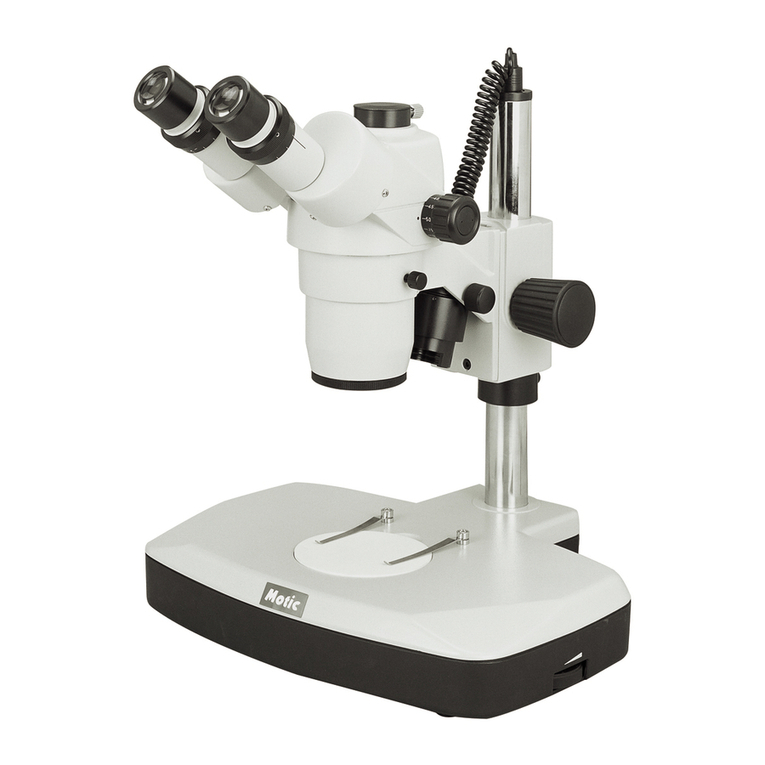
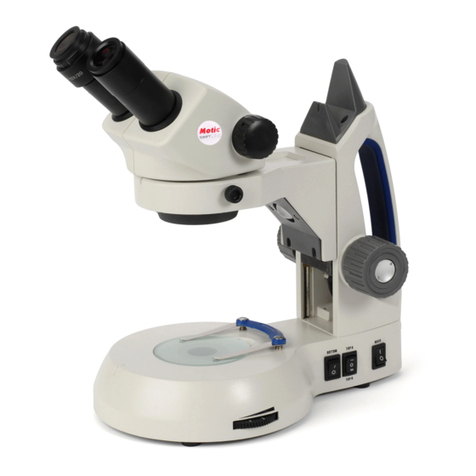
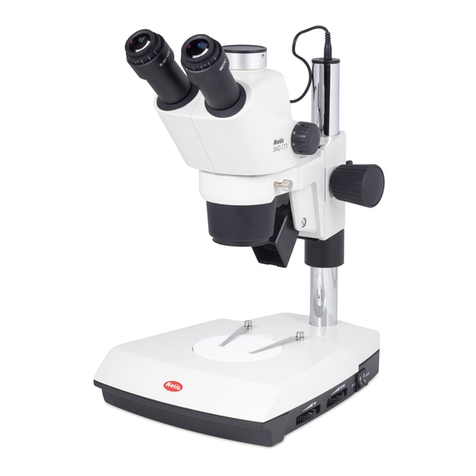
4
MICROSCOPE TERMINOLOGY
Abbe Condenser
A two-lens sub-stage condenser located below
the stage of a microscope and functions to collect
light and direct it onto the object being examined.
Its high numerical aperture makes it particularly
suited for use with most medium- and high-
magnification objectives.
Aperture, Numerical (N.A.)
The numerical aperture is an important factor
determining the efficiency of the condenser and
objective. It is represented by the formula: (N.A.
= ηsinα), where ηis the refractive index of a
medium (air, water, immersion oil etc.) between
the objective and the specimen or condenser,
and αis half of the maximum angle at which light
enters or leaves the lens from or to a focused
object point on the optical axis.
Cover Glass Thickness
Transmitted light objectives are designed to
image specimens that are covered by a thin
cover glass (cover slip). The thickness of this
small glass piece is now standardized at 0.17
mm for most applications.
Diaphragm, Condenser
A diaphragm, which controls the effective size of
the condenser aperture. A synonym for the
condenser illuminating aperture diaphragm.
Depth of Focus
The axial depth of the space on both sides of the
image plane within which the image is sharp. The
larger the N.A. of objective, the shallower the depth
of focus.
Field of View (F.O.V.)
That part of the image field, which is imaged on the
observer’s retina, and hence can be viewed at any
one time. The field of view number is now one of
the standard markings of the eyepiece.
Filter
Filters are optical elements that selectively transmit
light. It may absorb part of the spectrum, or reduce
overhaul intensity or transmit only specific
wavelengths.
Immersion Oil
Any liquid occupying the space between the object
and microscope objective. Such a liquid is usually
required by objectives of 3-mm focal length or less.
Magnification
The number of times by which the size of the
image exceeds the original object. Lateral
magnification is usually meant. It is the ratio of the
distance between two points in the image to the
distance between the two corresponding points in
the object.
Micrometer: um
A metric unit of length measurement
= 1x10-6 meters or 0.000001 meters