Miller Maxstar 300 User manual
Other Miller Welding System manuals

Miller
Miller Spectrum 375 X-TREME User manual

Miller
Miller Multimatic 220 AC/DC User manual

Miller
Miller PipeWorx 400 User manual

Miller
Miller MILLERMATIC 70A User manual

Miller
Miller SRH-333 User manual

Miller
Miller SuitCase 8RC User manual

Miller
Miller Legend 302 User manual

Miller
Miller ST-24w User manual

Miller
Miller Dynasty 400 User manual

Miller
Miller ST 44 Series User manual

Miller
Miller Migmatic 175 User manual

Miller
Miller ALT 304 User manual

Miller
Miller Dynasty 280 DX User manual

Miller
Miller MigMatic 300 User manual

Miller
Miller Coolmate 3.5 CE User manual

Miller
Miller RAD-400 User manual

Miller
Miller AG-BAG G6060 User manual

Miller
Miller EnPak Mechanic OM-240 113H User manual
Miller
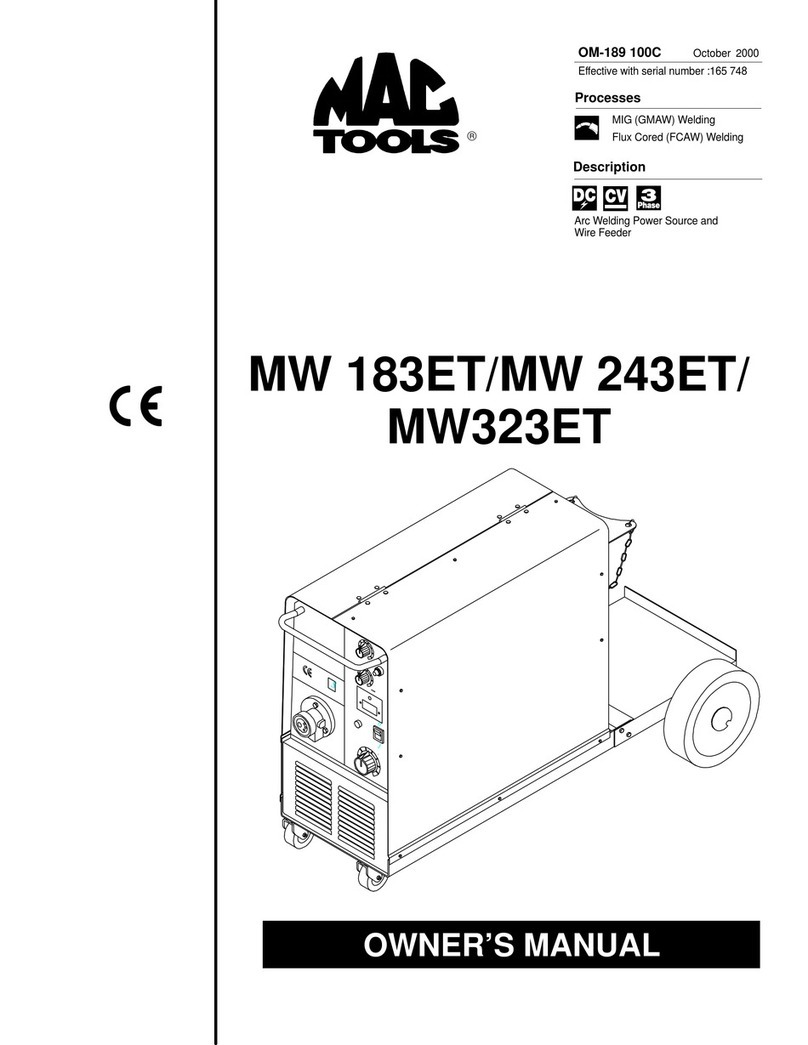
Miller MAC TOOLS MW 183ET User manual

Miller
Miller hydracool 270 CE User manual
Popular Welding System manuals by other brands

TAFA
TAFA 30*8B35 owner's manual

Lincoln Electric
Lincoln Electric INVERTEC V350-PRO CE Technical specifications

ESAB
ESAB Buddy Arc 145 instruction manual

CIGWELD
CIGWELD 636804 use instructions

Red-D-Arc
Red-D-Arc DC-400 Operator's manual

Hobart Welding Products
Hobart Welding Products Spool Gun DP 3035-10 owner's manual

























