range, the
coordinates of the point cloud will be expressed as (0, 0, 0) in Cartesian coordinates and as (0, θ, φ)
in Spherical coordinates.
Figure 5.1.1 Coordinates of the Mid-70
x= r×sin(θ)×cos(φ)
y = r×sin(θ)×sin(φ)
z = r×cos(θ)
Figure 5.2.1.1 Relationship between Cartesian coordinates and Spherical coordinates
16.2
32.4
70.4°
35.2°
X
Y
Z
XY
Z
o
70.4°
35.2°
X
Z
Y
16.2
32.4
70.4°
35.2°
X
Y
Z
X
M
Y
Z
o
θ
P(r,θ,φ)
φ
70.4°
35.2°
X
Z
Y
Unit: mm

Livox Mid-70 User Manual
16
©2020 Livox Tech. All Rights Reserved.
Tags: Indicates the return type of the laser and if the point detected is a noise. The format of the tag is as
shown below:
bit7 bit6 bit5 bit4 bit3 bit2 bit1 bit0
Point property based
on nearby waveform
distortion:
00: Normal
01: Nearby waveform
distortion
10: Reserved
11: Reserved
Return number:
00: return 0
01: return 1
10: return 2
11: Reserved
Point property based on
intensity:
00: Normal
01: Noise that does not meet
intensity expectations
10: Reserved
11: Reserved
Point property based on
spatial position:
00: Normal
01: High condence level of
the noise
10: Moderate confidence
level of the noise
11: Low condence level of
the noise
Each tag is composed of one byte. In this byte, bit7, and bit6 are Group 1, bit5 and bit4 are Group 2, bit3 and
bit2 are Group 3 while bit1 and bit0 are Group 4.
Group 1 indicates if the sampling point is a noise based on the nearby waveform distortion. Due to the optical
system characteristics of the machine, nearby return signal will be distorted by the stray light inside the system,
leading to unreliable depth calculation results (especially when the return signal energy is small). "01" indicates
that nearby return signal is distorted; "00" indicates that waveform is normal.
Group 2 indicates the return sequence of the sampling point. Featuring a coaxial optical path, the Mid-70 itself
will generate a laser return even if there is no detectable object around. This return is recorded as return 0. After
that, if there is any object within the detectable range, the rst laser that returns to the Mid-70 is recorded as
return 1, and then return 2, and so on. If the object is too close to the Mid-70, such as 1.5 m away, the rst
eective return will be merged into return 0, and be recorded as return 0.
Group 3 indicates if the sampling point is a noise based on the intensity of the return. Normally, the intensity
of the returns of the noises generated due to the interference of atmosphere particles such as dust, rain, fog,
and snow is quite low. Therefore, the noises are divided into two categories based on the intensity of the return
received. "00" stands for normal point cloud; "01" stands for low intensity of the return, indicating that the
samples have a high possibility of being noises such as dust, rain, and fog. The lower the condence level of
the sample is, the lower the possibility that it is a noise.
Group 4 indicates if the sampling point is a noise based on its spatial position. Normally, when the Mid-70 sensors
detect two objects in close proximity of each other, there will be some thread-like noises between the two
objects. The noises are divided into three categories. The lower the condence level of the noise is, the lower
the possibility that it is noise.
Timestamp
There are three ways to synchronize data with the Mid-70: IEEE 1588-2008, Pulse Per Second (PPS), and GPS
(PPS+UTC).
IEEE 1588-2008: IEEE 1588-2008 is the Precision Time Protocol (PTP) enabling precise synchronization of
clocks in measurement and control systems by Ethernet. Livox LiDAR sensors, as the ordinary clock in the PTP,
only supports UDP/IPV4 for PTP. Livox LiDAR sensors support the following message events: Sync, Follow_up,
Delay_req, and Delay_resp.
PPS: PPS uses the sync cable for data synchronization. Refer to the Cables section for more information. The
synchronization logic is shown in the gure below. The pulse interval in PPS is 1s (t0 = 1000 ms) while the
continuous time of high-level voltage is from 20 ms to 200 ms (20 ms <t1<200 ms). The rising edge of PPS
resets the timestamp to zero, so the timestamp of the point cloud data indicates the duration between the point

Livox Mid-70 User Manual
©2020 Livox Tech. All Rights Reserved.
17
Figure 5.2.2.1 Pulse Per Second
Figure 5.2.2.2 UTC Time Commands
GPS: GPS is a way to synchronize the data using the sync cable and UTC time. The PPS port logic is the same
as the PPS synchronization mentioned above. Users are able to send the UTC time of each pulse to the Mid-
70 via SDK communication protocol. Refer to the SDK Communication Protocols section for more information
about commands. The logic of the UTC Time and PPS signal command are shown below. The timestamp of
the point cloud data stands for the UTC sampling time of the point cloud once GPS synchronization is in use.
PPS
UTC
1
0
t0
t1
t4
t0: 1000 ms
t1: 20 ms ≤ t1 ≤ 200 ms
t4: 10 ms ≤ t4 ≤ 500 ms
Status Description
Temperature status Indicates if there is any temperature abnormality. Temperature status includes
normal, warning, and error.
Voltage status Indicates if there is any internal voltage abnormality. Voltage status includes normal,
warning, and error.
Motor status Indicates if there is any internal motor abnormality. Motor status includes normal,
warning, and error.
Dust warning Indicates if a signicant amount of dust is detected on the optical window or if the
optical window is covered by objects.
Service life warning Indicates if the LiDAR sensor is nearing the end of its service life. The LiDAR sensor
can still work for a short period once this warning appears. It is recommended to
replace the LiDAR sensor once this warning appears.
PPS signal status Indicates whether the PPS sync signal is working normally.
Status Codes
The status codes display the current working status of the Mid-70 sensors. By checking the status codes,
users can see the temperature status, voltage status, motor status, dust warning, service life warning, and PPS
signal status. Status codes can be viewed in Livox Viewer or the Livox SDK. Refer to the Livox Viewer User
Manual for more information about how to check status codes.
Pulse Per Second
(PPS)
t0
t1
t0=1s
1ms<t1<300ms
秒脉冲
(PPS)
t0
t1
t0=1000 ms
20 ms < t1 <200 ms
cloud sampling and the PPS rising edge.

Livox Mid-70 User Manual
18
©2020 Livox Tech. All Rights Reserved.
Figure 5.3.2 Relationship between the dierent working modes available in Livox Viewer
The Mid-70 also has three working modes: Normal, Standby, and Power Saving. These modes can be set in
Livox Viewer and the Livox SDK.
Working states Description
Initializing The LiDAR sensor is powering on.
Normal The LiDAR sensor is powered on and working normally.
Standby The LiDAR sensor is powered on, but the laser beams are not active.
Power saving All components are powered o apart from the communication module.
Error The LiDAR sensor will enter error status when an error is detected and all the
components are powered o apart from the communication module.
Working States & Working Modes
The working states of the Mid-70 includes initializing, normal, standby, power saving, and error.
Dual Return Mode
The Mid-70 can be set to Dual Return mode using Livox Viewer or the Livox SDK. The Mid-70 can
generate a point cloud of up to two returns in Dual Return mode, which has a point rate of 200,000
points per second.
To set the return mode, run Livox Viewer after the Mid-70 is connected.
Click the desired device under Device Manager. Click to select the return mode.
Figure 5.2.1 Relationship between the dierent working states
Power
saving
Initializing
Error
Standby
Normal
Power
saving
Standby
Normal

Livox Mid-70 User Manual
©2020 Livox Tech. All Rights Reserved.
19
• Turn o rewalls on your computer before using Livox Viewer. Otherwise, Livox Viewer may not be able
to detect the Livox LiDAR sensors. Make sure the graphics driver is correctly installed. Otherwise, Livox
Viewer may not launch or may crash.
Livox Viewer
Livox Viewer is a computer software designed for Livox LiDAR sensors and Livox Hub. Users can check real-
time point cloud data of all the Livox LiDAR sensors connected to a computer, and also record the point cloud
data to view oine or for future application. The simple interface makes it easy to use.
Visit www.livoxtech.com to download the latest Livox Viewer. Livox Viewer supports Windows® 7/8/10 (64 bit)
and UbuntuTM 16.04 (64 bit).
For Windows users: unzip the Livox Viewer le and click to open the .exe le named “Livox Viewer.”
For Ubuntu users: unzip the Livox Viewer le and click to open the “./livox_viewer.sh” le under the root directory.
For more information, download the Livox Viewer User Manual from the ocial website www.livoxtech.com.
Software Development Kit (SDK)
Besides using Livox Viewer to check real-time point cloud data, users can also use the SDK to apply the point
cloud acquired from Livox LiDAR sensors to dierent scenarios.
SDK Communication Protocol
With the SDK Communication Protocol, users can learn how to customize the Livox LiDAR sensors. The SDK
Communication Protocol encompasses the following three types of data:
Control Command Data: Conguration and query of LiDAR parameters and status information.
Point Cloud Data: Point cloud data generated by LiDAR.
All data is stored in little-endian format.
Visit http://www.livoxtech.com/sdk to learn more information about SDK communication protocol, Livox SDK
API reference.
Storage, Transportation, and Maintenance
Storage
The storage temperature range for the Mid-70 is from -20° to 65° C (-4° to 149° F). Keep Mid-70 sensors in a
dry and dust-free environment.
• Make sure Mid-70 sensors are not exposed to environments containing poisonous or corrosive gases or
materials.
• DO NOT drop Mid-70 sensors and be careful when placing a LiDAR sensor in storage or taking it out of
storage.
• If a Mid-70 sensor is not to be used for more than three months, regularly check the sensors and connectors
for abnormalities.
Transportation
Before transportation, place Mid-70 sensors in a suitable box for transportation and make sure it is secure.
Make sure to place foam inside the transportation box and that the box is clean and dry.
DO NOT drop Mid-70 sensors and always be careful when carrying a LiDAR sensor.

Livox Mid-70 User Manual
20
©2020 Livox Tech. All Rights Reserved.
Issue Resolution
Cannot detect the LiDAR
sensor
• Make sure that all cables are correctly wired.
• Make sure the voltage and power supply is suitable. The voltage should
be between 10 and 15 V. If a Livox Converter 2.0 is in use, the supported
voltage range of the external power source is from 9 to 30 V.
• Make sure that the LiDAR sensor is not connected to other software.
• Make sure the LAN is selected.
• Make sure no security software is installed that would block Ethernet
broadcasts.
If the issue persists, try to turn o all rewalls and search again.
Confirm the packet outputs for all connected devices using another
application (e.g., Wireshark).
Cannot connect to the
detected LiDAR sensor/
Cannot start sampling
• Make sure that all cables are correctly wired.
• Make sure the voltage and power supply is suitable. The voltage should
be between 10 and 15 V. If a Livox Converter 2.0 is in use, the supported
voltage range of the external power source is from 9 to 30 V. If the issue
persists, reboot the LiDAR sensor and restart the software.
No data received Confirm the packet outputs for all connected devices using another
application (e.g., Wireshark).
Maintenance
In normal conditions, the only maintenance required for the Mid-70 is to clean the optical window of the LiDAR
sensor. Dust and stains on the optical window can negatively aect the performance of the LiDAR sensor. Make
sure to regularly clean the optical window to prevent this from happening.
First, check the surface of the optical window to see if cleaning is necessary. If it is necessary to clean, follow
the steps below:
1. Use compressed or canned air: DO NOT wipe a dusty optical window, as it will only cause more damage.
Dust the optical window with compressed or canned air before wiping the optical window.
Note that if the optical window has no visible stains afterward, it is not necessary to wipe also.
2. Wipe the stains:
DO NOT wipe using a dry lens tissue, as it will scratch the surface of the optical window. Use the lens tissue
provided with isopropyl alcohol. Wipe slowly to remove the dirt instead of redistributing it on the surface of
the optical window.
If the optical window is still dirty, a mild soap solution can be used to gently wash the window. Repeat Step
2 to remove any remaining soap residue.
Troubleshooting
The table below shows you how to troubleshoot and resolve common issues with Mid-70 sensors. If the issue
persists, contact Livox.
35.5 35.5
61.0
64.0
46.0
62.7
6.0
1.0
4.0 1.3
4-M3 4.8
4.0 1.3
4-M3 5
46.0
61.0
6.0
1.0
35.5 35.5
4.0 1.5
4.0 1.5
15.4
18.2
32.4
97.0
15.8
12.5°
21.7
35.5 35.5
61.0
64.0
46.0
62.7
6.0
1.0
4.0 1.3
4-M3 4.8
4.0 1.3
4-M3 5
46.0
61.0
6.0
1.0
35.5 35.5
4.0 1.5
4.0 1.5
15.4
18.2
32.4
97.0
15.8
12.5°
21.7
Other manuals for Mid-70
1
Table of contents
Other Livox Accessories manuals