Maple Systems HMI5000 Series User manual






Table of contents
Other Maple Systems Touch Terminal manuals

Maple Systems
Maple Systems HMI5070Bv3 User manual
Maple Systems
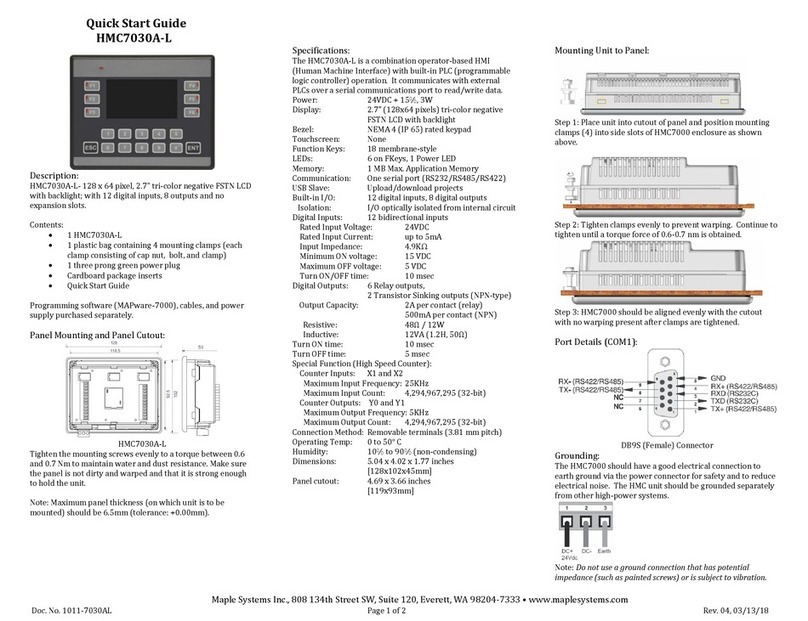
Maple Systems HMC7030A-L User manual
Maple Systems
Maple Systems HMI5000L Series User manual

Maple Systems
Maple Systems Silver Series User manual

Maple Systems
Maple Systems HMC7030A-M User manual

Maple Systems
Maple Systems AEx-100 Series User manual

Maple Systems
Maple Systems OIT 3160B User manual

Maple Systems
Maple Systems Blue Series User manual

Maple Systems
Maple Systems HMI5040BN User manual
Popular Touch Terminal manuals by other brands

SCM
SCM eHealth100 manual

UTC RETAIL
UTC RETAIL 2200 Series Back Office Workstation Bundle... installation guide

Variquest
Variquest Design Center 1000 Unpacking and setup instructions

Beckhoff
Beckhoff TwinSAFE EL6910 Operation manual

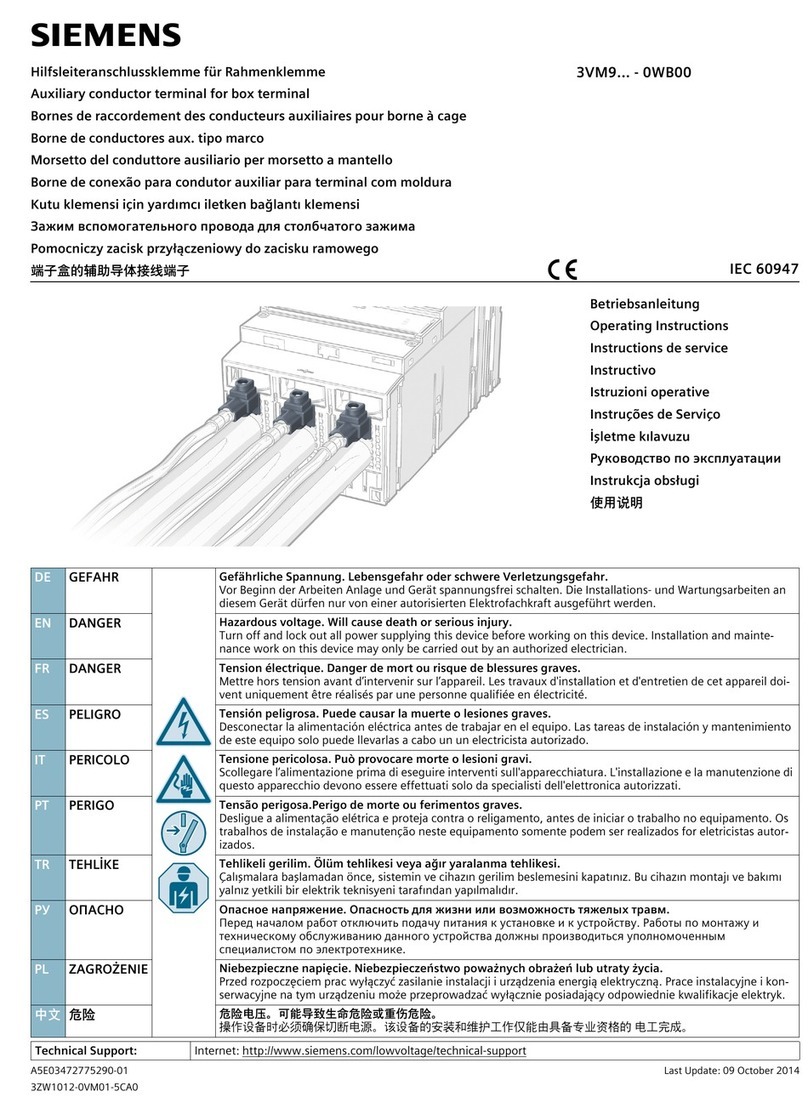
Siemens
Siemens Ay user manual

Digital Equipment
Digital Equipment VT103 LSI-11 user guide