9
22
22
2
11
11
1
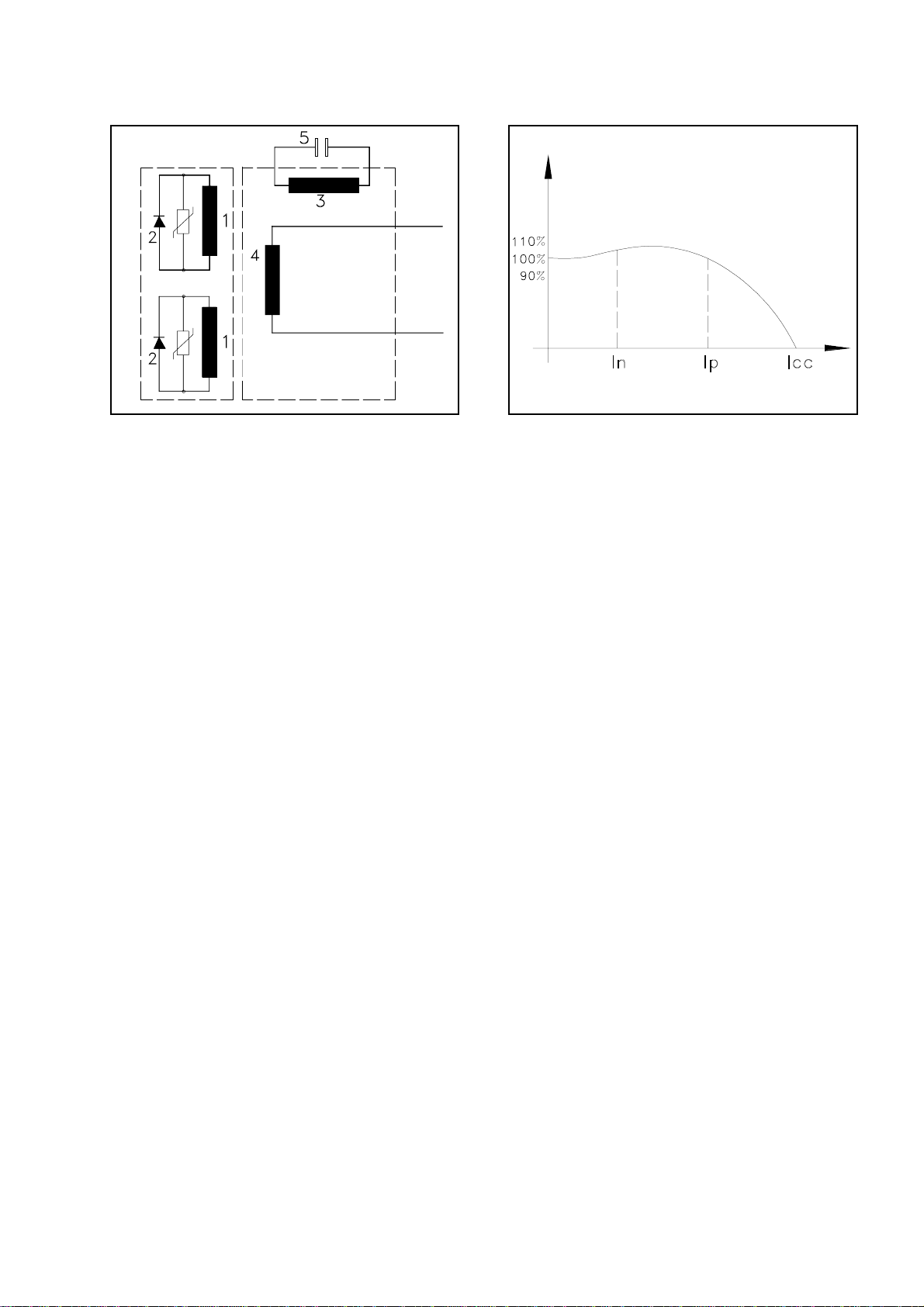
IS 2500 generators are equipped with two pole
synchronousbrushlessalternators.Thesealter-
natorsarealsoself-regulatingandself-exciting
with capacitor (Fig. 1 Ref. 5) connected to the
auxiliary winding of the stator (Fig. 1 Ref. 3).
The alternators generate an alternating voltage
attheterminalsofthemainwinding(Fig.1Ref.
4)havingafrequencyof50or60Hz.(Depend-
ingon whetherthe engineruns at3000 or3600
R.P.M.).
Thegenerationofcurrentisinaccordancewith
the principle described here below:
On starting the unit, the magnetic force of the
rotor (residual magnetism of the nucleus) in-
duces a voltage in the auxiliary winding of
excitation (Fig. 1 Ref. 3). This voltage is fed to
the capacitor (Fig. 1 Ref. 5) which creates a
capacitive current circulating in the closed cir-
cuit constituted of the capacitor and the auxil-
iarywinding.
Thiscapacitivecurrent,createsamagneticfield
reinforcing the magnetism of the rotor, thus
creating in it a voltage which rectified by the
diodes (Fig. 1 Ref. 2) makes a D.C. current
circulate in the induction windings (Fig. 1 Ref.
1).Asaresultofwhicharotatingmagneticfield
is created which generates the rated output in
theprincipal winding (Fig.1Ref. 4)andwhich
can be tapped at the terminals.
The voltage and current values (denoted in
percentagetermsofratedvaluesareasshownin
the diagram (Fig. 2).
As you will note, it is possible to get energy up
to the nominal value. With voltage practically
constant (+/- 5%). Moreover, the alternator at
a voltage not inferior to 70-75% of the rated
voltage,isabletofurnish,asinitialpowerrush,
up to 3 times the rated amperage.
As we know, this initial rush, typical of this
alternator is extremely important to start asyn-
chronous motors.
I generatori della serie IS 2500 sono dotati di
alternatorisenza spazzole,sincroni, adue poli,
autoregolati, autoeccitati, con condensatore
(Fig. 1 Rif. 5) collegato con l'avvolgimento
ausiliario di statore (Fig. 1 Rif. 3). Gli alterna-
torigeneranounatensionealternata,disponibi-
leaimorsettidell'avvolgimentoprincipale(Fig.
1 Rif. 4) a una frequenza di 50/60 Hz. (Corri-
spondenti ad una velocità del motore primo di
3000/3600 giri) secondo il principio di seguito
descritto.
All'avviamento il magnetismo di rotore (ma-
gnetismoresiduodelnucleo)inducenell'avvol-
gimentoausiliario di eccitazione(Fig.1 Rif.3)
una tensione.
Questa tensione è applicata al condensatore
(Fig.1 Rif. 5)e facircolare nelcircuito chiuso,
costituitodalcondensatoreedall'avvolgimento
ausiliario, una corrente capacitiva.
Questa corrente produce un campo magnetico
cherafforzailmagnetismodirotore,generando
in esso una tensione che, raddrizzata dai diodi,
(Fig.1Rif.2)facircolareunacorrentecontinua
negli avvolgimenti induttori (Fig. 1 Rif. 1).
Ilcampomagneticorotantedovutoallacircola-
zione di questa corrente genera a sua volta
nell'avvolgimento principale (Fig. 1 Rif. 4) la
tensione nominale ai morsetti del generatore.
I valori (intesi come percentuale dei valori
nominali) di tensione e corrente disponibili ai
morsetti hanno l'andamento riportato nel dia-
gramma(Fig.2).Comesipuònotareèpossibile
prelevare corrente fino al valore nominale a
tensione praticamente costante (+/- 5%). Ed
inoltre l'alternatore, ad una tensione non infe-
rioreal70-75%delvalorenominale,èancorain
grado di fornire una corrente di picco pari a
circa 3 volte il valore nominale.
Questacaratteristica,tipicadiquestoalternato-
re è particolarmente utile nella fase di avvia-
mento dei motori elettrici asincroni.
3) PRINCIPLE OF POWER3) PRINCIPLE OF POWER
3) PRINCIPLE OF POWER3) PRINCIPLE OF POWER
3) PRINCIPLE OF POWER
GENERATIONGENERATION
GENERATIONGENERATION
GENERATION
1) PRINCIPIO DI FUNZIONAMENTO1) PRINCIPIO DI FUNZIONAMENTO
1) PRINCIPIO DI FUNZIONAMENTO1) PRINCIPIO DI FUNZIONAMENTO
1) PRINCIPIO DI FUNZIONAMENTO