Metrodata PacketLINK User manual

PacketLINK
www.metrodata.co.uk
Metrodata Ltd
Laxton House
Crabtree Office Village
Eversley Way
Egham
Surrey TW20 8RY
United Kingdom
tel: +44 (0) 1784 744700
fax: +44 (0) 1784 744701
email: [email protected]
website: www.metrodata.co.uk Part No: 76-02-106C
Metrodata PacketLINK
User Manual

Contents
1. Introduction 3
1-1 Functional Description 3
1-2 Features 3
1-3 PacketLINK Image 3
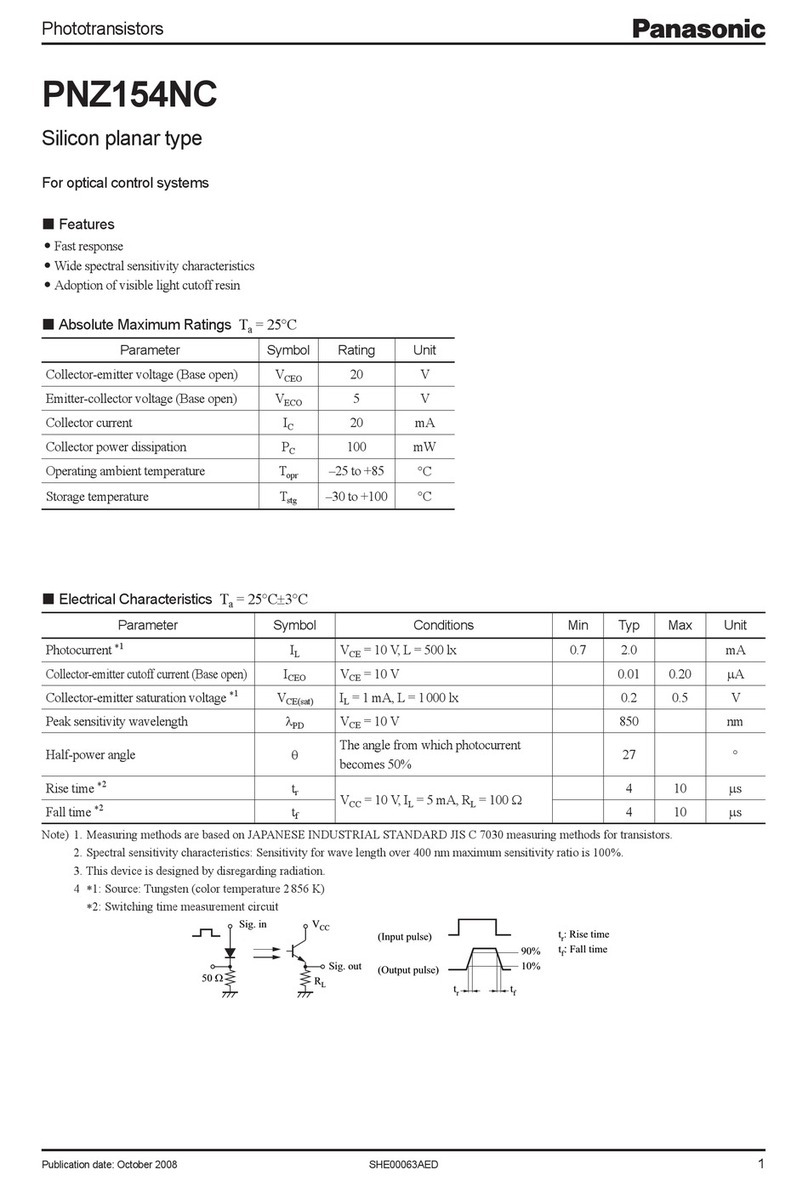
1-4 Technical Specifications 4
2. Overview 5
2-1 Description 5
2-2 Front Panel 5
2-3 Rear Panel 6
2-4 IP Configuration, important considerations 6
2-5 Interface Configuration, important considerations 6
2-6 Fault Reporting 7
2-7 Default Factory Settings 7
2-8 Using the CLI to Configure the Unit 7
2-8-1 Using the Console Port 7
2-8-2 Using Telnet 7
2-8-3 Using the CLI 8
2-8-4 Save Configuration 8
2-9 Setting up a Working Configuration 8
2-9-1 Setup the units on a bench. 8
2-9-2 CO unit TCP/IP Configuration 9
2-9-3 CPE unit TCP/IP configuration 10
2-9-4 CPE unit CES Configuration 11
2-9-5 CO unit CES Configuration 11
2-9-6 Testing 11
3. CLI Commands 12
4. Quick Start Guide 19
4-1 Introduction 19
4-2 Requirements 19
4-3 Getting Started 19
4-4 Configuration 20
4-5 Test 20
5. Scripts 21
5-1 PL1820: CO, enable 16 E1 channels, unframed, E1 receive timing 21
5-2 PL1820: CPE, enable 16 E1 channels, unframed, E1 adaptive timing 23
5-3 PL1400: CO, enable 4 E1 channels, unframed, E1 receive timing 25
5-4 PL1400: CPE, enable 4 E1 channels, unframed, E1 adaptive timing 26
5-5 PL1100: CO, enable 1 E1 channel, unframed, E1 receive timing 27
5-6 PL1100: CPE, enable 1 E1 channel, unframed, E1 adaptive timing 27

PacketLINK User Manual
3
1. Introduction
1-1 Functional Description
The PacketLINK family is a “Multi-service (TDM and Ethernet) over Ethernet” bridge, which
transports up to 16 ports of E1 and one LAN over an Ethernet network. Its target application is
the replacement of E1 leased lines, by enabling the interconnection of E1 equipment via an
Ethernet WAN circuit.
The E1 over IP algorithm is compliant with the IETF “CES over IP” standard. LEDs are
provided for alarms and status indication.
1-2 Features
• PL1100 supports 1x E1 connection over an Ethernet WAN
• PL1400 supports up to 4x E1 connections over an Ethernet WAN
• PL1820 supports up to 16x E1 connections over an Ethernet WAN
• User Ethernet LAN port also available
• Full-duplex 100Mbps Ethernet Interface
• Auto-negotiation
• Flexible E1 clocking
• Activity and alarm LEDs for each E1 port
• Link/Activity and Link Speed LEDs for each Ethernet port
• Standalone desktop unit, with optional 19” rack mount brackets
• Integral universal AC and -48VDC power supplies
1-3 PacketLINK Image

PacketLINK User Manual
4
1-4 Technical Specifications
Physical Dimensions:
• Height: 44mm (1U)
• Width: 320mm
• Depth: 125mm
• Weight: 1.2kg ~ 1.3kg (depending upon model)
100M Ethernet Interface
• Compliant with 802.3/802.3u standards
• 100-BaseT with RJ45 connector
• Full-duplex
• Auto-negotiation
• LED indicators: Link/Activity and Link Speed
TDM Interfaces: E1
• Data Rate: 2.048 Mbit/s ± 50 ppm
• Line Code: HDB3
• Impedance: 120 ohms ± 5% resistive, balanced.
• LED indicators: Activity and Alarm
• Connector Type: RJ45
Power Supply
• AC: 85V to 264V, 47~63Hz and DC: -36V to -72V
• Both supplies can be used simultaneously for added resilience
• Maximum Power Consumption: < 10 watts
Operating Environment
• Ambient temperature: 0 ~ 40 °C
• Storage temperature: 0 ~ 85 °C
• Relative humidity: 5 ~ 95% non-condensing

PacketLINK User Manual
5
2. Overview
2-1 Description
PacketLINK units have connectors on both the front panel and the rear panel, examples
are shown below.
2-2 Front Panel
PL1400
System Indicators
PWR (Power On/Off LED)
ALM (failures/errors from any of E1 link)
Reset Button
Use this button to restart the system.
LAN Ethernet Connector and Indicators
The Ethernet interface is an RJ45 connector with two LED indicators:
GREEN LED:
Solid Green indicates Ethernet link is up
Blinking Green indicates Tx / Rx traffic is traversing the port.
ORANGE LED:
Solid Orange indicates 100 Mbps link speed
Off indicates 10 Mbps link speed.
E1 Interface Connectors and Indicators
The E1 interface is an RJ45 connector with two LED indicators:
GREEN LED:
Solid Green indicates E1 port is enabled and traffic is traversing the port
Off indicates E1 port is disabled.
ORANGE LED:
Solid Orange Indicates E1 link error has occurred
Off indicates no alarms or failures.
The Orange LED indicates one of the following alarms has occurred:
E1 LOS, LOF, AIS or RAI alarm

PacketLINK User Manual
6
RS232 Console Port
Console port with RS232 interface via a DB9 (female) connector, operating at 115200bps, 8 data
bits, no parity, 1 stop bit, no flow control.
NMS Ethernet port
Supports local or remote management via Telnet or SNMP.
2-3 Rear Panel
Rear Panel
WAN Ethernet Interface
The Ethernet interface is an RJ45 connector with two LED indicators:
GREEN LED:
Solid Green indicates Ethernet link is Up
Blinking Green indicates Tx/Rx traffic is traversing the port.
ORANGE LED:
Solid Orange indicates 100 Mbps link speed
Off indicates 10 Mbps link speed.
AC Power Socket and Switch:
The AC power supply operates with an input voltage range of 85V to 264V AC.
DC Power Socket and Switch:
The DC power supply operates with an input voltage range of -36V to -72V DC.
2-4 IP Configuration, important considerations
The IP address, subnet mask and default gateway are configured using the console port.
N.B The LAN port and WAN port IP addresses are on the same subnet.
N.B. The WAN port and NMS port IP addresses must be on different subnets.
2-5 Interface Configuration, important considerations
The LAN Ethernet port is normally data rate limited to ensure that it doesn’t affect the E1
circuits. The 16 data rate limits available are 50K, 100K, 150K, 200K, 250K, 300K, 350K, 400K,
800K, 1.6M, 3.2M, 6.4M, 12.8M, 25.6M, 51.2M and 100M.
Each E1 port can be enabled or disabled. The E1 LEDs are lit when the E1 channel is enabled.

PacketLINK User Manual
7
The Jitter Buffer is used to compensate for packet delay variations between two devices, and the
jitter buffer size has 8 settings of 11, 23, 40, 75, 99, 145, 192 and 239 ms based on the standard
Ethernet frame size of 1518 bytes. The default jitter buffer size of 23ms corresponds to sufficient
buffering to compensate for 11.5ms of packet delay variation in each direction.
2-6 Fault Reporting
Active E1 alarms can be displayed by executing the CLI command almall. The alarms are
interpreted as follows:
E1LOS: Loss of E1 signal from the equipment connected to the E1 port.
E1AIS: AIS alarm received from the equipment connected to the E1 port.
PWLBIT: RAI alarm received from the equipment connected to the E1 port.
PWRBIT: Packet loss has occurred at the remote Ethernet WAN port.
PWSEQNUMERR: Packets received out of sequence at the local Ethernet WAN port.
JBUFEMP: Jitter buffer empty has occurred. (Possible reasons could be due to WAN
port Ethernet link down or pseudowire ID mismatched.)
JBUFOV: Jitter buffer overflow has occurred.
2-7 Default Factory Settings
The PacketLINK default factory settings are shown below.
CO device
(Factory Defaults)
NMS port IP address 192.168.1.11
NMS port subnet mask 255.255.255.0
Default gateway 172.16.1.2
WAN port IP address 172.16.1.1
WAN port subnet mask 255.255.255.0
LAN to WAN port bandwidth 400Kbps
2-8 Using the CLI to Configure the Unit
2-8-1 Using the Console Port
To use the console port, configure your terminal as follows:
115200bps, 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit, no flow control
2-8-2 Using Telnet
The PacketLINK units support Telnet service for remote configuration via the command
line interface. However the Telnet port number has been changed to port 8888 due to the
security issues with default port 23.

PacketLINK User Manual
8
To telnet to a PacketLINK device (with default settings) from your computer, connect your
computer to the LAN port with an Ethernet cable, then follow these steps:
Step 1: Configure your computer IP address as 172.16.1.100 and subnet mask set to 255.255.255.0
Step 2: On the command terminal of your computer, type telnet 172.16.1.1 8888.
2-8-3 Using the CLI
The commands available via the console port or via Telnet are the same.
Login details:
Password: admin, logs you in as a basic user
CLI> passwd
Enter Password: gciadmin, logs you in as an administrator which is required for most
configuration changes
See section 3 for the list of CLI commands.
2-8-4 Save Configuration
After changing the device settings, please execute the csave CLI command to save the new
settings to the device. This will prevent configuration loss if the device is rebooted or power
cycled.
2-9 Setting up a Working Configuration
The following instructions will configure a working TDM over IP network including the settings
in the table below. This network will offer a single E1 connection from the E1 clock master
unit (which should be connected to the CO device) to the E1 clock slave unit (which should be
connected to the CPE device).
CO device
(Factory Defaults)
CPE device
NMS port IP address 192.168.1.11 192.168.2.11
NMS port subnet mask 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0
Default gateway 172.16.1.2 172.16.1.1
WAN port IP address 172.16.1.1 172.16.1.2
WAN port subnet mask 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0
LAN to WAN port bandwidth 400Kbps 400Kbps
2-9-1 Setup the units on a bench.
Connect the PC COM port to the PacketLINK front panel console port. This will be our CO
unit for the test.

PacketLINK User Manual
9
Open terminal (115200,8,N,1) and power on the PacketLINK device. The unit takes about a half
minute to boot up and display the password prompt.
Password: admin, logs you in as a basic user
CLI> passwd
Enter Password: gciadmin, logs you in as an administrator which is required for most
configuration changes
2-9-2 CO unit TCP/IP Configuration
The following commands clear and display the CO unit TCP/IP configuration
CLI>gci
====== CLI: Initial ======
GetMAC: Name=eth0, MAC=00:02:AB:A8:01:0B FA=1.
GetMAC: Name=eth0, MAC=00:02:AB:A8:01:0B FA=1.
GetMAC: Name=eth1, MAC=00:02:AB:10:01:01 FA=1.
GetSrcMAC: Name=eth1, MAC=00:02:AB:10:01:01, FA=1.
GetRoute: Name=eth1, Dst=0 Gw=172.16.1.2 F=3.
Initial MW_OS ...
===== Initial All_Chips from here =====
===== Reset CESOP(2) Data Struct.
Base=x30000000, ChipId=x75 x81 x60 xA1.
Return CESOP Type=22
--> Found ‘CESOP-E1’ at Addr=0x30000000.
==> Init ‘CESOP-E1’ at Addr=0x30000000.
===== Initial All_Chips done here =====
GetMAC: Name=eth1, MAC=00:02:AB:10:01:01 FA=1.
GetSrcMAC: Name=eth1, MAC=00:02:AB:10:01:01, FA=1.
GetRoute: Name=eth1, Dst=0 Gw=172.16.1.2 F=3.
Init FM OK !
Init ISR OK !
Init PM OK !
Init FM Notification=x100131A8.
Hist_SemMT=x1011BECC already Created.
HAC_MsgId=x8001 already Created.
HAC_Task=x1005 already Created.
CLI>cdisp
====== CLI: CFG Display ======
====== Config: IP Addr = 192.168.1.11
====== Config: Net Mask = 255.255.255.0
====== Config: GW Addr = 172.16.1.2
====== Config: Trap EN = 0. (Disable)
====== Config: Trap IP = .
====== Config: NTP EN = 0. (Disable)
====== Config: NTP IP = .
====== Config: CESoPSN-IP (16-Ports) ======

PacketLINK User Manual
10
CESOP(Dev#1): SrcAddr=00:02:AB:10:01:01, SrcIP=172.16.1.1, SrcMask=255.255.255.0
ChVLan En=0
CLI>
The gci command will re-initialize the CES (Circuit Emulation Services) engine. The cdisp
command will display the configuration. Note that the IP Addr, Net Mask and GW are the
settings of the NMS port (out-band). The NMS port’s IP must reside on a subnet different from
the WAN port. The WAN port is the Ethernet trunk which will carry the CES between two
PacketLINK units.
The SrcAddr (MAC) for this unit’s WAN port is automatically generated from the WAN IP
address (CTC OID+last three bytes of IP address). The channel settings require addressing the
remote unit via its MAC address. Therefore, we will need to know each PacketLINK unit’s MAC
in order to do the configuration. The SrcIP is the IP address assigned to the WAN Ethernet port.
We will leave this PacketLINK’s LAN and WAN settings as they are (and call this the CO unit).
We’ll configure the matching unit differently (and call it the CPE unit).
This setting example will only configure the Ch1 E1 link. The CLI can have scripts pasted,
avoiding repeated keying of data and possible mistakes keying.
Text may be pasted into PuTTY by using [shift + Insert] key combination. TeraTerm uses
[Alt+V].
Example scripts are provided in Section 5 which configure all E1 ports. These scripts can be
modified offline by engineers and used for quick configuration in the field.
2-9-3 CPE unit TCP/IP configuration
Connect the PC COM port to the console port on the other PacketLINK unit. This will be our
CPE unit for the test. We will update the NMS management and WAN IP configuration, note
the source MAC, configure CES on the CPE device and then go back and do the CO unit’s CES
configuration.
CLI>gci
CLI>srcnet 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.0 //setup WAN IP and subnet
CLI>ipset 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 172.16.1.1 //setup CPE NMS, IP subnet and GW
CLI>csave //save
CLI>cdisp
====== CLI: CFG Display ======
====== Config: IP Addr = 192.168.1.10
====== Config: Net Mask = 255.255.255.0
====== Config: GW Addr = 172.16.1.1
====== Config: Trap EN = 0. (Disable)
====== Config: Trap IP = .
====== Config: NTP EN = 0. (Disable)

PacketLINK User Manual
11
====== Config: NTP IP = .
====== Config: CESoPSN-IP (16-Ports) ======
CESOP(Dev#1): SrcAddr=00:02:AB:10:01:02, SrcIP=172.16.1.2, SrcMask=255.255.255.0
ChVLan En=0
2-9-4 CPE unit CES Configuration
The following CLI commands are required and documented here as to their usage.
CLI>cespwidset 1 1 1 //setup the pseudo-wire IDs, 1 1 1, 2 2 2, ... 16 16 16
CLI>pktsize 1 1 //setup ch1 packet size (0:1514, 1:782, 2:178, 3:306 bytes)
CLI>jitterbd 1 1 //setup jitter buffer to compensate for latency
(0:11ms, 1:23ms, 2:40ms, 3:75ms, 4:99ms, 5:145ms, 6:192ms, 7:239ms) since packet size is set to
782 bytes, about half the size of 1514 packet, the jitter buffer of 23ms will provide about 11.5ms
latency coverage (23ms/2=11.5ms)
CLI>ceschclkset 1 0 //setup channel clock to adaptive (0:Adaptive, 1:Internal, 2:RxLine)
CLI>ceschset 1 1 172.16.1.1 //destination IP and MAC
CLI>csave //config save
CLI>reboot //restart device with new configuration
2-9-5 CO unit CES Configuration
Connect the PC COM port back to the CO PacketLINK unit console port.
CLI>cespwidset 1 1 1 //setup the pseudo-wire IDs, 1 1 1, 2 2 2, ... 16 16 16
CLI>pktsize 1 1 //setup ch1 packet size (0:1514, 1:782, 2:178, 3:306 bytes)
CLI>jitterbd 1 1 //setup jitter buffer to compensate for latency
(0:11ms, 1:23ms, 2:40ms, 3:75ms, 4:99ms, 5:145ms, 6:192ms, 7:239ms) since packet size is set
to 782 bytes, about half the size of 1514 packet, the jitter buffer of 23ms will provide about
11.5ms latency coverage (23ms/2=11.5ms)
CLI>ceschclkset 1 2 //setup channel clock to recovery (0:Adaptive, 1:Internal, 2:RxLine)
CLI>ceschset 1 1 172.16.1.2 00:02:ab:10:01:02 //destination IP and MAC
CLI>csave //config save
CLI>reboot //restart device with new configuration
2-9-6 Testing
Your settings are now configured ready for testing.
The E1 device that is the clock master (i.e. that sources the E1 timing) should be connected to
the CO unit.
The E1 device that is the clock slave (i.e. that is configured for E1 loop timing) should be
connected to the CPE unit.

PacketLINK User Manual
12
3. CLI Commands
The CLI commands are summarized as the following table:
CLI Command Description
System Command
?Display a full list of commands
logout Logout CLI System
cdisp Display current configuration
csave Save current configuration
cload Load configuration setting from FLASH
passwd Enter password to change user-mode. (i.e. View/Setup/
Admin mode)
p.s: If inputted password is not for “setup” or “admin”, it
will enter the “view” mode
setpass mode Modify password for user-mode.
mode: ‘s’ for setup mode, ‘a’ for admin mode, ‘c’ for CLI
login
ipset ip_addr net_mask
gw_addr
Set NMS port IP address, subnet mask and gateway
address. ip_addr: NMS port IP address to be assigned.
net_mask: subnet mask of IP address.
gw_addr: gateway IP address.
Example: ipset 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.254
ipget Display NMS port current IP address
trapset mode trap_ip_addr Set SNMP Trap Mode & Host IP
mode:
0: disable SNMP trap
1: enable SNMP trap
Example: trapset 1 192.168.1.200
(enable SNMP trap function and set host 192.168.1.200 to
receive the trap message)
trapget Get SNMP Trap Mode & Host IP

PacketLINK User Manual
13
CLI Command Description
ntpset mode server_ip_
addr
Set NTP Enable Mode & NTP Server IP
mode:
0: disable NTP function,
1: enable NTP function
Example: ntpset 1 192.168.1.201
(enable NTP function and set NTP server address to
192.168.1.201)
ntpget Get NTP Enable Mode & NTP Server IP
upgrade tftp_server_ip
file_name
Upgrade SW image file from TFTP server
tftp_server_ip: TFTP server IP address
file_name: the file name of software image to be upgraded
Example: upgrade 172.16.1.101 PL1820_sw_210218.bin
backup tftp_server_ip
file_name
Backup the system configuration to TFTP server
tftp_server_ip: TFTP server IP address
file_name: backup file name
Example: backup 172.16.1.101 CO_config_110418
restore tftp_server_ip
file_name
Restore the backup system configuration from TFTP server
tftp_server_ip: TFTP server IP address
file_name: backup file name
Example: restore 172.16.1.101 CO_config_170518
timeset hour min sec Set current time with ‘hour’, ‘minute’ and ‘second’.
Example: timeset 7 30 00
(set PacketLINK’s real time clock to 7:30AM)
dateset year month day Set current date with ‘year’, ‘mouth’ and ‘day’
Example: dateset 2011 07 05
(set PacketLINK’s date to July 5, 2011)

PacketLINK User Manual
14
CLI Command Description
timeget Get current time and date
ping ip_addr Use ICMP to check connection
Example: ping 192.168.1.11
version Display software version and related information
logout Quit PacketLINK CLI session and return to CLI login
prompt
reboot Restart the software. This command will interrupt the
operation of the unit.
Provision Command
gci Initialise the unit.
srcnet ip_addr net_mask
[source_mac(AA:BB:CC)]
Set WAN port IP address, subnet mask, gateway IP address
and its MAC address. If source_mac is omitted, the last
three numbers of WAN port IP address will be used as its
MAC address.
ip_addr: WAN port IP address to be assigned.
net_mask: subnet mask of IP address.
[source_mac(AA:BB:CC)](OUI is fixed):
WAN port MAC address.
Example: srcnet 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0
(WAN port MAC address will be set to OUI+10:01:01)
Example: srcnet 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 0A:0B:0C
(WAN port MAC address will be set to OUI+0A:0B:0C)
lanset enable bandwidth Enable LAN port and set its maximum bandwidth on WAN
enable: 0 (disable maximum bandwidth policing)
enable: 1 (enable LAN port bandwidth policing)
bandwidth:
0: 50Kbps, 1: 100Kbps, 2: 150Kbps, 3: 200Kbps,
4: 250Kbps, 5: 300Kbps, 6: 350Kbps, 7: 400Kbps,
8: 800Kbps, 9: 1.6Mbps, 10: 3.125Mbps, 11: 6.25Mbps
12: 12.5Mbps, 13: 25Mbps, 14: 50Mbps, 15: 100Mbps
Example: lanset 1 7 (enable LAN port and limit its
bandwidth to 400Kbps)

PacketLINK User Manual
15
CLI Command Description
vlanset op_mode Enable or disable E1 channel vlan mode
op_mode:
0: disable
1: enable
Example: vlanset 1 (enable E1 channel vlan mode)
ceschset ch_no enable
[dest_ip] [dest_mac]
Set CESoPSN Channel and its destination IP and MAC
address of the remote device.
ch_no: E1 channel number (1~16)
enable:
0:disable
1: enable.
[dest_ip]: destination IP address. Can be omitted if disable
E1 channel.
[dest_mac]: destination MAC address.
Example 1:
Enable E1 port #1, set the dest_ip, then automatically get
the dest_mac address from the remote device only if the
local device can communicate with the remote device via
its WAN port.
Example: ceschset 1 1 172.16.1.2
Example 2:
Enable E1 port #1 and specifically set the destination ip and
mac address of the remote device.
Example: ceschset 1 1 172.16.1.2 AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF
cespwidset ch_no TrPWID
PrPWID
Set CESoPSN Channel TrPWID and PrPWID.
ch_no: E1 channel number (1~16)
TrPWID: Transmit PW ID.
PrPWID: Provision PW ID.
Example: cespwidset 1 1 1

PacketLINK User Manual
16
CLI Command Description
jitterbd ch_no depth Set CESoPSN Channel Jitter Buffer Depth.
ch_no: E1 channel number (1~16)
depth (pktsize=0): jitter buffer depth 0~7
(0:11ms, 1: 23ms, 2: 40ms, 3: 75ms,
4: 99ms, 5: 145ms, 6: 192ms, 7: 239ms )
Example: jitterbd 1 1 (set jitter buffer to 23msec when
pkt_size is set to 1518 Bytes)
pktsize ch_no pkt_size Set CESoPSN Channel Packet Size
ch_no: E1 channel number (1~16)
Pkt_size: 0 ~ 3
( 0: 1514Byte, 1: 782Byte, 2: 178Byte, 3: 306Byte)
Example: pktsize 1 1
ceschclkset ch_no clksrc Set Channel transmit clock source
ch_no: E1 channel number (1~16)
clksrc:
0:Adaptive
1:Internal
2:RxLine
lpkset ch_no mode enable Enable/Disable E1 channel loopback mode.
ch_no: E1 channel number (1~16)
mode:
0: Disable-All
1: E1-Remote (FE), 2:E1-Local (NE)
enable:
0: disable
1: enable.
Example: lpkset 1 1 1
lpkget Get current loopback mode of E1 channel.

PacketLINK User Manual
17
CLI Command Description
cesfe1mode ch_no en(1/0) Set TDM PW to Transparent E1 (SAToP) or Fractional E1
N x 64k mode (CESoPSN)
ch_no: E1 channel number (1~16)
enable:
0: disable
1: enable.
Example: cesfe1mode 1 1
(Set E1 port #1 to Fractional E1 (CESoPSN) mode)
cesfe1crc ch_no en(1/0) E1 G.704 CRC4 generation/analyze control for Fractional
E1 mode. This setting only affect E1 ports set to FE1 N x
64k mode, for E1 ports set to Transparent E1 mode this
setting has no effect.
ch_no: E1 channel number (1~16)
enable:
0: disable
1: enable.
Example: cesfe1crc 1 1 (Enable G.704 CRC4 generation/
analyze on E1 port #1.)
cesfe1tsmap ch_no TsMap Set 64k PCM channel number to be transported over the
TDM PW for FE1 (CESoPSN) mode. This setting only affect
E1 ports set to FE1 N x 64k mode, for E1 ports set to
Transparent E1 mode this setting has no effect.
ch_no: E1 channel number (1~16)
TsMap: bit mask for DS0, b31:TS31 ~ b0:TS0
Example: cesfe1tsmap 1 x000007FE
Timeslot #1 ~ 10 of E1 port #1 will be transported over
the TDM PW.
x000007FE (hexadecimal)=0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0111 1111 1110 (binary)
TS31: the most left bit, TS0: the most right bit, TS0 is used
for frame alignment and can’t be counted in your timeslots
and always set to 0.

PacketLINK User Manual
18
CLI Command Description
ceschvlanvlpid ch_no vlp id Set CESoPSN Channel vlan tag
ch_no: E1 channel number (1~16)
vlp: vlan priority, 0 ~ 7(highest priority)
id: vlan id, 0 ~ 0xFFF
Example: ceschvlanvlpid 1 7 5 (set E1 port #1 traffic with
vlan tag, set priority to 7 and set vlan ID to 5)
Alarm Command
almall Display alarm status

PacketLINK User Manual
19
4. Quick Start Guide
4-1 Introduction
This procedure will help the field engineer to bench test the PacketLINK units and to
become familiar with the CLI operation.
4-2 Requirements
• A pair of PacketLINK units and AC power cables (with local plugs).
• A PC or laptop, TCP/IP enabled, with RS-232 COM port or with USB-to-RS232 adapter.
• Terminal emulation program (PuTTY or TeraTerm Pro)
• An E1 BERT tester configured with internal timing
• Miscellaneous cables including: an E1 loop back plug, UTP patch cables and serial console cable
(plus 15 E1 crossovers for the PL1820 or 3 E1 crossovers for the PL1400).
4-3 Getting Started
1. Place both CO and CPE PacketLINK devices on a flat work surface.
2. Connect the CO unit’s WAN port to the CPE unit’s WAN port using an Ethernet cable.
3. Ensure that CO and CPE PacketLINK devices are both switched on.
4. Check there are no problems shown on the status LEDs of the WAN Ethernet
ports as shown in the table below.
LED Name State Description
PWR Green Power is on.
Off No power present
Ethernet Link /
Activity
Green Ethernet link is up
Blinking Green Tx / Rx traffic is traversing the port
Off Ethernet Link is down
Ethernet Link
Speed
Orange 100Mbps
Off 10Mbps
E1 ACT Green E1 port is enabled and traffic is traversing the
port
Off E1 port is disabled
E1 ALM Orange E1 link error has occurred
Off No alarm present
ALM Red Alarms raised from any E1 link
Off No alarm present
LED Indications

PacketLINK User Manual
20
4-4 Configuration
1. Connect the PC or laptop COM port to the PacketLINK console port
2. Open Terminal (115200, 8, N, 1) and login in to the PacketLINK unit.
Password: admin, logs you in as a basic user
CLI> passwd
Enter Password: gciadmin, logs you in as an administrator which is required for most
configuration changes
3. Cut and paste the relevant CO script from Section 5
4. Connect the PC or laptop to the CPE PacketLINK console port and repeat the above process
using the relevant CPE script from Section 5.
4-5 Test
1. Connect the E1 BERT tester to the CO PacketLINK E1 port number 1
2. If PL1100 units then connect the E1 loopback plug into CPE PacketLINK E1 port
3. If PL1400 units then connect the E1 crossover cables from E1 ports 2-3 on the CO unit and
E1 ports 1-2 and 3-4 on the CPE unit. Connect the E1 loopback plug into CO E1 port 4.
4. If PL1820 units then connect the E1 crossover cables from E1 ports 2-3, 4-5, 6-7, 8-9, 10-11,
12-13 and 14-15 on the CO unit and E1 ports 1-2, 3-4, 5-6, 7-8, 9-10, 11-12, 13-14 and 15-16
on the CPE unit. Connect the E1 loopback plug into the CO E1 port 16.
5. Test the pair of PacketLINK units using the E1 BERT tester
Table of contents
Other Metrodata Network Hardware manuals