PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–3
Disassembly & Troubleshooting Instructions
Page 2 Original, 11/97
CONTENTS
Page No
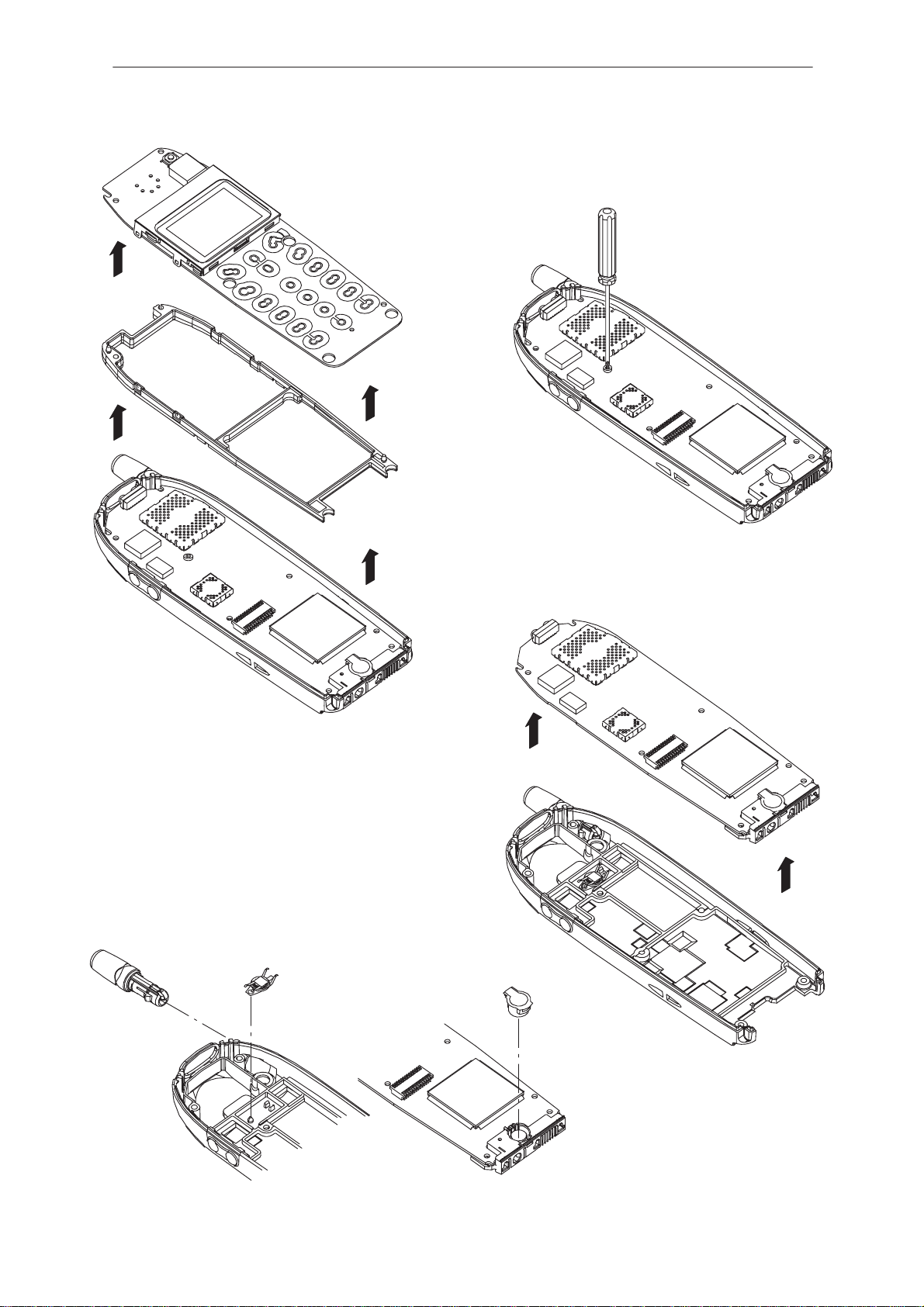
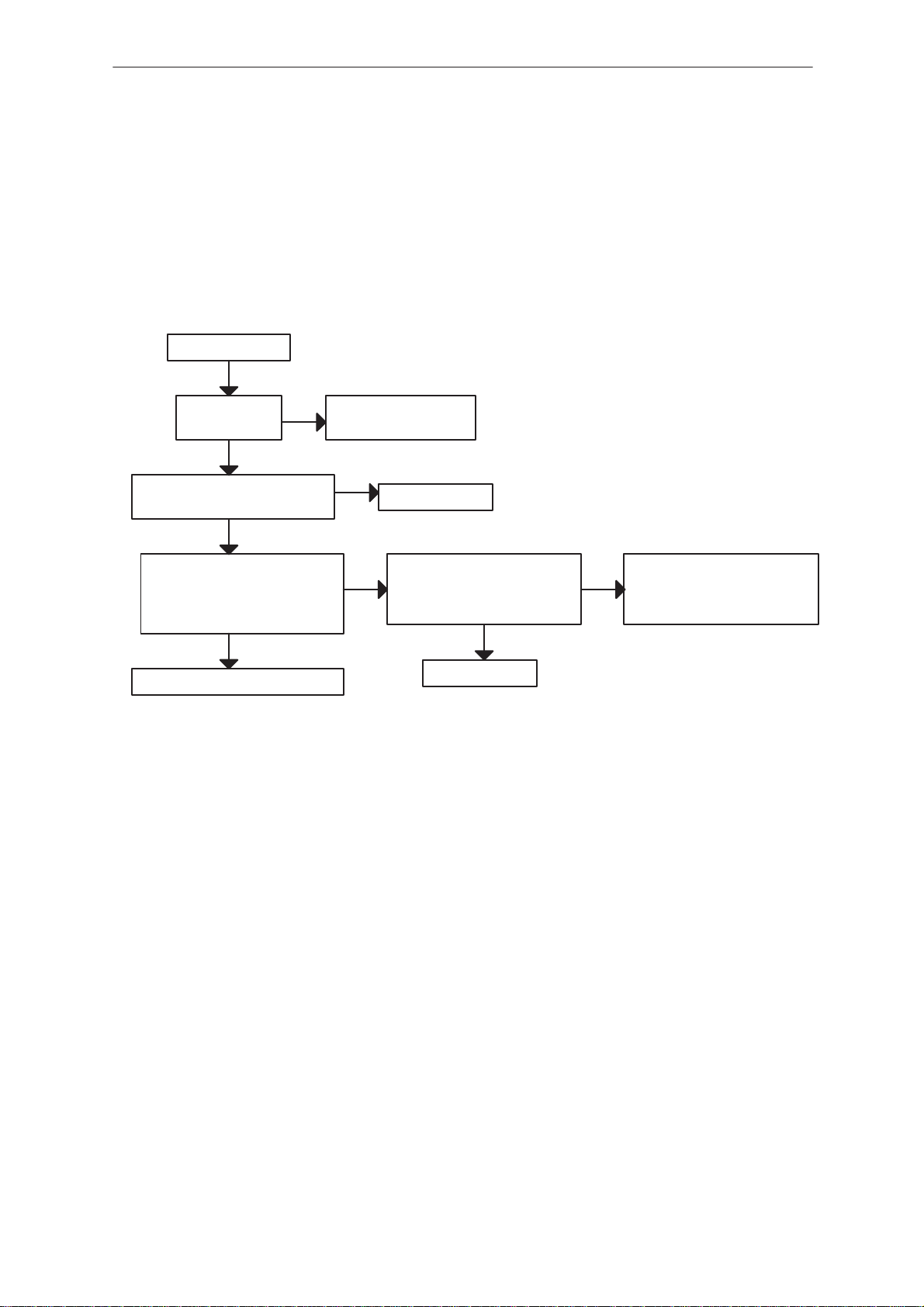
Disassembly 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Trouble Shooting 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
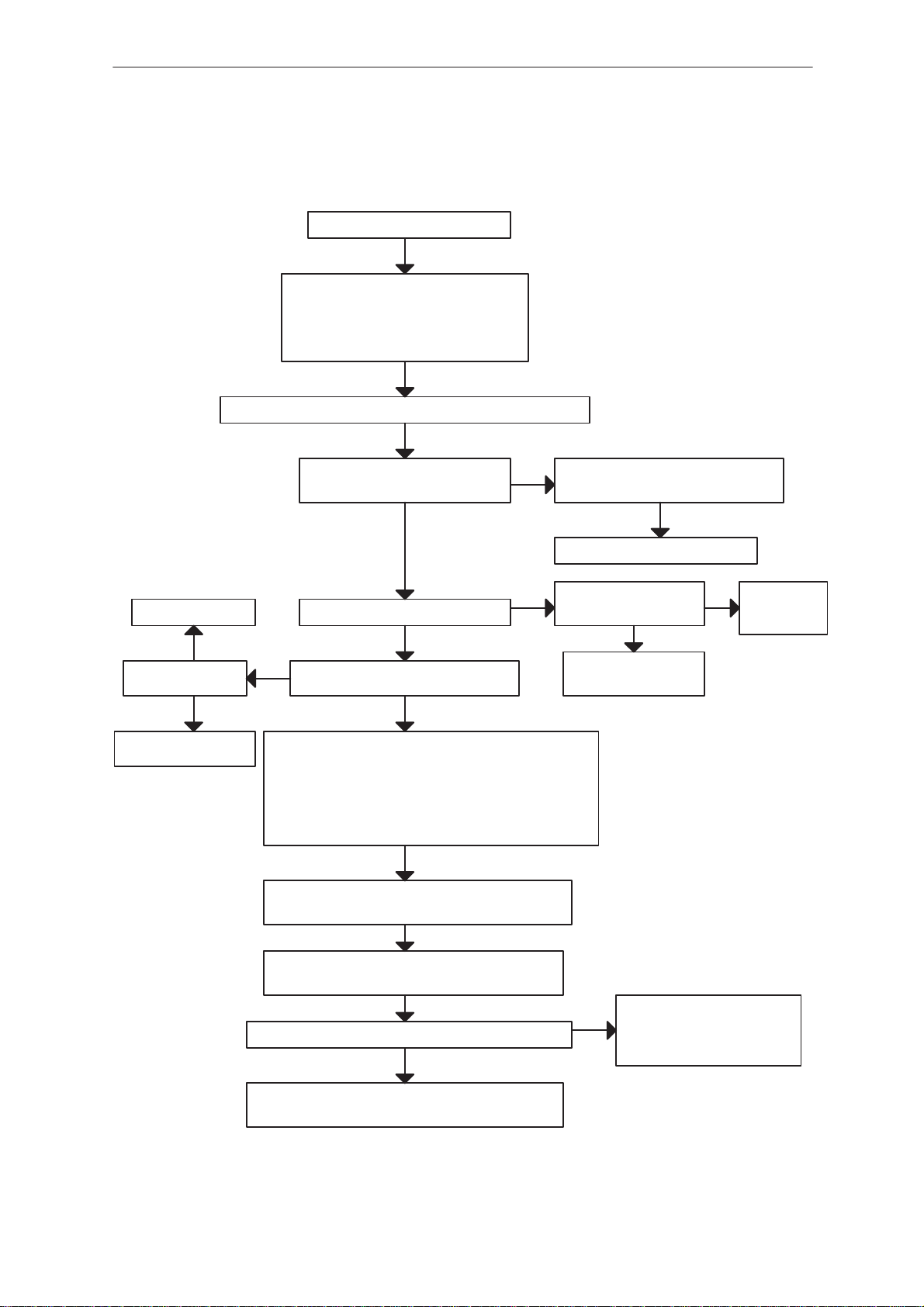
Phone is totally dead 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Flash programming doesn’t work 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Flash Programming (1) 8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
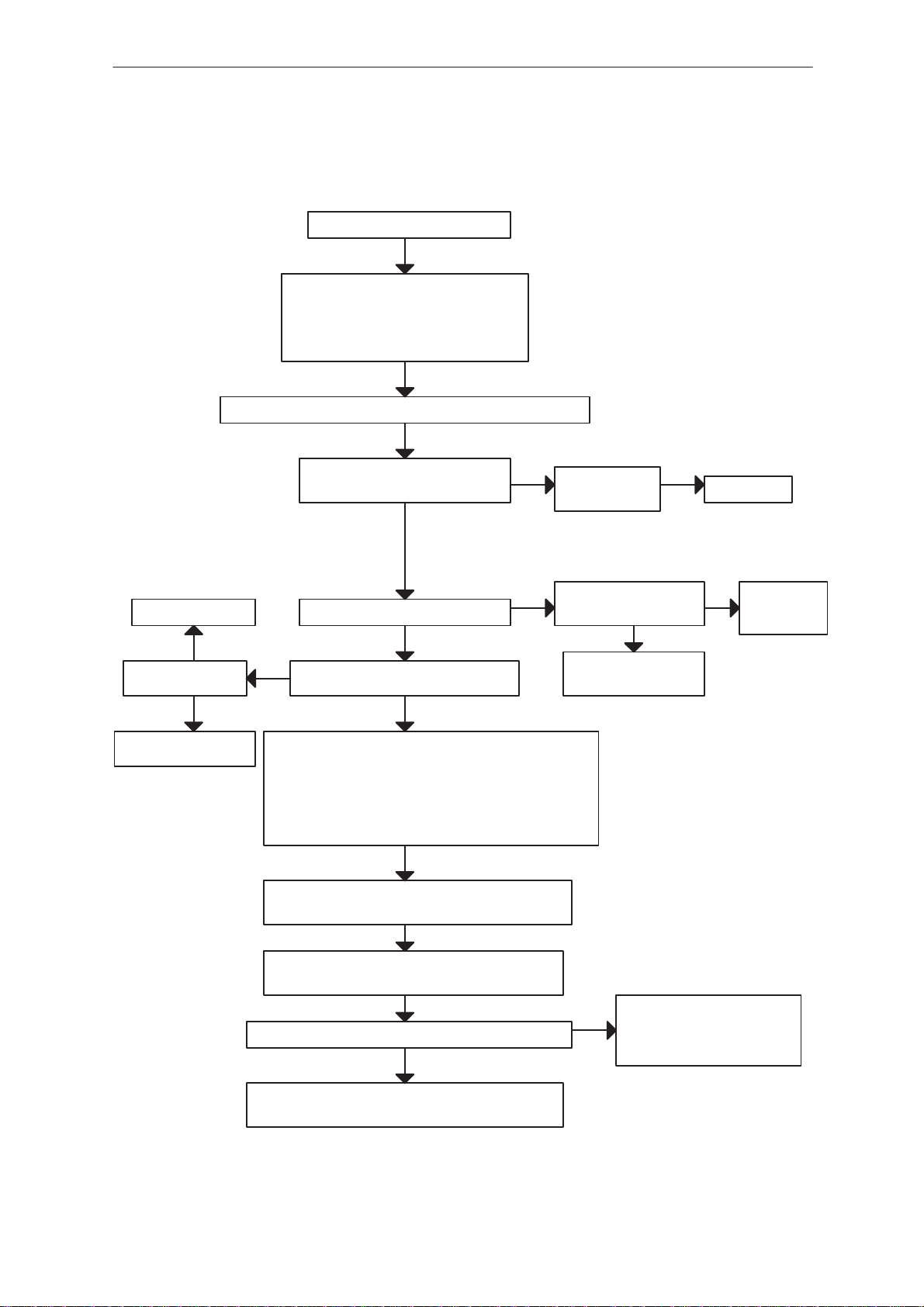
Flash Programming failure (2) 9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Flash Programming failure (3) 10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Flash Programming failure (4) 11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power doesn’t stay on, or phone is jammed 12. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Display Information: Contact Service 13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
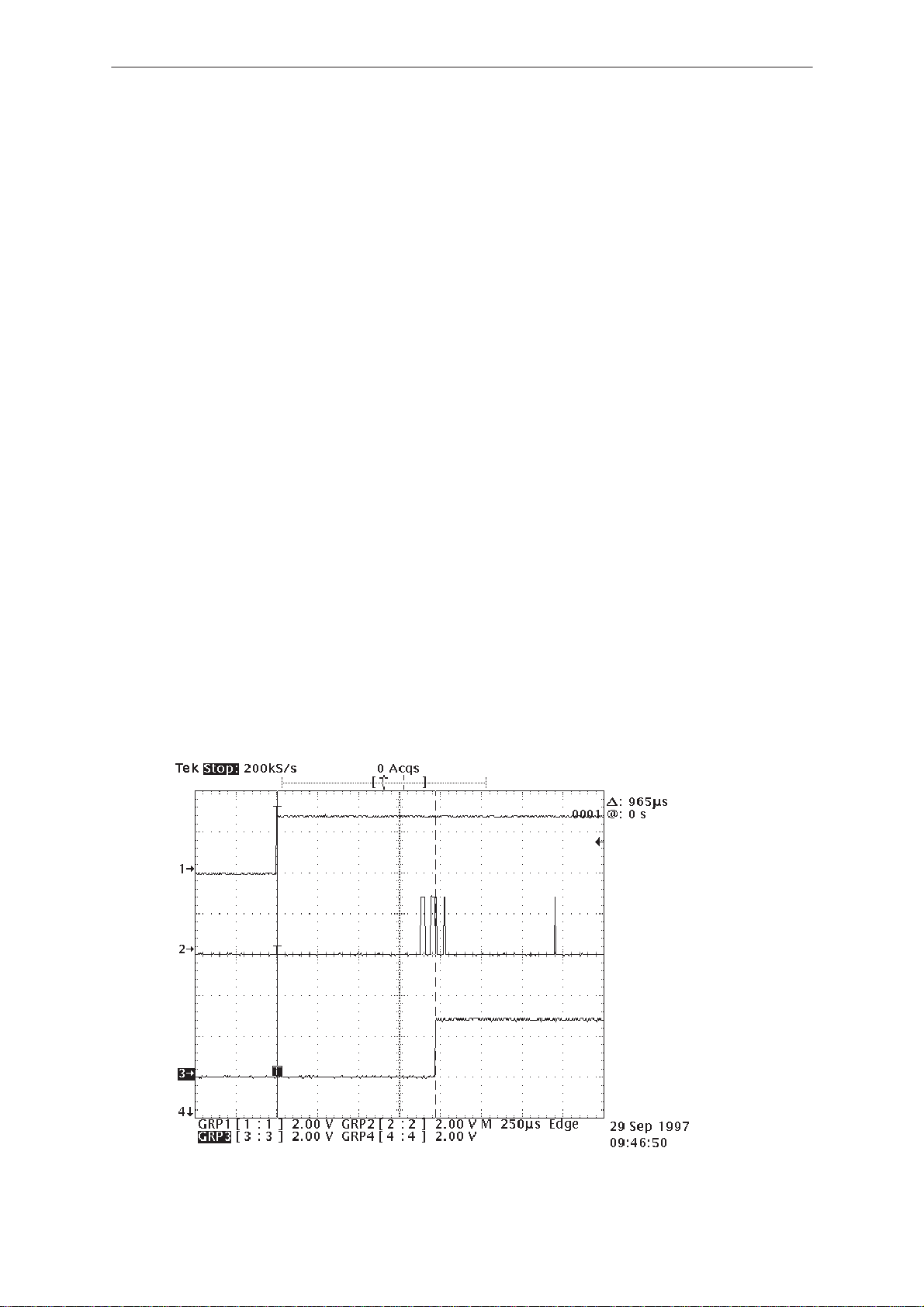
The phone doesn’t register to the network or phone doesn’t make a call 13
Phone register failure 15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SIM card is out of order 16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SIM Card failure 17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Audio failure (1) 18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Audio failure (2) 19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Charger failure 20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Receiver Fault (1) 21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Receiver Fault (2) 22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Receiver Fault (3) 23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Receiver Fault (4) 24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Receiver Fault (5) 25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Receiver Fault (6) 26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Receiver Fault (7) 27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmitter Fault (1) 28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmitter Fault (2) 29. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmitter Fault (3) 30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Appendix A 31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Appendix B 32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Appendix C 33. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Appendix D 34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .