Metasys NCM 200 Series User manual

Metasys Network Technical Manual 636
Control Modules Section
Technical Bulletin
Issue Date 1297
© 1997 Johnson Controls, Inc. 1
Code No. LIT-636025
Engineering Page 3
•
Description *3
•
Theory of Operation *4
•
Design Considerations *10
•
Components *17
•
NCM Cable Guidelines *20
•
Software Set Up *30
Commissioning Procedures 33
•
Overview *33
•
Setting the N2 End-of-Line Switch 33
•
Installing the Submodules *34
•
NCSETUP *37
Troubleshooting Procedures 39
•
NCM Power Up *39
•
Communications *45
•
Related Commissioning Problems 51
•
Service 53
Specifications and Order Codes *55
•
Specifications *55
•
Ordering Information *56
Network Control Module 200 Series
* Indicates those sections where changes have occurred since the last printing.

2 Control Modules—Network Control Module 200 Series

Control Modules—Network Control Module 200 Series 3
Engineering
The 200 Series Network Control Module (NCM200) is the main
processing module in the Network Control Unit (NCU). Fully
programmable, the NCM200 coordinates and supervises the control
activities for all objects and control loops hardwired to the NCU, as well
as the remote Network Expansion Units (NEUs) and Application Specific
Controllers (ASCs) connected to it over a local bus.
An NCM200, via the N1 Local Area Network (N1 LAN), also has the
ability to control activities for objects located in other NCMs. An example
of exchanged control would be objects shed or restored by the Demand
Limiting/Load Rolling feature.
Different program sets download to an NCM200 to support a variety of
devices on its local buses. The program sets are of two types: Standard
Functionality and Migration Functionality. The Standard Functionality
supports one of the following applications:
•Standard NCM software supports the following: NEUs, Heating,
Ventilating, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) Applications such as Air
Handling Unit (AHU) Controllers, Variable Air Volume (VAV)
Controllers, VAV Modular Assemblies (VMA), Unitary (UNT)
Controllers, Lab and Central Plant (LCP) Controllers, DX-9100/9120,
and Application Specific Controllers (ASCs) on the N2 Bus, plus
C210/C260 controllers on an L2 Bus.
•Fire Management software integrates the fire and safety
IFC-1010/2020 controller to Metasys®, as well as supporting Point
Multiplex Modules (XMs) and HVAC ASCs on the N2 Bus.
•Intelligent Access Controller software integrates the access IAC-600
Controller to Metasys, as well as supporting XMs and HVAC ASCs
on the N2 Bus.
•As an alternative to the Network Terminal (NT), Operator Terminal
(OT) software connects a VT100, or a Personal Computer (PC) with
VT100 emulation software to the NCM200. An NCM with an
Operator Terminal connected supports NEUs, Intelligent Lighting
Controllers (ILCs), and ASCs, including the LCP.
In addition, an Operator Terminal connected to one NCM on the
N1 network can display, schedule, and control Fire, Access, S2, or
L2 Bus applications connected to other NCMs on the network.
Description

4 Control Modules—Network Control Module 200 Series
The Migration Functionality program set builds pathways from the
NCM200 to other systems. While it can support any of the Standard
Functionality program sets described earlier, Migration Functionality can
also connect one of the following applications to Metasys:
•S2 Migration software brings JC/85 field gear, object information, and
control directly into Metasys from the JC/85 trunks.
•JC/85 Gateway allows Metasys object information to integrate with
the JC/85 Central Processing Unit (CPU). In the Gateway application,
the NCM serves as a high-level protocol translator, making Metasys
object information available to a JC/85 headend.
•The Network Port application lets you monitor and control the
Metasys system from a third-party host. The host computer must be
able to communicate with an ALLEN-BRADLEY PLC-5®
(Programmable Logic Controller). The host, in turn, communicates
with the Network Port, which emulates some features of a PLC-5.
Note: For complete information about the Network Port, refer to the
Network Port Technical Bulletin (LIT-6295050) in the Metasys
Connectivity Technical Manual (FAN 629.5).
The NCM200 is a microprocessor-based intelligent node in the Metasys
Network. It integrates three streams of information:
•system and data base information
•application programs
•data and I/O information arriving from the communication ports
Figure 1 illustrates the basic components and functions of the NCM200.
N1 LAN
N2 Bus Lines Operator
Workstation
TBC
Microprocessor
Clock/Calendar
RS-232 Port
NT Port
Communications
Submodule Slot
Battery
Submodule
Network Identity
Module Slot
Reset Button
Optional L2
Bus Lines
NIM: Memory and
Functionality
N2 Interface
1
5
200TC1
N1 Interface
12
6
3
8
9
10
13
Figure 1: Block Diagram of the NCM200
Theory of
Operation

Control Modules—Network Control Module 200 Series 5
A Network Identity Module (NIM) (Item 1in Figure 1) is a submodule
that configures features and data base capacity for the NCM200.
The NIM206 covers all applications supported by previous NIMs. When
replacing an NIM (for example, an NIM102), use the NIM206. The
NIM206 is factory installed in the NCM201.
200TC02
Figure 2: Network Identity Module (NIM)
The microprocessor (Item 2 in Figure 1) applies the various supervisory
programs to the combined data, and controls the modules and devices that
connect to the NCM via a local bus.
This supervision and control operates in the same manner when any of the
Standard Functionality program sets (standard, fire management,
intelligent access control, or Operator Terminal) are downloaded.
For the Migration Functionality program set, the microprocessor translates
data from the field gear into compatible code for the target system:
•For S2 Migration, the microprocessor integrates the incoming S2 data
into Metasys and extends NCM supervisory and control functions
over the objects on the S2 trunk.
•For JC/85 Gateway, the NCM microprocessor:
- executes commands from the JC/85 headend to objects on the
Metasys side
- provides attribute information for all objects on the Metasys side
- translates and sends Metasys reports to the JC/85 devices
Network Identity
Modules
Microprocessor

6 Control Modules—Network Control Module 200 Series
•In Network Port applications, the microprocessor:
- translates the host-generated requests to Metasys commands
- applies the various supervisory programs to the combined data,
supporting those functions that relate to the mapping of data
objects to the host computer (mapped analog data and binary data
objects)
All the software applications and supervisory routines take place inside the
NCM; data base exceptions and historical files are uploaded to the
Operator Workstation (OWS) (Item 3in Figure 1)for reporting and
archival purposes.
The I/O subsystem supports a multi-user environment consisting of
integrated network connections (N1 and N2), submodule ports, and direct
I/O communication (NT [or Operator Terminal], RS-232).
N1 Local Area Network
N1 LAN communication is provided by the built-in N1 interface (Item 4
in Figure 1) terminating at a BNC connector at the bottom of the NCM200
module.
The N1 LAN is composed of the standard ARCNETchip set and
hardware, allowing communication with both OWSs and other NCMs.
Each NCM and OWS on the system contains a “node manager” task,
whose responsibilities include:
•broadcast once per minute that it is still online
•listen to other node managers to track on and offline trunks
•issue a time stamp for every global data base in its memory
•compare the time stamps of its own data bases to the received time
stamps of other node managers’ data bases, and update the current
data base if necessary
•monitor the printer for online or offline status
The node with the lowest address number on the system issues time and
date information once per day to ensure system synchronization. Time
and date information is backed up by a clock/calendar chip (Item 5in
Figure 1). The node manager also monitors broadcasts and issues
online/offline advisories.
In the event of a severed N1 network, each separated LAN forms an
independent network.
Communications

Control Modules—Network Control Module 200 Series 7
Local Bus: N2
The N2 Bus communications are also provided by a built-in interface
(Item 6in Figure 1). Devices on the N2 Bus constitute a local network,
controlled by the NCM. The NCM polls the devices according to a
user-set priority level, which is set at each device’s definition window.
The N2 connects in a daisy chain fashion, and provides the transmission
medium for modules installed within the base frame (e.g., a Digital
Control Module or Point Multiplex Module), as well as the external
devices (application specific controllers--including the IFC-1010/2020
Intelligent Fire Controller and IAC-600 Intelligent Access Controller).
External devices connect to the N2 interface via the Terminal
Communications Board (TBC) (Item 7in Figure 1).
An NCM200 can accept both N2 and L2 communications at the same time
when using the Standard NCM software (not fire management, intelligent
access, or OT software).
Note: Starting with Metasys Release 6.0, a second N2 Bus can be added
using an N2 submodule connected to the NCM’s Communication
Submodule slot (Item 8in Figure 1). For complete information,
see the Dual N2 Bus Application Note (LIT-6363145).
Local Bus: L2
The optional L2 Bus is dedicated to connecting C210A and C260A ASCs
on a local, external trunk, controlled by the NCM. L2 communications are
enabled by installing an L2 submodule in the NCM’s Communication
Submodule slot (Item 8in Figure 1).
The L2 Bus connects in a daisy chain fashion. As is the case with the
N2 Bus, connections from the external lines to the NCM are made at the
Communications Terminal Board. The devices on it are polled with equal
priority.
An NCM200 can accept both N2 and L2 communications at the same time
when using the Standard NCM software (not fire management, intelligent
access, or OT software).
Submodules
Submodule slots (Items 8 and 10 in Figure 1)on the NCM allow users to
plug in submodules to add or change functions to the system.
The Network Identity Module slot (Item 9in Figure 1)is reserved for
NIMs to configure the NCM200. An NIM module must be installed for
the NCM200 to operate.
The Battery Submodule slot (Item 10 in Figure 1)is reserved for the
battery submodule, which allows the NCM to retain code and data base
memory for up to 72 hours in event of a power failure.

8 Control Modules—Network Control Module 200 Series
The Communications Submodule slot (8) allows installation of one of the
following submodules to provide different communications options:
•the L2 submodule, to integrate a C210 or C260 controller to Metasys
•the N2 submodule for connection to a second N2 Bus to integrate N2
devices. See the Dual N2 Bus Application Note (LIT-6363145) for
details.
•an internal modem submodule, to connect to remote operator devices
such as a printer or OWS
•an RS-232C submodule, connecting to a printer, external modem,
S2 Migration Trunk, JC/85 Trunk, Operator Terminal, or directly
connected OWS
The RS-232C submodule is also the means by which you connect
Metasys to a host system in the Network Port application. Refer to
the Network Port Technical Bulletin (LIT-6295050) in the Metasys
Connectivity Technical Manual (FAN 629.5).
RS-232 Submodule: S2 Migration
S2 communications are made via an RS-232 submodule on the NCM200
to a Table Top Modem (TTM). The TTM then interfaces with the JC/85
trunk.
•The S2 parameters are identical to those of the JC/85 trunks.
•S2 Migration connections from the submodule to other devices on the
N1 LAN are identical to those of a Standard Functionality NCM200.
•The S2 Migration NCM does not accept a second submodule for a
local L2 Bus, or other devices via the integrated N2 Bus.
•For S2 Migration applications that require a dial-up port, you must
use the NCM401 instead of the NCM200.
RS-232 Submodule: Gateway to JC/85
The RS-232 connection on the JC/85 headend connects directly into the
RS-232 submodule on the Gateway NCM.
•The Metasys objects on Gateway are connected from throughout the
Metasys Network via the N1 LAN in the same manner as a Standard
Functionality NCM200.
•The Gateway NCM does not accept a second submodule for a local
L2 Bus, or other devices, via the integrated N2 Bus.

Control Modules—Network Control Module 200 Series 9
RS-232 Submodule: Operator Terminal
When using the Operator Terminal (OT) program set, the VT100 (or PC
with VT100 emulation software) connects to the NCM via the RS-232
submodule, replacing the use of the Network Terminal. (Instead of
connecting to the RS-232 port, an OT can connect to the NT Port.
However, only one OT can be connected at a time.)
An Operator Terminal provides a higher level of capability than the
Network Terminal, allowing you to read and write to each attribute of a
Control System (CS) object, as well as define and build data bases for the
Trend and Totalization features. Refer to the Operator Terminal
Technical Bulletin (LIT-636015).
Note: When an Operator Terminal connects to an NCM through either
the submodule (Port 2) or the NT Port (Port 4), the integrated
RS-232 port (Port 3) will also support an unconfigured OWS. An
example of this situation is using a laptop computer to download
software into the NCM.
Additional I/O Support
The Network Terminal Port (Item 11 in Figure 1)supports a connection
from the Network Terminal Unit or Operator Terminal to provide local
operator I/O. The RS-232C Port (Item 12 in Figure 1) provides a
connection to a local workstation or printer.
The NCM powers up in either a cold start condition or a warm start
condition. In the cold-start condition, the NCM automatically requests the
OWS to download the code and data base information into the NCM’s
memory. Refer to the Operator Workstation User’s Manual (FAN 634).
In a warm start condition, the code and data base are stored in memory;
the NCM is immediately and fully operational following the initial
diagnostic tests.
By retaining memory during a power cycle, the battery backup provides a
warm start condition when power returns to the NCM.
A System Reset button (Item 13 in Figure 1) manually resets the NCM
under cold start conditions, which generates a request for code and data
download.
Power Up
Conditions

10 Control Modules—Network Control Module 200 Series
The NCM’s environmental requirements are identical to those of the NCU.
For more information, reference Network Control Unit/Network
Expansion Unit Technical Bulletin (LIT-636020). Power is supplied by an
associated, and separately ordered, Power Supply Module.
Note: For S2 Migration applications that require a dial-up port, you must
use the NCM300/350 instead of the NCM200.
Since Port 1 of the NCM200 is always the built-in N2, the S2 trunk must
be moved from Port 1 on an NCM401 to Port 2 on the NCM200.
1. Remove any configured devices from Port 2 from the Global Data
Definition Language (DDL) file.
2. Move the S2 trunk from Port 1 to Port 2 in both the Global DDL file
and the NC DDL file.
3. After recompiling the NC and Global DDL files, all Graphic
Programming Language (GPL) and JC-BASIC processes must be
translated.
Note: If objects have been added online, these will be lost when you
recompile the NC file. To avoid losing these objects, first perform
a decompile (using UNDDL), and then make the port changes to
the decompiled file.
Mount the NCM200 into a standard 1-slot NCU, into Slot 2 of a 2-slot
NCU, or into Slot 3 of a 5-slot NCU (Figure 3). Make sure to terminate
the N1 cable to the BNC connector at the bottom of the NCM200 module.
5-slot Base Frame 2-slot Base Frame 1-slot Base Frame
200TC03
Figure 3: Mounting the NCM200 into a Standard 1-Slot,
2-Slot, or 5-Slot Base Frame
Design
Considerations
Replacing an
NCM401 with an
NCM200
Mounting

Control Modules—Network Control Module 200 Series 11
In addition, a simpler, streamlined version of the base frame is available
for the N1 direct-connect NCM (NCM200). This NCM-only base frame
(Figure 4) is for applications that require the NCM200’s supervision and
control over local trunks, but does not require direct wiring to field
devices, or the flexibility of interchanging other electronic modules.
Migration applications, for example, could be installed into the NCM-only
base frame since they are not used to communicate with DCMs or XMs,
and have no field devices connected to the NCU.
Includes Power
Assembly and
Communications
Board
TBC Cover
Opened
to Reveal
N2 and L2 Bus
Connections
Power Supply
NCM200
NCM-Only
Base Frame
N1 LAN Connection
200TC04
5(6(7
Figure 4: Mounting the NCM200 and Power Supply in the
NCM-Only Base Frame (BSF121)

12 Control Modules—Network Control Module 200 Series
The NCM200 requires Release 4.0 or higher of the Metasys software.
S2 Communications Tuning Parameters Modified for Telephone Lines
Due to timing delays over telephone lines, some trunk configurations may
require modification of the following S2 Communications parameters
(using NCSETUP) in order to bring the field gear online:
1. Delay between polls to field devices
2. The polling timeout delay
3. The number of polling retries
See the NCSETUP for Windows Technical Bulletin (LIT-6360251d) for
information on changing these parameters.
Directly Connectable Hardware for Each Software Type of NCM
The NCM Software Options Technical Bulletin (LIT-636023) in the
Control Modules section of the Metasys Network Technical Manual
(FAN 636), describes which Metasys hardware devices function, for each
type of downloadable software, when connected to that NCM. Please
refer to it for the latest software options.
The NIM206 is the only NIM now used. When replacing any NIM, order
the NIM206. For reference when using existing NIMs, the data base
capacity for a NIM102/202 = 300K; NIM104/204 = 600K; and the
NIM106/206 = 1200K.
Standard Functionality: Standard NCM
The load capacity for an NCM depends on the available memory
determined by the installed NIM, in addition to the software configuration
of the connected devices.
Refer to the Network Control Unit/Network Expansion Unit Technical
Bulletin (LIT-636020) for information about the object loading of the
individual electronic modules connected to the NCM via the base frame.
Standard Functionality: Fire Management
Along with the Release 4.0 or higher Metasys software needed for the
NCM200, the fire management software requires the IFC-2020
Release 3.0 or higher firmware. A fire NCM handles one IFC-1010/2020
controller with up to 240 fire zones attached to that controller. Each zone
counts as one object for the purpose of memory sizing.
Software
Configurations
NCM Capacity

Control Modules—Network Control Module 200 Series 13
The following guidelines list other kinds of devices that the fire
management NCM is capable of processing:
•HVAC ASCs (AHUs, VAVs, VMAs, UNTs, PHXs, LCPs,
DX-9100s, etc.)
•Point Multiplex Modules (XM) (Multiplex Binary, Multiplex Relay
Latched, Multiplex Relay Momentary, Multiplex Relay Electrically
Maintained)
The IFC is a building fire management controller, and in most situations it
is alone on the NCM. However, if there are a few remaining ASC or XM
points that do not justify a separate NCM, they can be added to an NCM
supporting the IFC, up to the memory limits of that NCM.
Standard Functionality: Intelligent Access Control
The Intelligent Access Control (IAC) software requires Release 4.0 or
higher Metasys software and IAC-600 Release PS130B firmware. For
Metasys Release 6.0, the IAC NCM handles one or two IAC-600
controllers and up to 16 readers attached to each controller. (Prior to
Release 6.0, the IAC NCM handles one IAC-600 controller and up to
16 readers attached to that controller.)
The following guidelines list other kinds of devices that the intelligent
access control NCM is capable of processing:
•HVAC ASCs (AHUs, VAVs, VMAs, UNTs, PHXs, LCPs,
DX-9100s, etc.)
•Point Multiplex Modules (XM) (Multiplex Binary, Multiplex Relay
Latched, Multiplex Relay Momentary, Multiplex Relay Electrically
Maintained)
The IAC-600 is a building access controller, and in most situations it is
alone on the NCM. However, if there are a few remaining ASC or
expansion module points that do not justify a separate NCM, they can be
added to an NCM supporting the IAC-600, up to the memory limits of that
NCM.
Standard Functionality: Operator Terminal
The Operator Terminal NCM has a load capacity similar to that of the
standard NCM, including support of the Intelligent Lighting Controller
(ILCs) and Lab and Central Plant Controller.
It differs from the standard NCM in that it replaces the Network Terminal,
and does not support the DSC-1000 family of controllers (i.e., C210A,
C260A, C260X, C500X) connected to the same NCM.
An Operator Terminal NCM may, however, interact with DSC-1000
controllers if they are connected to another NCM on the N1 LAN.

14 Control Modules—Network Control Module 200 Series
Migration Functionality: Gateway
An NCM200 with a 200 series NIM and Gateway software can connect
one gateway trunk (via the RS-232 submodule) and map up to 1400 JC/85
Level 3 points. This trunk requires a dedicated RS-232 port on the JC/85
headend. An NIM206 handles the largest JC/85 data base allowed.
Migration Functionality: Network Port Application
See the Network Port Technical Bulletin (LIT-6295050).
Migration Functionality: S2 Migration
An NCM200 with a 200 series NIM and S2 software can connect
one JC/85 trunk through one Table Top Modem (for example, if
four trunks were originally connected to the JC/85 headend, four NCMs
are required unless the trunks can be reconfigured). The data base size of
each trunk can be calculated with the NCM Memory Estimator.
The following are countable JC/85 objects:
•FPU device
•FPU hardware points (the SST101 counts as two objects)
•DSC-8500 device
•DSC-8500 hardware points
•DSC-8500 data points
•DSC-8500 status variables
In addition to the memory required by the object count and Metasys
standard features, also calculate additional memory used for written
programs of GPL equivalents to JC/85 features. See How to Use the
Metasys GPL HVAC Library (LIT-636121), under the App. Notes: GPL
HVAC Library tab of the Metasys Network Technical Manual (FAN 636).
Applications of interest to JC/85 users are:
•interlocks
•computed points
•chiller sequencing
Application notes exist for each of these processes in Volume IV of the
Metasys Network Technical Manual (FAN 636).
Among the considerations about adapting JC/85 code to Metasys, here are
a few that may adjust the memory requirements:
•Auto Shutdown
When converting JC/85’s Auto Shutdown feature to Metasys, write an
equivalent GPL process for Metasys and add the file object size to the
NCM’s memory usage.

Control Modules—Network Control Module 200 Series 15
•ESO (Enthalpy Switch Over)
When converting the JC/85 ESO feature to Metasys, you must choose
one of the four economizer features utilized in Metasys. Details and
specifications about each of these programs are listed in How to Use
the Metasys GPL HVAC Library (LIT-636121).
- ECONEN Comparison Enthalpy Economizer
- ECONOE Outdoor Air Enthalpy Economizer
- ECONDB Outdoor Air Dry Bulb Economizer
- ECONRA Differential Temperature Economizer
Table 1 shows applications and port restrictions when installing
submodules into an NCM200 with a Standard Functionality software set
downloaded (standard, fire management, intelligent access control, OT).
Table 1 : Standard Functionality NCM200 Serial Port Configuration
Connection
Maximum
Concurrent
Connections5
Port 1
(RS-485)
Port 2
(Dial) 6, 9
Port 3
(Laptop)2
Port 4
(NT) 11, 12
N2
2
✓
✓
L2 1
1
✓
S2
1
✓
JC-85 Gateway
1
✓
Network Port
1
✓
OWS-Direct (configured 8)
2
✓
✓
OWS-Dial 7
1
✓
✓, 3
OWS (unconfigured 10 )
1
✓
NT
1
✓
NT-Emulator
1
✓
OT 4
1
✓
✓
✓
OT-Dial 4, 7
1
✓
✓
NC Printer
2
✓
✓
NC Printer-Dial 7
1
✓
✓
N1 – ARCNET
Ethernet
Maximum Speed
--
19.2K
19.2K
19.2K
19.2K
Notes:
1 The L2 Bus connection requires an L2 submodule.
2 Direct connection is recommended on Port 3 for the OWS. This allows connection to
systems locally.
3 Download from remote OWS is only available on the NCM350/361.
4 Use of the Operator Terminal replaces the Network Terminal and disables the NT port.
Continued on next page . . .
Configuring the
NCM
Submodules:
Standard
Functionality

16 Control Modules—Network Control Module 200 Series
Notes: (Cont.)
5 The maximum number of connections of that type on the NCM. For example, there can
be two N2 connections on the NCM, on Ports 1 and/or 2. There can be one OWS Dial
connection on the NCM, on Port 2, 3, 5, or 6.
6 Use RS-232 cable to connect devices to the integrated RS-232 port. Connections at the
integrated ports are independent of each other; for example, a printer can be connected
to both ports at the same time. An RS-232 submodule is required for these connections.
7 Dial-up printer, OWS, or OT connected to phone line via a modem.
8 A configured OWS is an OWS that is defined in the data base.
9 N2 Bus can connect to this port via an RS-232 to RS-485 converter.
10 An unconfigured OWS is not defined in the data base (for example, a laptop computer).
It can be used to run logs and summaries, or to download a data base. They cannot be
connected directly to the Ethernet LAN.
11 Either an NT or an OT directly connects to the RJ-12 port via the NT Emulator cable.
12 An OT, or a PC with NT Emulator software, connects directly to the RS-232 port via
RS-232 cable.
Table 2 illustrates applications and port restrictions when installing
submodules into an NCM200 with one of the Migration Functionality
software sets downloaded (for the Network Port Application, see the
Network Port Technical Bulletin, LIT-6295050).
Note: When installing a Migration NIM, you have the option of loading
any of the Standard Functionality software sets instead of a
Migration software set.
Table 2: Migration Functionality NCM200 Serial Port Configuration
Port Application
(Ports must be configured via system software for
appropriate application.)
NT Port Network Terminal directly connects via the NT cable.
Integrated RS-232 Port
(Port 3)
All devices connect to the integrated RS-232 port via an
RS-232 cable.
Configured OWS (i.e., defined in the data base)
Printer
Unconfigured OWS (i.e., not defined in the data base): An
example would be a laptop computer. May be used to run logs
and summaries, or to download a data base.
Communications
Submodule Port
(Port 2)
S2 Migration, connected via RS-232 submodule to JC/85 trunk
via Table Top Modem.
JC/85 Gateway, connected via RS-232 submodule to JC/85
headend. (Connection may alternately be via a high-speed
modem over a dedicated phone line.)
Note: JC/85 Gateway: To send the NCM print file to the JC/85 printer, define the printer as
“Port 2” (the communications submodule slot--the same port definition as you assign
to Gateway). To print to a printer connected directly to the NCM200, connect the
printer into the RS-232 port (Port 3--the integrated port).
Configuring the
NCM
Submodules:
Migration
Functionality

Control Modules—Network Control Module 200 Series 17
Figure 5 illustrates the ports and submodule positions on the NCM.
5(6(7
RS-232 Port - Port 3
(Laptop Operator Workstation or Printer)
NTU Port (6-pin Telephone Plug)
Slot for Communications
Submodule - Port 2
Battery Submodule (Included)
Reset Button
LED
Board N2 End-of-Line Switch
Slot for Network Identity Module
N1 LAN Connection
200TC05
Note: The integrated
N2 Bus is Port 1.
Figure 5: Port and Submodule Positions on the NCM
The L2 submodule provides compatible signals for a DSC-1000 L2 Bus
(C210 and C260 controllers). The L2 submodule inserts in only
one orientation. There is one switch to set on the L2 submodule:
Channel A/B Switch: Indicates which terminal blocks the L2 connects to
on the communication panel. Set to Channel B, corresponding with the
TB2 terminals on the TBC.
For applications requiring a second N2 Bus, use the N2 submodule, which
provides compatible signals for N2 devices. For complete information,
see the Dual N2 Bus Application Note (LIT-6363145) in this manual.
The N2 submodule inserts in only one orientation. There are two switches
to set on the N2 submodule:
Channel A/B Switch: Indicates which terminal blocks the N2 connects to
on the communication panel. Set to Channel B, corresponding to the TB2
terminals on the TBC.
End-of-Line (EOL) Switch: Indicates whether the NCM is one of the
two EOL devices on the N2 bus. Setting the N2 EOL to In means the
NCM is EOL. Out means that other modules are daisy-chained (in the
backplane) both upline and downline of the NCM.
The RS-232 submodule provides input/output at standard RS-232C levels.
The RS-232 submodule inserts in only one orientation.
There are no switches to set. However, because of the recessed connector
on the NCM, a special right-angle cable with a narrow profile shell is
required to attach to the RS-232 submodule. One end of this cable
(NU-CBL101-0) arrives pigtailed.
Components
L2 Submodule
N2 Submodule
RS-232
Submodule

18 Control Modules—Network Control Module 200 Series
The user connects the pigtailed wires into a separately ordered hood, either
male (MHK101) or female (FHK101), according to the pinout
requirements.
The internal modem is Hayes® compatible, with the baud rate
automatically configuring to either 300 bps or 1200 bps. The module
inserts in only one orientation. This modem is compatible with the
Metasys Network and resides within the NCM. An external modem
(Hayes compatible) may be preferred if faster communication rates or
different performance characteristics are needed. Connecting an external
modem requires the use of the RS-232 submodule.
There are no switches to set on the internal modem. Two phone jacks are
evident on the module face. The phone line connects to the upper jack
marked Line. A telephone handset can be connected into the lower jack
marked Handset.
The Network Terminal plugs into this 6-pin telephone jack, which
supports Transmit, Receive, and Data Terminal Ready lines. There are no
switches to set on this built-in port.
This port is non-functional when the Operator Terminal software set is
downloaded. The NT port does not support the Zone Bus Terminal.
!
CAUTION: Do not plug a phone line into the NT port. Plugging a
phone line into the RJ-12 port may damage the port
and render it unusable.
There are no switches to set on the built-in RS-232C port (Port 3), which
is used to support a local OWS or local printer. All RS-232 connections to
third-party equipment must be made with shielded cable. A typical
application may utilize the built-in RS-232 port in addition to the RS-232
submodule, for a total of two RS-232 connections.
The battery submodule automatically recharges from the NCM, and
maintains Random Access Memory (RAM) programs and data bases for
up to a 72-hour power failure. The module installs in the field and inserts
in only one orientation. There are no switches to set.
The TTM-10n Table Top Modem provides an interface between the
RS-232 submodule on the S2 Migration NCM and one JC/85
communications trunk. A TTM-10n modem consists of an external power
supply, a circuit board with enclosure, and one master modem card.
Three models (and one alternative) of the TTM-10n are available:
Internal Modem
Submodule
RJ-12 Network
Terminal Port
RS-232C Port
Battery
Submodule
Table Top
Modem

Control Modules—Network Control Module 200 Series 19
TTM-101 Provides the interface necessary to communicate to a
18 AWG proprietary, shielded, twisted-pair trunk.
A TRM-101 comes mounted to the printed circuit card, and
is available for single-trunk applications only.
TTM-102 Provides the interface necessary to communicate to a
dedicated leased type 3002 phone line. A DPM-101 comes
mounted to the printed circuit card.
TTM-103 Provides the interface necessary to communicate on a
JC/LINK Generic Bridge. The Rolm bridge version is not
available.
MDM-101 An alternative modem to interface between an RS-232
(UDS-202) submodule from the S2 NCM and a remote MDM-101
(outside vendor modem would be the UDS-202) over a
voice-grade type 3002 leased phone line.
The printers are not a component of the NCM200. However, the specific
printer models approved for the NCM200 are the IBMProprinter III
and the LexmarkModel 2380 (set to emulate an IBM Proprinter III).
Notes: Smoke control applications require a printer connection to the
NCM. If the Fire OWS is not being used, a UL Listed PRN-3/-4
printer must be connected directly to at least one UL Listed
NCM200/201-0 or NCM300/350-2 running the smoke control
algorithm and the NCM must be configured as “NC Direct.”
Figure 19 illustrates the pinout connections to the NCM’s
integrated RS-232 port or RS-232 submodule.
To properly configure the printer for the NCM200, use the individual
printer instructions as a guide to set the mode and DIP switches to the
following configurations:
Card: Serial Interface
Mode: RS-232
Polarity: No reverse polarity (typically--this setting could change,
depending on the individual computer system and cabling.)
Baud Rate: Set to the rate established in DDL. Default is 9600.
Data Bits: 8
Parity: No
Stop Bits: 1
Protocol: XON/XOFF
Operation: Normal
Cable connections are illustrated in the following section, NCM Cable
Guidelines.
Printers

20 Control Modules—Network Control Module 200 Series
This section starts by illustrating the N1 LAN connections for new and
retrofit applications. N2 cabling to the communications terminal board is
described in the Network Control Unit/Network Expansion Unit Technical
Bulletin (LIT-636020), and the N2 Communications Bus Technical
Bulletin (LIT-636018).
This section then organizes cable connections by device (such as by OWS,
printer, etc.) and finally by migration type (Gateway or S2). Devices
connecting to both the RS-232 submodule and the integrated RS-232 port
show two cables, since the pinouts for those connections are different.
Using the NCM-Only Base Frame
Connect the N1 cable via a T-connector to the bottom of the NCM200
module, as shown in Figure 6. Ensure that no metal part of the connection
(EOL cap, T-connector, or exposed metal part of the cable) is touching a
case or any metal on the base frame. Black tape, or a clip-on plastic
shroud, will protect the metal from inadvertent contact.
Power Supply
NCM200
TC200_6
N1 LAN Connection
Add terminal cap or
continue N1 LAN at
left side of "T."
Apply black tape or
plastic shroud around
metal connections.
1.
2.
Figure 6: Making N1 LAN Connections Using
NCM-Only Base Frame
NCM Cable
Guidelines
NCM200 N1 LAN
Connection
Other Metasys Control Unit manuals
Popular Control Unit manuals by other brands
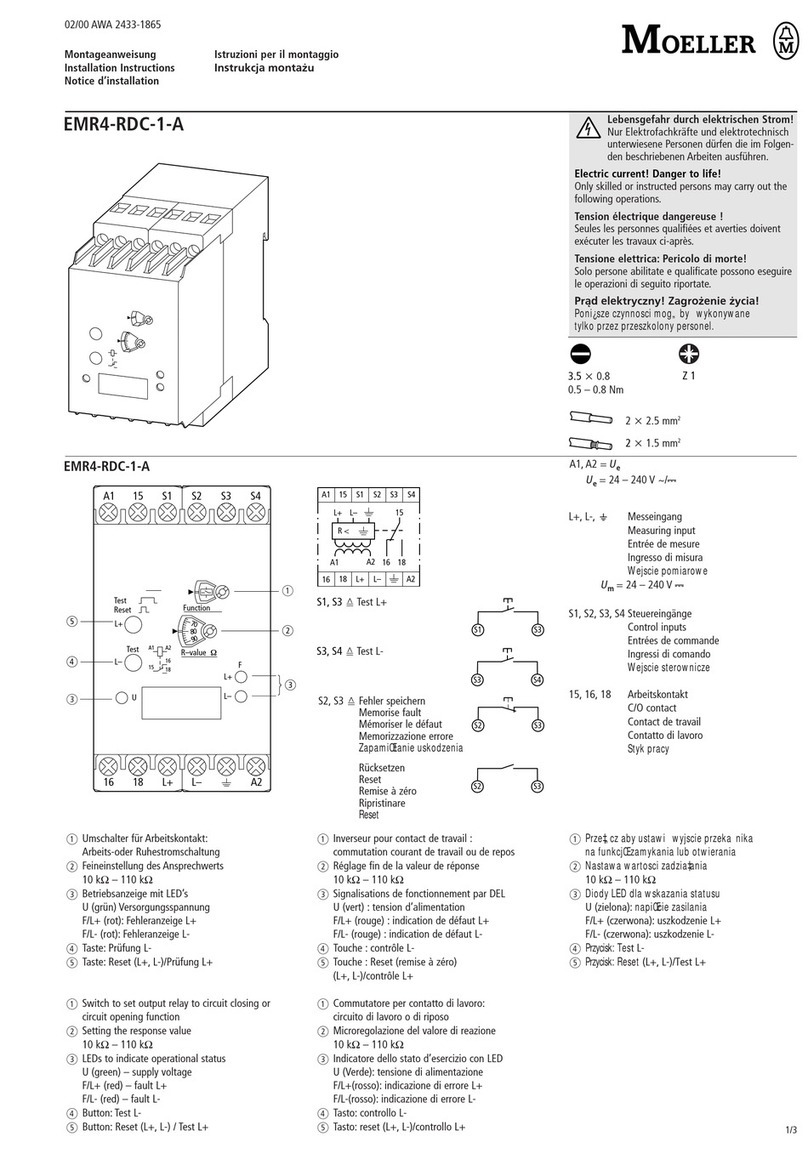
Moeller
Moeller EMR4-RDC-1-A installation instructions

Dickey-John
Dickey-John Land Manager SE manual

Wöhner
Wöhner CRITO CrossBoard Mounting instructions

Meinberg
Meinberg IMS-GNS181-UC Setup guide
Wilo
Wilo PLR Installation and operating instructions

Gemu
Gemu 707 Installation, operating and maintenance instructions